Nichrome and Kanthal are popular materials for coil building in vaping and heating elements, each offering unique thermal properties and durability. Nichrome heats up faster and provides a smoother ramp-up time, making it ideal for quick temperature adjustments. Kanthal boasts superior oxidation resistance and longevity, ensuring consistent performance over extended use.
Table of Comparison
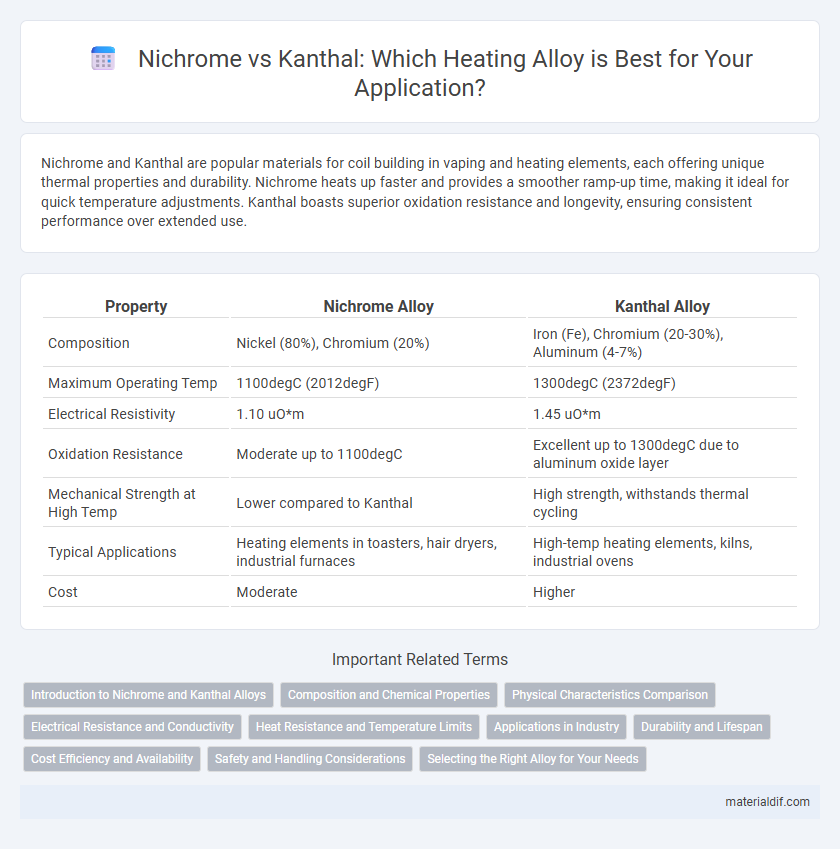
| Property | Nichrome Alloy | Kanthal Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Nickel (80%), Chromium (20%) | Iron (Fe), Chromium (20-30%), Aluminum (4-7%) |
| Maximum Operating Temp | 1100degC (2012degF) | 1300degC (2372degF) |
| Electrical Resistivity | 1.10 uO*m | 1.45 uO*m |
| Oxidation Resistance | Moderate up to 1100degC | Excellent up to 1300degC due to aluminum oxide layer |
| Mechanical Strength at High Temp | Lower compared to Kanthal | High strength, withstands thermal cycling |
| Typical Applications | Heating elements in toasters, hair dryers, industrial furnaces | High-temp heating elements, kilns, industrial ovens |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Nichrome and Kanthal Alloys
Nichrome and Kanthal alloys are widely used in high-temperature applications due to their excellent resistance to oxidation and stable electrical resistance. Nichrome, primarily composed of nickel and chromium, offers superior resistance to oxidation up to 1200degC and is commonly used in heating elements and resistors. Kanthal, based on iron, chromium, and aluminum, provides exceptional oxidation resistance up to 1400degC and is favored in industrial furnaces and electric heating elements for its longer lifespan.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Nichrome primarily consists of nickel (around 80%) and chromium (about 20%), offering excellent oxidation resistance and thermal stability due to its stable oxide layer formation. Kanthal, an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy, contains approximately 70% iron, 20-30% chromium, and 4-7% aluminum, which enhances its oxidation resistance and formation of a protective aluminum oxide scale. The distinct compositions result in Nichrome having higher electrical conductivity, while Kanthal exhibits superior high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance, making each alloy suitable for specific high-temperature applications.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Nichrome alloy, primarily composed of nickel and chromium, exhibits higher electrical resistance and superior corrosion resistance compared to Kanthal, an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy known for its excellent oxidation resistance and higher melting point. Nichrome typically operates efficiently at temperatures up to 1,200degC, while Kanthal can withstand temperatures approaching 1,400degC, making Kanthal more suitable for high-temperature applications. The ductility of Nichrome allows for easier shaping and coiling, whereas Kanthal's brittleness requires careful handling during fabrication.
