Die-cast aluminum offers superior dimensional accuracy and smoother surface finishes compared to sand-cast aluminum, making it ideal for precise and high-volume production runs. Sand-cast aluminum, while more cost-effective for low-volume and larger components, typically results in a rougher surface and less intricate detail. Choosing between die-cast and sand-cast aluminum depends on production scale, detail requirements, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
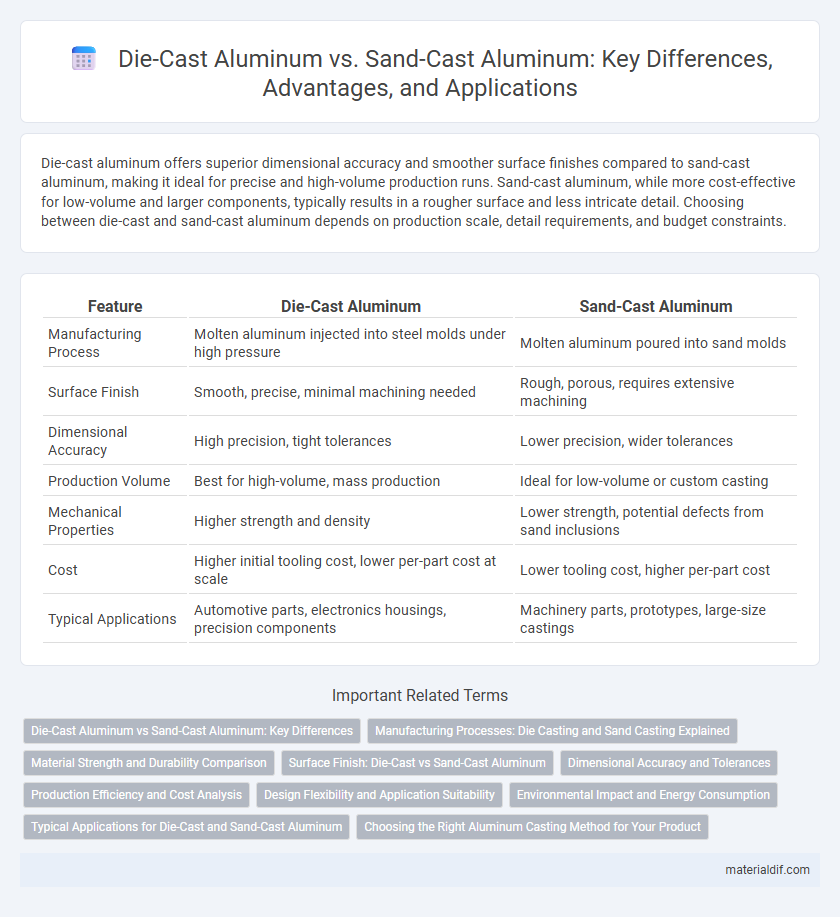
| Feature | Die-Cast Aluminum | Sand-Cast Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Molten aluminum injected into steel molds under high pressure | Molten aluminum poured into sand molds |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, precise, minimal machining needed | Rough, porous, requires extensive machining |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High precision, tight tolerances | Lower precision, wider tolerances |
| Production Volume | Best for high-volume, mass production | Ideal for low-volume or custom casting |
| Mechanical Properties | Higher strength and density | Lower strength, potential defects from sand inclusions |
| Cost | Higher initial tooling cost, lower per-part cost at scale | Lower tooling cost, higher per-part cost |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, electronics housings, precision components | Machinery parts, prototypes, large-size castings |
Die-Cast Aluminum vs Sand-Cast Aluminum: Key Differences
Die-cast aluminum features high precision and smooth surface finishes due to the forced injection of molten metal into steel molds, making it ideal for complex, thin-walled components. Sand-cast aluminum uses a sand mold that allows for larger, heavier parts but results in a rougher surface and lower dimensional accuracy. Die-cast parts generally exhibit higher strength and better mechanical properties compared to sand-cast counterparts due to rapid solidification and finer grain structures.
