Aluminum composite panels consist of two thin aluminum sheets bonded to a non-aluminum core, offering lightweight strength, durability, and enhanced insulation compared to solid aluminum panels. Solid aluminum panels provide superior structural integrity and resistance to impacts, making them ideal for applications requiring high strength and rigidity. Choosing between the two depends on the specific needs for weight, insulation, and mechanical performance in architectural or industrial projects.
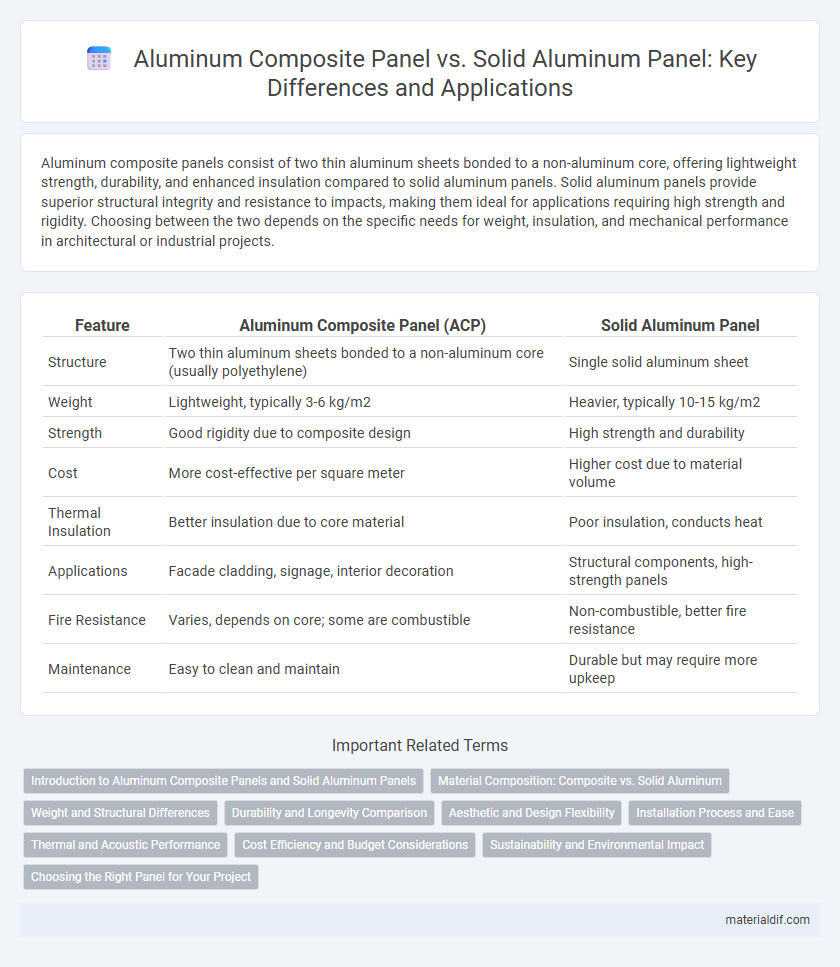
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aluminum Composite Panel (ACP) | Solid Aluminum Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Two thin aluminum sheets bonded to a non-aluminum core (usually polyethylene) | Single solid aluminum sheet |
| Weight | Lightweight, typically 3-6 kg/m2 | Heavier, typically 10-15 kg/m2 |
| Strength | Good rigidity due to composite design | High strength and durability |
| Cost | More cost-effective per square meter | Higher cost due to material volume |
| Thermal Insulation | Better insulation due to core material | Poor insulation, conducts heat |
| Applications | Facade cladding, signage, interior decoration | Structural components, high-strength panels |
| Fire Resistance | Varies, depends on core; some are combustible | Non-combustible, better fire resistance |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and maintain | Durable but may require more upkeep |
Introduction to Aluminum Composite Panels and Solid Aluminum Panels
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACPs) consist of two thin layers of aluminum bonded to a non-aluminum core, providing lightweight strength and flexibility ideal for facades and signage. Solid Aluminum Panels are single sheets of pure aluminum known for superior durability, corrosion resistance, and structural integrity in industrial applications. ACPs offer enhanced design versatility and cost-effectiveness, while solid panels excel in environments requiring maximum durability and load-bearing capacity.
