Zinc flake coating provides superior corrosion resistance through a sacrificial barrier that protects metal surfaces without compromising their mechanical integrity. Zinc-rich paint contains a high percentage of zinc particles but offers limited durability compared to zinc flake coatings, especially in harsh environmental conditions. Choosing zinc flake coating ensures longer-lasting protection and enhanced performance for industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
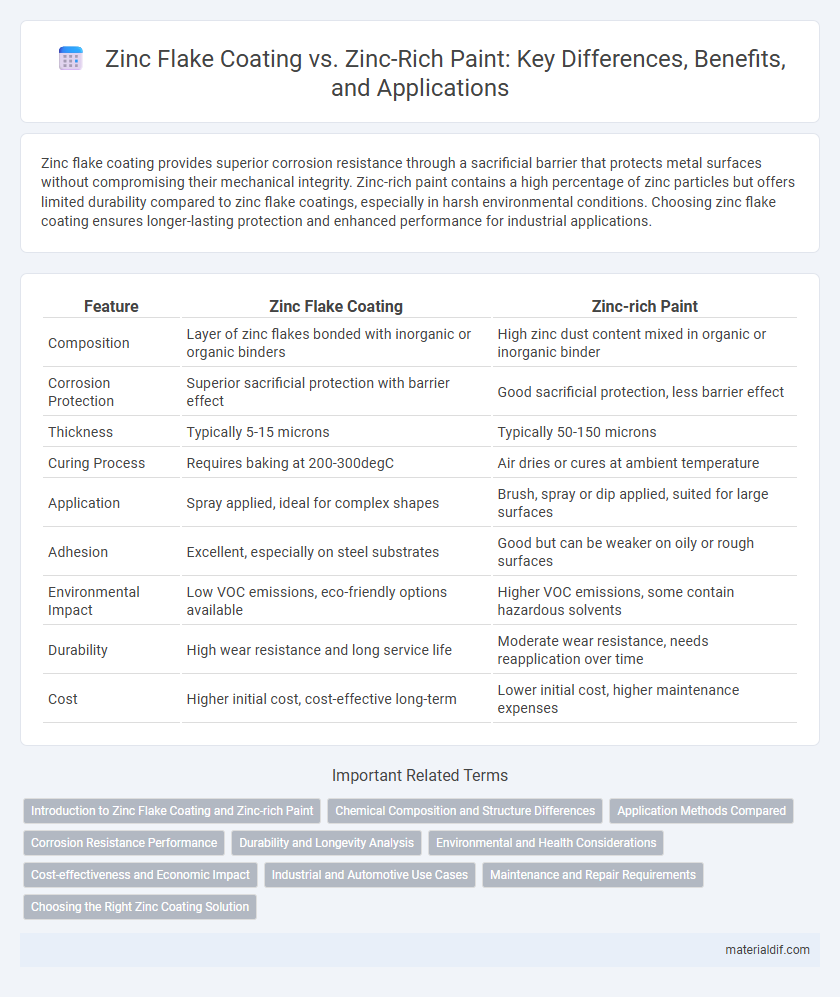
| Feature | Zinc Flake Coating | Zinc-rich Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Layer of zinc flakes bonded with inorganic or organic binders | High zinc dust content mixed in organic or inorganic binder |
| Corrosion Protection | Superior sacrificial protection with barrier effect | Good sacrificial protection, less barrier effect |
| Thickness | Typically 5-15 microns | Typically 50-150 microns |
| Curing Process | Requires baking at 200-300degC | Air dries or cures at ambient temperature |
| Application | Spray applied, ideal for complex shapes | Brush, spray or dip applied, suited for large surfaces |
| Adhesion | Excellent, especially on steel substrates | Good but can be weaker on oily or rough surfaces |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOC emissions, eco-friendly options available | Higher VOC emissions, some contain hazardous solvents |
| Durability | High wear resistance and long service life | Moderate wear resistance, needs reapplication over time |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, cost-effective long-term | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance expenses |
Introduction to Zinc Flake Coating and Zinc-rich Paint
Zinc flake coating is a thin, chromium-free anti-corrosion layer composed of zinc and aluminum flakes, providing superior resistance to corrosion without the need for electroplating. Zinc-rich paint contains a high percentage of zinc pigment suspended in a binder, offering sacrificial protection by corroding preferentially to the underlying steel. Both methods are widely used to enhance the durability of metal substrates in automotive, construction, and industrial applications, with zinc flake coatings delivering longer lifespan and environmental benefits.
