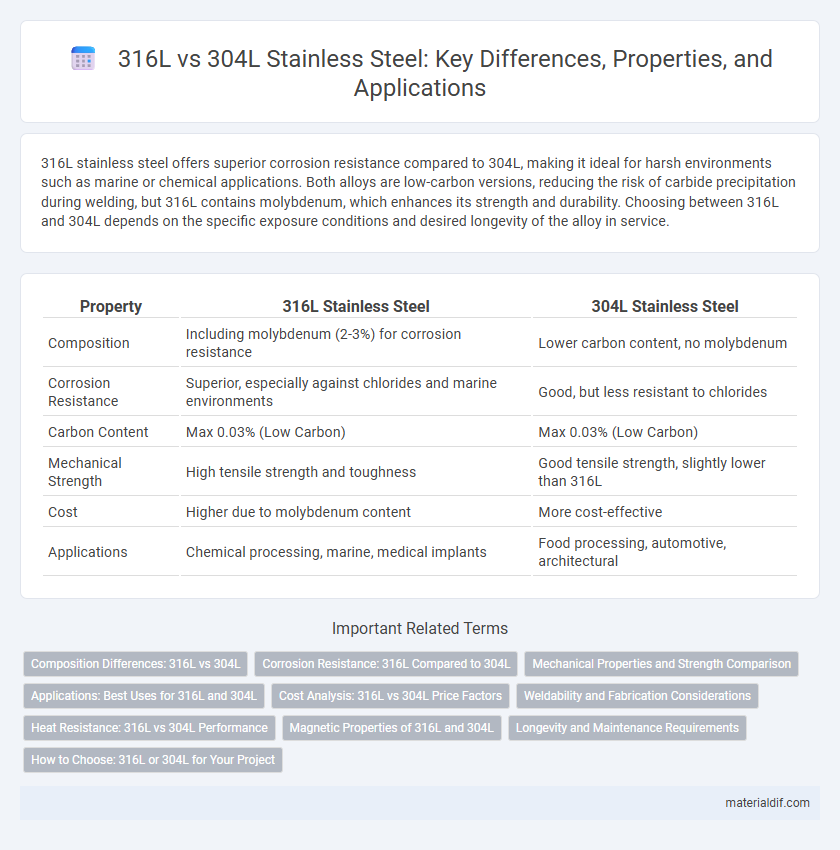
316L stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance compared to 304L, making it ideal for harsh environments such as marine or chemical applications. Both alloys are low-carbon versions, reducing the risk of carbide precipitation during welding, but 316L contains molybdenum, which enhances its strength and durability. Choosing between 316L and 304L depends on the specific exposure conditions and desired longevity of the alloy in service.
Table of Comparison
| Property | 316L Stainless Steel | 304L Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Including molybdenum (2-3%) for corrosion resistance | Lower carbon content, no molybdenum |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior, especially against chlorides and marine environments | Good, but less resistant to chlorides |
| Carbon Content | Max 0.03% (Low Carbon) | Max 0.03% (Low Carbon) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and toughness | Good tensile strength, slightly lower than 316L |
| Cost | Higher due to molybdenum content | More cost-effective |
| Applications | Chemical processing, marine, medical implants | Food processing, automotive, architectural |
Composition Differences: 316L vs 304L
316L stainless steel contains 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum, which enhances its corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides and industrial solvents. In contrast, 304L stainless steel features 18-20% chromium and 8-12% nickel without molybdenum, making it less resistant to pitting and crevice corrosion. The lower carbon content in both alloys reduces carbide precipitation, but 316L's molybdenum provides superior performance in harsh environments.
Corrosion Resistance: 316L Compared to 304L
316L stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance to 304L, especially in chloride-rich environments such as marine and chemical processing industries. The presence of molybdenum in 316L enhances its ability to withstand pitting and crevice corrosion more effectively than the chromium-nickel alloy composition of 304L. This makes 316L the preferred choice for applications requiring prolonged exposure to aggressive corrosive agents and high salinity conditions.
Mechanical Properties and Strength Comparison
316L stainless steel exhibits superior tensile strength and enhanced corrosion resistance compared to 304L, making it ideal for aggressive environments. Both alloys showcase excellent ductility, but 316L maintains higher yield strength and better impact resistance at elevated temperatures. The mechanical properties of 316L provide improved durability in marine and chemical processing applications relative to 304L.
Applications: Best Uses for 316L and 304L
316L stainless steel excels in marine, chemical, and medical applications due to its superior corrosion resistance and high chloride tolerance. 304L is commonly used in food processing, architectural components, and general fabrication where moderate corrosion resistance and cost efficiency are priorities. The choice between 316L and 304L hinges on exposure to harsh environments and the need for enhanced durability against pitting and crevice corrosion.
Cost Analysis: 316L vs 304L Price Factors
316L stainless steel typically commands a higher price than 304L due to its increased molybdenum content, which enhances corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. The cost differences also reflect variations in raw material prices, manufacturing complexity, and supply demand dynamics within the stainless steel market. Selecting between 316L and 304L alloys requires balancing budget constraints with application-specific performance requirements to optimize overall project expenses.
Weldability and Fabrication Considerations
316L stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance in chloride environments compared to 304L, making it preferable for welded applications exposed to harsh chemicals. Its lower carbon content minimizes carbide precipitation during welding, reducing the risk of intergranular corrosion and enhancing joint integrity. Fabrication of 316L requires slightly higher heat input, but the alloy's austenitic structure ensures excellent formability and weldability for complex assemblies.
Heat Resistance: 316L vs 304L Performance
316L stainless steel exhibits superior heat resistance compared to 304L, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 870degC (1600degF), whereas 304L is effective only up to 925degC (1700degF) intermittently but 870degC continuously. The molybdenum content in 316L enhances oxidation resistance and prevents scaling in high-temperature environments. For applications requiring prolonged exposure to heat, 316L is preferred due to its better thermal stability and corrosion resistance under elevated temperatures.
Magnetic Properties of 316L and 304L
316L stainless steel exhibits lower magnetic permeability compared to 304L due to its higher nickel content and increased austenite phase stability, making it essentially non-magnetic in the annealed condition. 304L stainless steel, while also primarily austenitic, can develop slight magnetism when cold-worked due to martensitic transformation. This magnetic behavior difference influences applications requiring non-magnetic materials, with 316L preferred in environments demanding minimal magnetic interference.
Longevity and Maintenance Requirements
316L stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance compared to 304L, significantly enhancing longevity, especially in harsh environments such as marine or chemical exposure. This alloy's molybdenum content reduces maintenance frequency by preventing pitting and crevice corrosion, extending overall service life. In contrast, 304L requires more frequent upkeep and is less durable under aggressive conditions, affecting its long-term reliability.
How to Choose: 316L or 304L for Your Project
Choosing between 316L and 304L stainless steel depends on your project's environmental and chemical exposure requirements, as 316L offers superior corrosion resistance against chlorides and marine environments due to its molybdenum content. For applications involving high temperatures or acidic conditions, 316L provides enhanced durability and longevity, while 304L is suitable for general-purpose use with less aggressive conditions. Consider factors such as budget, environmental exposure, and mechanical properties when deciding the most appropriate alloy for your specific application.
316L vs 304L Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com