Electrical Resistance and Conductivity
Nichrome exhibits a higher electrical resistance, typically around 1.10 uO*m, compared to Kanthal's resistance of approximately 1.45 uO*m, making Kanthal suitable for applications requiring stable resistance under high temperatures. Kanthal alloys maintain superior conductivity at elevated temperatures due to their iron-chromium-aluminum composition, enhancing oxidation resistance and prolonging lifespan in heating elements. Nichrome's nickel-chromium base offers more consistent conductivity at moderate temperatures but is less efficient than Kanthal under extreme thermal conditions.
Heat Resistance and Temperature Limits
Nichrome alloys exhibit excellent heat resistance with a maximum operating temperature of around 1400degC, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid heating and thermal cycling. Kanthal, composed primarily of iron, chromium, and aluminum, withstands higher temperatures up to approximately 1500degC, providing superior scalability in high-temperature industrial furnaces and heating elements. Both alloys maintain their structural integrity at elevated temperatures, but Kanthal's higher oxidation resistance enhances its longevity in extreme heat environments.
Applications in Industry
Nichrome exhibits exceptional resistance to oxidation and high temperatures, making it ideal for heating elements in electric furnaces, toasters, and hair dryers. Kanthal offers superior durability and higher maximum operating temperatures, which suits applications requiring long-term thermal stability, such as industrial furnaces, kilns, and heat treatment equipment. Both alloys are essential in manufacturing processes demanding reliable, efficient heating solutions with specific temperature and environmental resilience.
Durability and Lifespan
Nichrome exhibits superior durability with high resistance to oxidation and corrosion, maintaining stable electrical properties under prolonged high-temperature use. Kanthal outperforms Nichrome in lifespan due to its ability to withstand extreme temperatures up to 1400degC without significant degradation. This makes Kanthal the preferred alloy for heating elements requiring extended operational life in harsh thermal environments.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Nichrome alloys typically offer better cost efficiency due to lower raw material expenses and widespread availability, making them a popular choice for heating elements in consumer appliances. Kanthal, while often more expensive, provides superior oxidation resistance and longer lifespan, which can offset initial costs in industrial applications. The availability of Nichrome in various grades and worldwide manufacturing presence ensures streamlined supply chains, whereas Kanthal's specialized production limits immediate access and increases lead times.
Safety and Handling Considerations
Nichrome alloy offers superior resistance to oxidation and lower risk of hazardous fumes during high-temperature applications, making it safer for prolonged use compared to Kanthal. Kanthal, while highly durable and resistant to oxidation, can generate potentially harmful particles if overheated or improperly handled. Proper ventilation, temperature control, and use of personal protective equipment are essential to mitigate risks associated with both Nichrome and Kanthal alloys in various industrial processes.
Selecting the Right Alloy for Your Needs
Nichrome and Kanthal are popular alloys used in heating elements, each offering distinct advantages for specific applications. Nichrome provides rapid heating and excellent oxidation resistance, making it ideal for precise temperature control in laboratory and kitchen appliances. Kanthal excels in high-temperature durability and long service life, suitable for industrial furnaces and electric heaters requiring sustained heat under harsh conditions.
Nichrome vs Kanthal Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com