Die cast zinc offers superior strength, durability, and precision compared to injection molded plastic, making it ideal for high-stress applications in the pet industry. Zinc's excellent corrosion resistance enhances product longevity, while injection molded plastic provides cost-effective, lightweight options with greater design flexibility. Choosing between die cast zinc and injection molded plastic depends on the balance between durability needs and budget constraints.
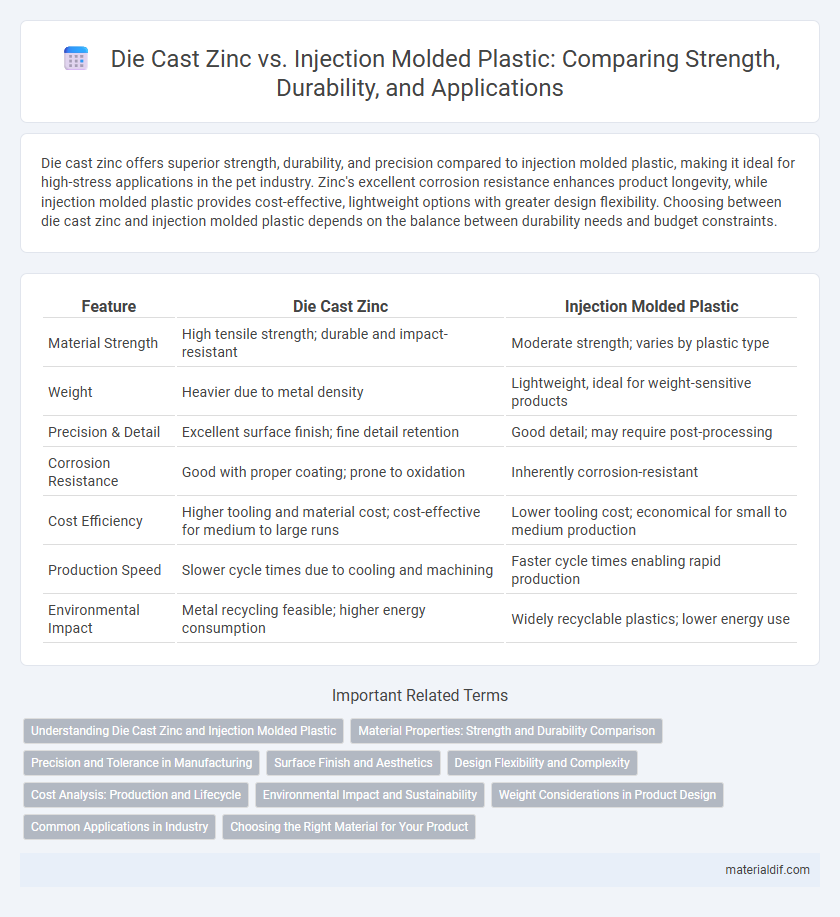
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Die Cast Zinc | Injection Molded Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Strength | High tensile strength; durable and impact-resistant | Moderate strength; varies by plastic type |
| Weight | Heavier due to metal density | Lightweight, ideal for weight-sensitive products |
| Precision & Detail | Excellent surface finish; fine detail retention | Good detail; may require post-processing |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good with proper coating; prone to oxidation | Inherently corrosion-resistant |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher tooling and material cost; cost-effective for medium to large runs | Lower tooling cost; economical for small to medium production |
| Production Speed | Slower cycle times due to cooling and machining | Faster cycle times enabling rapid production |
| Environmental Impact | Metal recycling feasible; higher energy consumption | Widely recyclable plastics; lower energy use |
Understanding Die Cast Zinc and Injection Molded Plastic
Die cast zinc offers superior strength, durability, and precision compared to injection molded plastic, making it ideal for high-stress applications requiring detailed metal components. Injection molded plastic is favored for lightweight, cost-effective production with versatile design flexibility but typically lacks the mechanical robustness and wear resistance of die cast zinc parts. Understanding these differences helps manufacturers select materials based on performance requirements, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
Material Properties: Strength and Durability Comparison
Die cast zinc exhibits superior strength and durability compared to injection molded plastic, with tensile strength typically ranging from 300 to 400 MPa, whereas common injection molded plastics like ABS or polycarbonate average between 40 to 70 MPa. Zinc alloys feature high impact resistance, excellent dimensional stability, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term wear and mechanical stress endurance. In contrast, injection molded plastics often suffer from lower mechanical strength and can degrade under UV exposure or chemical contact, limiting their use in heavy-duty or outdoor environments.
