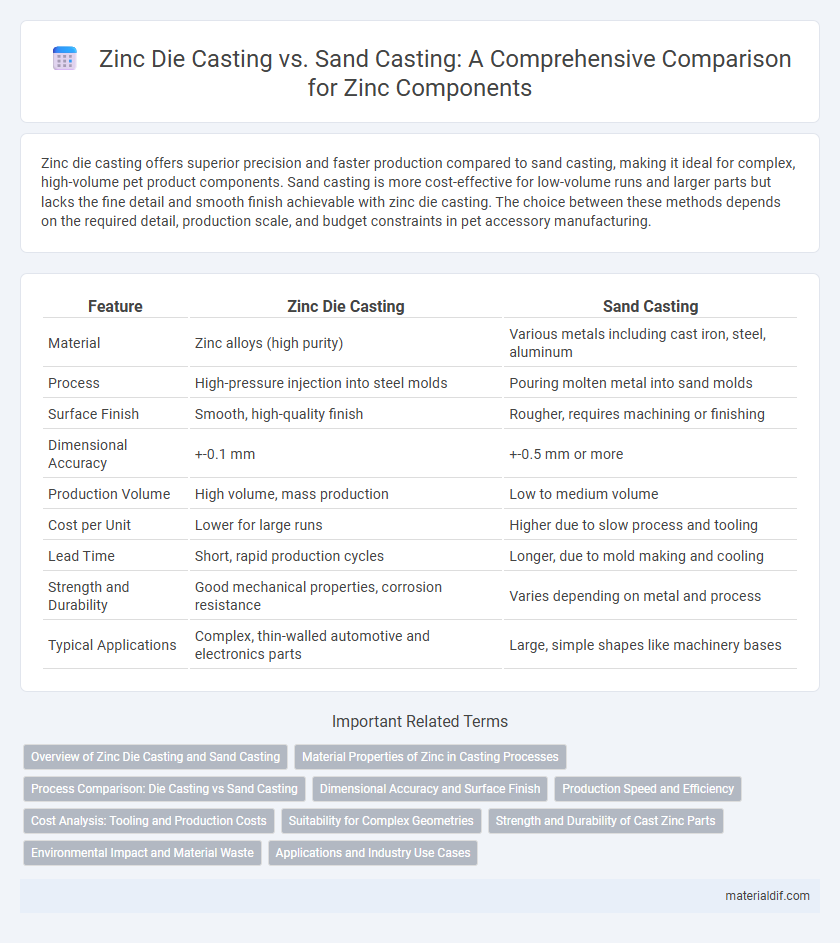
Zinc die casting offers superior precision and faster production compared to sand casting, making it ideal for complex, high-volume pet product components. Sand casting is more cost-effective for low-volume runs and larger parts but lacks the fine detail and smooth finish achievable with zinc die casting. The choice between these methods depends on the required detail, production scale, and budget constraints in pet accessory manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zinc Die Casting | Sand Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Zinc alloys (high purity) | Various metals including cast iron, steel, aluminum |
| Process | High-pressure injection into steel molds | Pouring molten metal into sand molds |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, high-quality finish | Rougher, requires machining or finishing |
| Dimensional Accuracy | +-0.1 mm | +-0.5 mm or more |
| Production Volume | High volume, mass production | Low to medium volume |
| Cost per Unit | Lower for large runs | Higher due to slow process and tooling |
| Lead Time | Short, rapid production cycles | Longer, due to mold making and cooling |
| Strength and Durability | Good mechanical properties, corrosion resistance | Varies depending on metal and process |
| Typical Applications | Complex, thin-walled automotive and electronics parts | Large, simple shapes like machinery bases |
Overview of Zinc Die Casting and Sand Casting
Zinc die casting involves injecting molten zinc into a steel mold under high pressure, producing precise, complex shapes with smooth surface finishes and tight dimensional tolerances. Sand casting uses a sand-based mold to shape molten metal, offering flexibility for large parts but resulting in rougher surfaces and less accuracy. Zinc die casting is ideal for mass production of small to medium-sized components, while sand casting suits larger, simpler designs with lower volume requirements.