Chemical Composition and Structure Differences
Zinc flake coating consists of micronized zinc particles suspended in a binder system, forming a thin, inorganic layer with exceptional cathodic protection properties and high resistance to corrosion and wear. Zinc-rich paint contains a higher concentration of zinc dust mixed with organic binders, creating a thicker, more porous layer that provides sacrificial protection through the electrochemical activity of zinc particles embedded within the paint film. The structural distinction lies in zinc flake coating's dense, non-electrolytic barrier compared to the more porous and organic matrix of zinc-rich paint, influencing durability, adhesion, and environmental resistance.
Application Methods Compared
Zinc flake coating is applied through a controlled dip-spinning or spray process, resulting in a thin, uniform layer that offers superior corrosion resistance without the need for heat curing. Zinc-rich paint is typically applied using conventional methods such as brush, roller, or spray but requires multiple coats and longer drying times to achieve effective protection. The application efficiency and uniformity of zinc flake coatings make them preferable for high-performance industrial components compared to the thicker, more labor-intensive zinc-rich paint.
Corrosion Resistance Performance
Zinc flake coating provides superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc-rich paint due to its uniform, thin-layered structure that offers enhanced barrier protection and sacrificial anodic behavior. Zinc flake coatings achieve extended durability in aggressive environments by combining metallic zinc particles with inorganic binders, reducing the risk of rust formation for over 1,000 hours in salt spray tests. Zinc-rich paints generally offer less consistent coverage and shorter lifespan, making them less effective for long-term corrosion protection in harsh industrial applications.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Zinc flake coating provides superior durability by offering a thin, uniform layer that resists corrosion even in harsh environments, outperforming zinc-rich paint which often requires thicker applications to achieve similar protection. The superior adhesion and cathodic protection of zinc flake coatings significantly extend the lifespan of metal substrates, reducing maintenance frequency and cost. Zinc-rich paint, while effective, can degrade faster under mechanical stress and UV exposure, resulting in shorter longevity compared to zinc flake coating.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Zinc flake coating offers a solvent-free, low-VOC alternative to zinc-rich paint, significantly reducing harmful emissions and occupational exposure to volatile organic compounds. Zinc-rich paint often contains heavy metals and solvents that can pose environmental risks during application and disposal, whereas zinc flake coatings produce less hazardous waste and demonstrate better corrosion resistance without toxic binders. Choosing zinc flake coating enhances workplace safety and supports eco-friendly practices by minimizing air and soil pollution associated with traditional zinc-rich coatings.
Cost-effectiveness and Economic Impact
Zinc flake coating generally offers a more cost-effective solution than zinc-rich paint due to its superior corrosion resistance and longer service life, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Zinc-rich paint, while initially lower in material cost, often incurs higher total costs because of more frequent reapplications and shorter durability. Investing in zinc flake coating can yield significant economic benefits by enhancing asset longevity and minimizing downtime in industrial applications.
Industrial and Automotive Use Cases
Zinc flake coating offers superior corrosion resistance and is ideal for industrial and automotive components exposed to harsh environments, providing a thin, uniform, and non-electrolytic layer that prevents rust without the risk of hydrogen embrittlement. Zinc-rich paint contains a high percentage of zinc dust, enabling it to act as a sacrificial anode, but it typically requires thicker application and frequent maintenance in heavy-duty industrial settings. In automotive manufacturing, zinc flake coatings enhance durability and aesthetic quality on complex parts, whereas zinc-rich paint is favored for large-scale steel structures and repair applications requiring cost-effective corrosion protection.
Maintenance and Repair Requirements
Zinc flake coatings require minimal maintenance due to their non-sacrificial corrosion protection, providing durable, long-lasting barriers without frequent touch-ups. Zinc-rich paints, while offering good corrosion resistance through sacrificial protection, typically need regular inspections and periodic recoating to maintain effectiveness in harsh environments. Repairing zinc-rich paint involves surface preparation and reapplication, whereas zinc flake coatings often allow spot repairs with less surface prep, reducing downtime and labor costs.
Choosing the Right Zinc Coating Solution
Zinc flake coating provides superior corrosion resistance through a thin, uniform layer ideal for automotive and industrial applications requiring long-term protection without compromising tight tolerances. Zinc-rich paint offers effective corrosion protection by incorporating high levels of zinc dust in a binder, making it suitable for maintenance and repair with ease of application on large structures. Selecting the right zinc coating solution depends on factors such as environmental exposure, durability requirements, substrate compatibility, and application method, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Zinc Flake Coating vs Zinc-rich Paint Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com