Manufacturing Processes: Die Casting and Sand Casting Explained
Die-cast aluminum involves injecting molten aluminum into a high-pressure steel mold, producing parts with precise dimensions, smooth surfaces, and thin walls rapidly and in large volumes. Sand-cast aluminum forms parts by pouring molten aluminum into a sand-based mold, allowing for complex shapes and larger sizes but resulting in rougher surfaces and lower dimensional accuracy. Die casting is optimal for high-volume production with fine details, while sand casting suits lower volume runs and parts requiring intricate or large geometries.
Material Strength and Durability Comparison
Die-cast aluminum exhibits higher material strength and superior dimensional accuracy due to its high-pressure molding process, resulting in denser and more uniform microstructure. Sand-cast aluminum, while offering greater design flexibility and thicker wall sections, generally has lower tensile strength and increased porosity, which can reduce durability under stress. For applications demanding enhanced mechanical performance and wear resistance, die-cast aluminum is typically preferred over sand-cast aluminum.
Surface Finish: Die-Cast vs Sand-Cast Aluminum
Die-cast aluminum offers a smoother, more precise surface finish due to high-pressure injection into steel molds, resulting in minimal porosity and fine detail reproduction ideal for aesthetic applications. Sand-cast aluminum produces a rougher, more textured surface because molten metal fills sand molds, often requiring additional machining or finishing for improved appearance. The superior surface quality of die-cast parts reduces post-processing costs, making it the preferred choice for components demanding intricate designs and consistent finish.
Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
Die-cast aluminum offers superior dimensional accuracy and tighter tolerances compared to sand-cast aluminum, due to its high-pressure injection process which ensures fine details and consistent thickness. Sand-cast aluminum typically exhibits looser tolerances and greater dimensional variability because the sand mold surface is less precise and can shift during casting. These differences make die-cast aluminum ideal for applications requiring precise fittings and complex geometries, while sand casting suits larger, less detailed components.
Production Efficiency and Cost Analysis
Die-cast aluminum offers superior production efficiency with faster cycle times and higher precision, enabling greater consistency and reduced labor costs compared to sand-cast aluminum. The automated nature of die-casting reduces material waste and post-processing requirements, leading to lower overall production expenses for large-volume manufacturing. Sand-cast aluminum, while more flexible for complex and low-volume parts, incurs higher labor and processing costs, making it less cost-effective for mass production runs.
Design Flexibility and Application Suitability
Die-cast aluminum offers superior design flexibility with its ability to create complex, intricate shapes and tight tolerances ideal for high-precision components in automotive and aerospace industries. Sand-cast aluminum, while less precise, is suitable for larger, simpler parts where structural integrity and cost-effectiveness are prioritized, commonly used in heavy machinery and construction. The choice between these processes depends on the required detail, production volume, and mechanical properties essential to the specific application.
Environmental Impact and Energy Consumption
Die-cast aluminum production typically consumes less energy than sand casting due to its efficient, automated process and reduced material waste, leading to a lower carbon footprint. Sand casting involves higher energy use from melting larger amounts of aluminum and the repeated preparation of sand molds, which also generates significant solid waste. Overall, die-casting offers a more environmentally sustainable option by minimizing both energy consumption and resource waste in aluminum manufacturing.
Typical Applications for Die-Cast and Sand-Cast Aluminum
Die-cast aluminum is commonly used in automotive components, aerospace parts, and electronic housings due to its high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finish. Sand-cast aluminum is preferred for large, complex parts such as engine blocks, pump housings, and heavy machinery components where thicker walls and lower tooling costs are advantageous. The choice between die-casting and sand-casting depends on production volume, part complexity, and mechanical property requirements.
Choosing the Right Aluminum Casting Method for Your Product
Die-cast aluminum offers superior surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and faster production cycles, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing of intricate parts like automotive components and electronics housings. Sand-cast aluminum provides greater design flexibility and is better suited for large, complex shapes or low-volume production runs with thicker walls. Selecting the right aluminum casting method depends on factors such as part complexity, tolerance requirements, production volume, and cost constraints to optimize product performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Die-Cast Aluminum vs Sand-Cast Aluminum Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com