Material Composition: Composite vs. Solid Aluminum
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACPs) consist of two thin aluminum sheets bonded to a non-aluminum core, typically polyethylene or fire-resistant mineral-filled core, offering lightweight properties and enhanced flexibility. Solid Aluminum Panels are made from a single, homogeneous sheet of aluminum, providing superior strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. The composite structure of ACPs allows for better thermal insulation and design versatility compared to the rigid, more robust nature of solid aluminum panels.
Weight and Structural Differences
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACP) consist of two thin aluminum sheets bonded to a non-aluminum core, making them significantly lighter than Solid Aluminum Panels, which are composed entirely of aluminum. ACPs offer enhanced flexibility and impact resistance due to their layered structure, while Solid Aluminum Panels provide superior strength and rigidity, suitable for applications demanding high structural integrity. Weight-wise, ACPs can be up to 50% lighter than Solid Aluminum Panels, facilitating easier handling and installation in construction and architectural projects.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACP) offer enhanced durability through their multi-layered structure, combining aluminum sheets with a polyethylene core for increased resistance to impact, weather, and corrosion compared to Solid Aluminum Panels. Solid Aluminum Panels, while inherently corrosion-resistant and robust, are more prone to dents and surface damage due to their single-material composition, potentially reducing their lifespan under harsh environmental conditions. The longevity of ACPs typically surpasses that of solid panels in demanding applications, making them ideal for exterior cladding where long-term performance and maintenance costs are critical factors.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACPs) offer superior aesthetic options with a wide range of colors, finishes, and textures, enabling architects and designers to create visually striking facades and interiors. Solid Aluminum Panels provide a sleek, uniform appearance with high durability but have limited design versatility compared to ACPs. The lightweight nature and customizable surface of ACPs enhance design flexibility for complex shapes and creative architectural expressions.
Installation Process and Ease
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACPs) feature a lightweight core sandwiched between two aluminum sheets, making them easier and faster to cut, drill, and install compared to solid aluminum panels. The reduced weight of ACPs significantly simplifies handling and reduces labor costs during installation, especially on large facades or complex shapes. Solid aluminum panels require more specialized tools and effort due to their thickness and weight, resulting in longer installation times and increased manpower.
Thermal and Acoustic Performance
Aluminum composite panels (ACP) offer superior thermal insulation due to their multi-layer structure, which typically includes a polyethylene or mineral core that reduces heat transfer compared to solid aluminum panels. Acoustic performance is enhanced in ACPs as the core material dampens sound vibrations more effectively than the dense, single-layer structure of solid aluminum panels. Solid aluminum panels, while durable and lightweight, provide minimal soundproofing and thermal resistance, making ACPs the preferred choice for applications requiring energy efficiency and noise reduction.
Cost Efficiency and Budget Considerations
Aluminum composite panels (ACPs) offer significant cost efficiency compared to solid aluminum panels due to their lightweight core material combined with thin aluminum sheets, reducing overall material and transportation expenses. Budget considerations favor ACPs for larger projects as they require less raw aluminum, lowering production costs while maintaining durability and aesthetic appeal. Solid aluminum panels, although more expensive, provide superior structural strength and longevity, which may justify higher initial investment for applications demanding enhanced performance.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACPs) offer enhanced sustainability by requiring less raw aluminum due to their layered structure, resulting in reduced overall material consumption and energy use during manufacturing compared to Solid Aluminum Panels. ACPs often incorporate recycled aluminum and can be recycled themselves, lowering landfill waste and minimizing environmental impact throughout their lifecycle. Solid Aluminum Panels, while durable and recyclable, involve higher energy inputs for production and require more raw aluminum, increasing their carbon footprint relative to composite alternatives.
Choosing the Right Panel for Your Project
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACP) offer lightweight construction, enhanced rigidity, and superior weather resistance, making them ideal for modern architectural facades and cladding applications. Solid Aluminum Panels provide greater durability, higher impact resistance, and better thermal conductivity, suitable for structural components and high-traffic environments requiring robust material performance. Evaluating project-specific factors such as budget, weight constraints, environmental exposure, and aesthetic requirements ensures the selection of the most appropriate aluminum panel type.
Aluminum Composite Panel vs Solid Aluminum Panel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com