Material Properties of Zinc in Casting Processes
Zinc's low melting point of approximately 420degC enables efficient die casting with rapid solidification, producing intricate and high-precision components. In contrast, sand casting, suitable for larger and less detailed parts, benefits from zinc's excellent fluidity and corrosion resistance but results in a coarser surface finish. The superior mechanical strength and dimensional accuracy achieved through zinc die casting make it preferable for mass production compared to the versatility but lower precision of sand casting.
Process Comparison: Die Casting vs Sand Casting
Zinc die casting involves injecting molten zinc into a steel mold under high pressure, resulting in precise, high-volume production with excellent surface finishes and tight tolerances. Sand casting uses a sand mold to shape molten zinc, offering greater flexibility for complex, large parts but with slower production cycles and rougher surface textures. Die casting provides faster cycle times and better dimensional accuracy, while sand casting is more cost-effective for low-volume runs and large components.
Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Finish
Zinc die casting offers superior dimensional accuracy compared to sand casting due to its precise mold design and high-pressure injection process, resulting in tighter tolerances and consistent part replication. The surface finish in zinc die casting is typically smoother and more refined, reducing the need for extensive post-processing, while sand casting produces rougher textures that often require additional machining or polishing. These distinctions make zinc die casting ideal for applications demanding detailed, high-quality components with minimal surface imperfections.
Production Speed and Efficiency
Zinc die casting offers significantly faster production speeds compared to sand casting due to its ability to rapidly inject molten metal into reusable steel molds, enabling high-volume manufacturing with minimal cycle times ranging from 15 to 45 seconds. In contrast, sand casting involves longer mold preparation and cooling times, reducing overall efficiency especially in mass production scenarios. The high precision and automation potential of zinc die casting further enhance manufacturing throughput, making it the preferred method for industries requiring rapid turnarounds and consistent quality.
Cost Analysis: Tooling and Production Costs
Zinc die casting offers lower per-unit production costs compared to sand casting due to its reusable metal molds that reduce wear and enable high-volume manufacturing. Initial tooling expenses for die casting are higher, often reaching several thousand dollars, but these costs are offset as production scales, resulting in significant cost savings for large runs. Sand casting incurs lower upfront tooling costs with expendable sand molds, but higher labor and longer cycle times increase overall expenses in mass production.
Suitability for Complex Geometries
Zinc die casting excels in producing intricate and complex geometries with high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes, making it ideal for detailed automotive and electronics components. In contrast, sand casting is more suitable for larger, less detailed parts where tight tolerances and fine details are not critical, due to its coarser surface texture and lower precision. The superior mold design and rapid cooling in zinc die casting enable intricate internal features and thin walls that sand casting cannot efficiently achieve.
Strength and Durability of Cast Zinc Parts
Zinc die casting produces parts with superior strength and durability due to its fine-grain microstructure and minimal porosity compared to sand casting. The high-pressure injection process in die casting ensures consistent density and reduced defects, enhancing mechanical performance. In contrast, sand-cast zinc parts often exhibit coarser grain structures and higher porosity, resulting in lower overall strength and reduced wear resistance.
Environmental Impact and Material Waste
Zinc die casting produces significantly less material waste compared to sand casting, as the process allows for precise molten metal injection and near-net-shape components, minimizing excess alloy usage. The environmental impact of zinc die casting is lower due to reduced energy consumption and higher recyclability of zinc scrap within the closed-loop recycling system. Sand casting generates more waste in the form of used sand and leftover metal, contributing to increased landfill use and higher resource consumption.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Zinc die casting is extensively used in the automotive, electronics, and hardware industries due to its ability to produce complex, high-precision components with smooth finishes, ideal for small to medium-sized parts like housings and connectors. In contrast, sand casting is favored in heavy machinery, aerospace, and foundry sectors for its versatility in creating large, robust parts with lower production volumes, such as engine blocks and industrial equipment bases. The choice between zinc die casting and sand casting depends largely on the required production scale, detail precision, and component size within specific industry applications.
Zinc Die Casting vs Sand Casting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com