Precision and Tolerance in Manufacturing
Die cast zinc offers superior precision and tighter tolerances compared to injection molded plastic, achieving dimensional accuracy often within +-0.005 inches. The metal's low thermal expansion and smooth flow during die casting minimize warping and shrinkage defects, ensuring consistent part quality. Injection molded plastic typically exhibits higher variability due to material shrinkage and mold wear, which can affect the repeatability of fine details and tight tolerance demands.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
Die cast zinc offers a superior surface finish and aesthetics compared to injection molded plastic, featuring a smooth, metallic luster with minimal post-processing needed. Zinc's high fluidity during casting captures intricate details and sharp edges, resulting in precise and consistent textures. Injection molded plastic often requires painting or coating to achieve comparable visual appeal but may lack the durability and premium feel inherent to die cast zinc components.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
Die cast zinc offers superior design flexibility and complexity compared to injection molded plastic, enabling intricate shapes and finer details with higher dimensional accuracy. Zinc's excellent fluidity during casting allows for thin walls and embedded threads, which are difficult to achieve with plastic. Injection molded plastic, while versatile, often requires more design compromises due to material shrinkage and lower structural strength in complex geometries.
Cost Analysis: Production and Lifecycle
Die cast zinc offers lower production costs for high-volume manufacturing due to faster cycle times and reduced material waste compared to injection molded plastic. Zinc's superior durability and corrosion resistance contribute to a longer product lifecycle, decreasing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Although initial tooling costs for zinc die casting are higher, the overall cost-effectiveness improves with large production runs and extended product use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Die cast zinc offers superior environmental benefits compared to injection molded plastic due to its recyclability and longer lifecycle, significantly reducing waste and resource consumption. Zinc manufacturing processes have improved energy efficiency and emit fewer greenhouse gases compared to plastic production, which relies heavily on petroleum-based materials. Sustainable zinc production supports circular economy principles, making it a greener choice for industries focused on reducing carbon footprints and minimizing ecological damage.
Weight Considerations in Product Design
Die cast zinc offers significantly higher density, resulting in heavier components compared to injection molded plastic, which is favored for its lightweight properties in product design. The weight of zinc enhances product durability and stability, making it ideal for parts requiring strength and impact resistance. In contrast, injection molded plastic allows for more intricate shapes with minimal weight, benefiting applications where reducing mass is critical for performance and handling.
Common Applications in Industry
Die cast zinc is widely used in automotive parts, electrical components, and hardware due to its strength, durability, and ability to create intricate shapes with excellent surface finishes. Injection molded plastic dominates in consumer electronics, packaging, and toys because of its lightweight nature, versatility, and cost-effective mass production. Industrial sectors often select die cast zinc for load-bearing or heat-resistant applications, while injection molded plastic suits designs requiring flexibility and complex geometries.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Product
Die cast zinc offers superior strength, durability, and intricate detail compared to injection molded plastic, making it ideal for high-stress applications and premium products. Injection molded plastic excels in cost efficiency, lightweight properties, and flexibility for complex shapes, suitable for mass production and lower-load components. Selecting the right material depends on balancing product requirements such as mechanical strength, cost constraints, and design complexity to achieve optimal performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Die Cast Zinc vs Injection Molded Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com