Particle board is made from compressed wood chips and resin, offering a smooth surface ideal for cabinetry and furniture but lacking the structural strength of oriented strand board (OSB). OSB consists of layered wood strands arranged in cross-oriented layers, providing superior durability and load-bearing capacity, making it preferable for subflooring and roofing. While particle board is cost-effective and easy to machine, OSB delivers enhanced moisture resistance and long-term performance in construction applications.
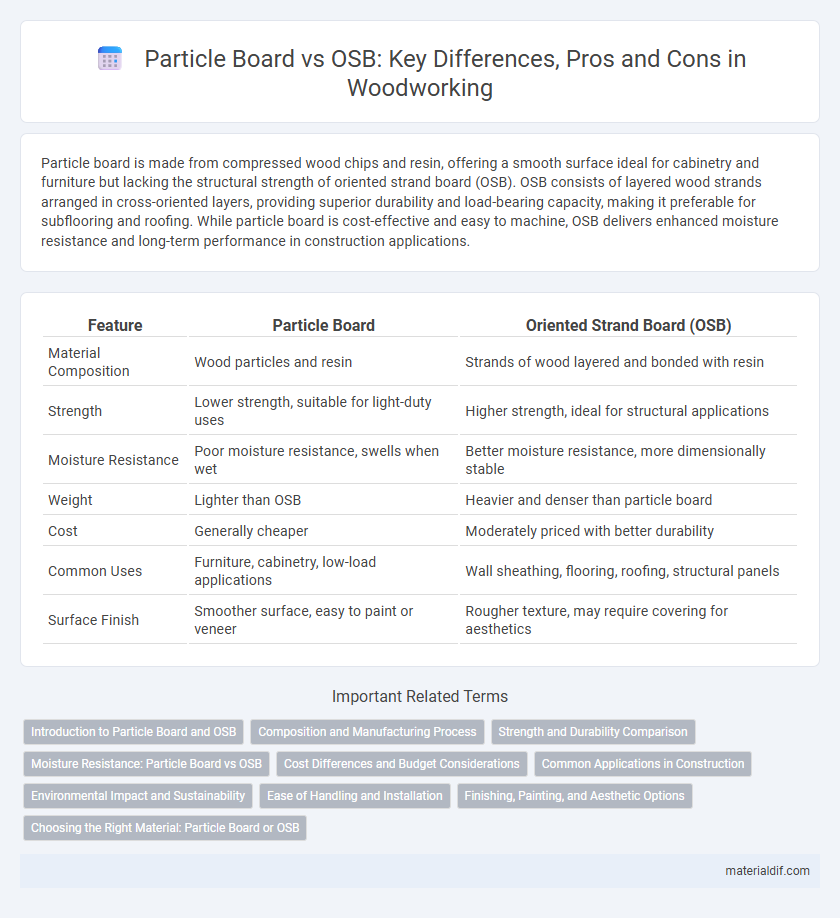
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Particle Board | Oriented Strand Board (OSB) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood particles and resin | Strands of wood layered and bonded with resin |
| Strength | Lower strength, suitable for light-duty uses | Higher strength, ideal for structural applications |
| Moisture Resistance | Poor moisture resistance, swells when wet | Better moisture resistance, more dimensionally stable |
| Weight | Lighter than OSB | Heavier and denser than particle board |
| Cost | Generally cheaper | Moderately priced with better durability |
| Common Uses | Furniture, cabinetry, low-load applications | Wall sheathing, flooring, roofing, structural panels |
| Surface Finish | Smoother surface, easy to paint or veneer | Rougher texture, may require covering for aesthetics |
Introduction to Particle Board and OSB
Particle board is an engineered wood product made from wood chips, sawmill shavings, and resin, compressed under heat to form dense panels commonly used in furniture and cabinetry. Oriented Strand Board (OSB) consists of large wood strands arranged in layers and bonded with adhesives, offering higher strength and moisture resistance, ideal for structural applications like subflooring and wall sheathing. Both materials provide cost-effective alternatives to plywood but differ significantly in composition, durability, and usage scenarios.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Particle board consists of wood chips, sawdust, and resin bonded under heat and pressure, creating a dense panel ideal for furniture and cabinetry. Oriented strand board (OSB) is made from large wood strands layered in specific orientations, then compressed with adhesives to enhance strength and rigidity. The manufacturing process of OSB emphasizes directional layering, resulting in superior structural stability compared to the randomly arranged particles in particle board.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Particle board consists of wood chips and resin, offering moderate strength but lower durability compared to Oriented Strand Board (OSB), which is made from compressed wood strands aligned in layers. OSB exhibits higher structural integrity, superior shear strength, and better resistance to moisture, making it more suitable for load-bearing applications and exterior use. The engineered composition of OSB enhances its durability against warping and swelling, outperforming particle board in long-term performance.
