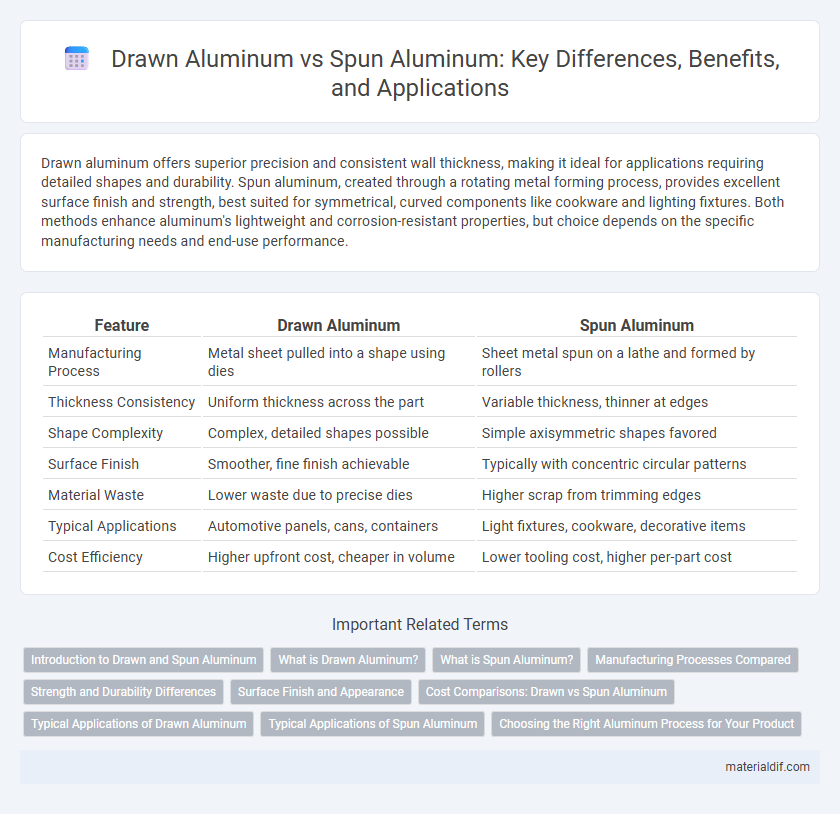
Drawn aluminum offers superior precision and consistent wall thickness, making it ideal for applications requiring detailed shapes and durability. Spun aluminum, created through a rotating metal forming process, provides excellent surface finish and strength, best suited for symmetrical, curved components like cookware and lighting fixtures. Both methods enhance aluminum's lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, but choice depends on the specific manufacturing needs and end-use performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drawn Aluminum | Spun Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Metal sheet pulled into a shape using dies | Sheet metal spun on a lathe and formed by rollers |
| Thickness Consistency | Uniform thickness across the part | Variable thickness, thinner at edges |
| Shape Complexity | Complex, detailed shapes possible | Simple axisymmetric shapes favored |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, fine finish achievable | Typically with concentric circular patterns |
| Material Waste | Lower waste due to precise dies | Higher scrap from trimming edges |
| Typical Applications | Automotive panels, cans, containers | Light fixtures, cookware, decorative items |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher upfront cost, cheaper in volume | Lower tooling cost, higher per-part cost |
Introduction to Drawn and Spun Aluminum
Drawn aluminum is produced by pulling a flat or beveled sheet through a die, resulting in a smooth, precise finish ideal for intricate shapes and high-strength applications. Spun aluminum involves rotating a flat disk at high speeds on a lathe, where it is shaped by rollers or pressure, creating symmetrical, seamless hollow parts with excellent surface quality. Both processes optimize aluminum's lightweight and corrosion resistance properties, but differ in forming techniques and typical product uses.
What is Drawn Aluminum?
Drawn aluminum refers to aluminum sheets or tubes shaped by pulling the metal through a die to elongate and form a specific profile, enhancing strength and surface finish. This process produces precise dimensions and smooth surfaces, making drawn aluminum ideal for applications requiring uniform thickness and high structural integrity, such as automotive components and architectural elements. The controlled deformation during drawing improves mechanical properties and allows for complex shapes without compromising material quality.
What is Spun Aluminum?
Spun aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal formed by rotating a flat aluminum disc at high speed while shaping it with a tool, resulting in smooth, symmetrical, and seamless components. This metalworking process enhances the structural integrity and surface finish, making spun aluminum ideal for automotive wheels, cookware, and aerospace parts. Compared to drawn aluminum, which is created through tensile forces pulling aluminum through a die, spun aluminum offers greater design flexibility for curved or round shapes.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Drawn aluminum is created through a deep drawing process where a flat aluminum blank is mechanically stretched into a die cavity, allowing for precise shapes with uniform walls, commonly used in automotive and cookware applications. Spun aluminum involves rotating a metal blank on a lathe while a tool selectively deforms it, producing symmetrical, cylindrical forms with smooth finishes often found in lighting fixtures and decorative components. The drawn aluminum process excels in complex, detailed geometry with thin walls, while spun aluminum offers faster production and enhanced surface texture control for round shapes.
Strength and Durability Differences
Drawn aluminum exhibits higher tensile strength due to the metal being mechanically stretched, which aligns its grain structure and enhances durability under stress. Spun aluminum, shaped through a rotational forming process, offers improved surface finish and uniform thickness but generally has lower strength compared to drawn aluminum. The choice between drawn and spun aluminum depends on the specific application requirements for strength and wear resistance.
Surface Finish and Appearance
Drawn aluminum features a smooth, uniform surface finish with minimal imperfections, making it ideal for applications requiring high aesthetic quality and precise detailing. Spun aluminum offers a more textured and circular grain pattern due to its manufacturing process, which can enhance visual interest and reflect light differently. The choice between drawn and spun aluminum depends largely on desired appearance and surface smoothness for specific design applications.
Cost Comparisons: Drawn vs Spun Aluminum
Drawn aluminum typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to complex tooling and slower production rates compared to spun aluminum. Spun aluminum offers a cost-effective alternative, leveraging faster production speeds and lower tooling expenses, making it ideal for large-volume applications. Cost efficiency in spun aluminum becomes especially significant in projects requiring consistent shapes and sizes, whereas drawn aluminum suits precision parts despite its premium price point.
Typical Applications of Drawn Aluminum
Drawn aluminum is commonly used in applications requiring precise, uniform shapes such as automotive body panels, appliance components, and aerospace parts due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and surface finish. Its ability to maintain dimensional accuracy makes it ideal for intricate, structural elements in electronics and architectural applications. Compared to spun aluminum, drawn aluminum is preferred for parts where consistent thickness and mechanical properties are critical.
Typical Applications of Spun Aluminum
Spun aluminum is widely used in automotive components, lighting fixtures, and kitchenware due to its strength, lightweight nature, and excellent surface finish. The metal's ability to be formed into complex shapes with smooth contours makes it ideal for decorative elements and functional parts such as lamp reflectors, pots, and pans. Its corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity further enhance its suitability for these typical applications.
Choosing the Right Aluminum Process for Your Product
Drawn aluminum offers precise dimensional control and is ideal for applications requiring uniform wall thickness and intricate shapes, making it suitable for automotive parts and aerospace components. Spun aluminum provides excellent strength and a smooth surface finish, perfect for producing symmetrical, round products like cookware and decorative elements. Selecting the right aluminum process depends on product requirements such as strength, finish, shape complexity, and production volume to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Drawn Aluminum vs Spun Aluminum Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com