Moisture Resistance: Particle Board vs OSB
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) offers superior moisture resistance compared to particle board due to its cross-oriented wood strands and water-resistant adhesives that enhance structural integrity in damp environments. Particle board, made from compressed wood particles and less water-resistant resin, tends to swell and degrade rapidly when exposed to moisture. This makes OSB a preferred choice for applications such as subflooring and roofing where moisture exposure is a significant concern.
Cost Differences and Budget Considerations
Particle board generally costs less than Oriented Strand Board (OSB) due to lower material and manufacturing expenses, making it a more affordable option for budget-conscious projects. OSB offers greater strength and moisture resistance, which can justify its higher price in applications requiring durability, despite the increased upfront cost. Budget considerations should weigh the initial cost savings of particle board against potential long-term performance benefits and maintenance costs associated with OSB.
Common Applications in Construction
Particle board is commonly used for indoor furniture, cabinetry, and underlayment due to its smooth surface and ease of finishing, making it ideal for non-structural applications. Oriented Strand Board (OSB) is favored in structural construction such as wall sheathing, roof decking, and subflooring because of its strength, durability, and resistance to moisture. Builders often select OSB for load-bearing applications, while particle board suits aesthetic and lightweight needs within interior settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Particle board and OSB (Oriented Strand Board) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability. Particle board is typically made from recycled wood fibers and adhesive resins, reducing waste but often contains formaldehyde-based binders that can emit harmful VOCs. OSB, produced from fast-growing, sustainably harvested small-diameter trees and using less adhesive, tends to have a lower environmental footprint and better structural strength, making it a more sustainable choice in eco-friendly building projects.
Ease of Handling and Installation
Particle board is lighter and easier to cut, making it more manageable for quick installations in smaller projects. OSB (Oriented Strand Board) offers greater strength and rigidity, but its denser composition requires more effort to handle and install, especially in large-scale construction. Both materials benefit from standard woodworking tools, but OSB often demands additional fasteners and protective measures to ensure durability during installation.
Finishing, Painting, and Aesthetic Options
Particle board offers a smooth surface ideal for veneers and laminates, making it suitable for painted finishes and decorative coatings that mask its lower aesthetic appeal. OSB features a textured, flaked wood pattern that can be stained or sealed but often requires specialized primers for uniform paint application due to its uneven surface. Both materials accommodate a range of finishing techniques, but particle board generally delivers a cleaner look for high-visibility projects while OSB suits more rustic or industrial aesthetics.
Choosing the Right Material: Particle Board or OSB
Particle board offers a smooth surface ideal for interior furniture and cabinetry where cost-efficiency is essential, but it lacks the moisture resistance and structural strength of OSB. Oriented Strand Board (OSB) provides enhanced durability and superior load-bearing capacity, making it suitable for subflooring, roofing, and exterior sheathing in construction projects exposed to weather elements. Selecting between particle board and OSB depends on the specific application requirements, including moisture exposure, load demands, and budget constraints.
Particle Board vs OSB Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com