Teak wood is highly valued for its exceptional durability, natural resistance to water, and rich golden-brown color, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and marine applications. Mahogany stands out with its deep reddish-brown hue, fine grain, and excellent workability, often used in high-end indoor furniture and cabinetry. Both woods offer unique aesthetic and functional qualities, but teak's superior weather resistance typically makes it more suitable for exterior use.
Table of Comparison
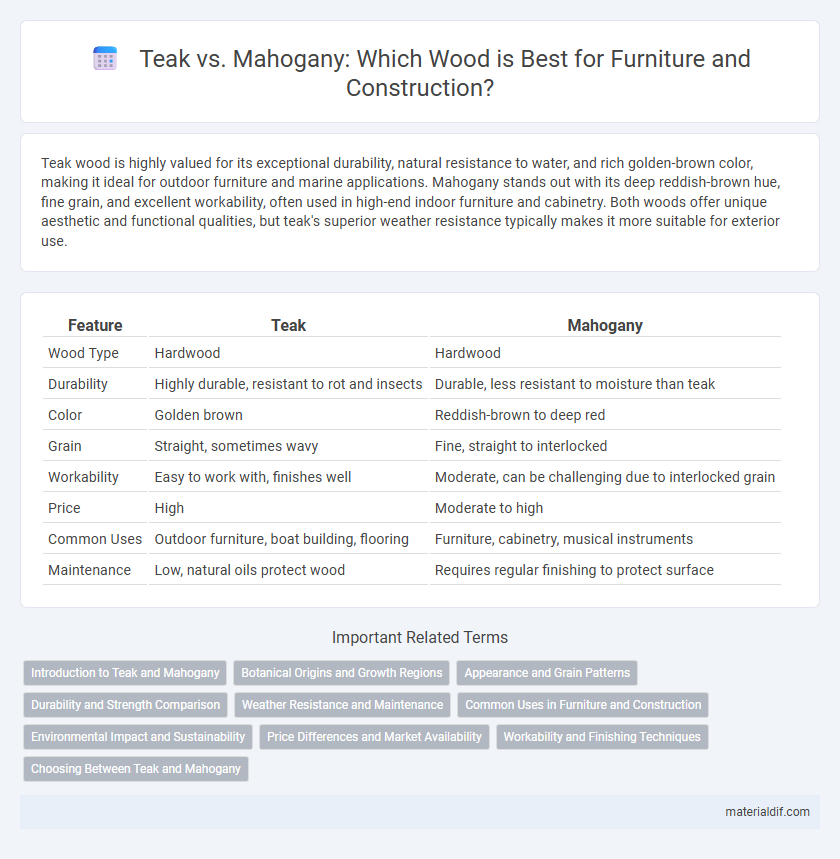
| Feature | Teak | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Hardwood |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to rot and insects | Durable, less resistant to moisture than teak |
| Color | Golden brown | Reddish-brown to deep red |
| Grain | Straight, sometimes wavy | Fine, straight to interlocked |
| Workability | Easy to work with, finishes well | Moderate, can be challenging due to interlocked grain |
| Price | High | Moderate to high |
| Common Uses | Outdoor furniture, boat building, flooring | Furniture, cabinetry, musical instruments |
| Maintenance | Low, natural oils protect wood | Requires regular finishing to protect surface |
Introduction to Teak and Mahogany
Teak and mahogany are two premium hardwoods prized for their durability and rich appearance, widely used in furniture and boat building. Teak is renowned for its natural oils, making it highly resistant to water, decay, and insects, ideal for outdoor use. Mahogany is celebrated for its fine grain and warm reddish-brown hue, frequently chosen for luxury indoor furnishings and decorative veneers.
Botanical Origins and Growth Regions
Teak (Tectona grandis) originates from the Lamiaceae family and primarily thrives in tropical regions of Southeast Asia, including India, Myanmar, and Thailand. Mahogany, belonging to the Meliaceae family, is native to the Americas, with major growth areas in Central and South America, particularly Honduras and Brazil. Both hardwoods differ significantly in botanical lineage and climatic adaptation, influencing their global distribution and timber characteristics.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Teak wood exhibits a rich golden-brown color with a straight, tight grain pattern often accompanied by natural oils, giving it a smooth, lustrous finish. Mahogany typically features a deep reddish-brown hue with a more pronounced interlocking grain pattern, creating a distinctive wavy or curly texture prized for elegant woodworking. Both woods offer unique aesthetic qualities, but teak's uniform grain contrasts sharply with mahogany's complex, decorative grain patterns.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Teak wood exhibits superior durability due to its natural oils that resist rot, insects, and water damage, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and marine applications. Mahogany offers substantial strength and a dense grain but is more vulnerable to moisture and insect attacks without proper treatment. Overall, teak outperforms mahogany in long-term resilience and structural integrity under harsh environmental conditions.
Weather Resistance and Maintenance
Teak wood is highly prized for its exceptional weather resistance due to its natural oils and dense grain, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and marine applications with minimal maintenance. Mahogany, while durable and resistant to rot, requires regular sealing and treatment to maintain its appearance and protect it from moisture and UV damage. The superior weather resistance of teak reduces upkeep needs, whereas mahogany demands more frequent maintenance to prevent cracking and fading in harsh weather conditions.
Common Uses in Furniture and Construction
Teak is highly valued in outdoor furniture and decking due to its natural oils that resist water, decay, and insects, making it ideal for marine and garden applications. Mahogany, prized for its rich, reddish-brown color and fine grain, is commonly used in high-end indoor furniture, cabinetry, and interior paneling, offering durability and a luxurious finish. Both woods are favored in construction for their strength, but teak's superior weather resistance sets it apart for exterior use, while mahogany excels in decorative and structural interior elements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Teak wood, primarily sourced from Southeast Asia, is valued for its durability but often linked to deforestation due to illegal logging and slow growth rates, raising sustainability concerns. Mahogany, commonly found in Central and South America, faces similar challenges with overharvesting and habitat loss, though certified plantations are promoting more responsible cultivation. Both woods demand careful management and certification like FSC to mitigate environmental impact and support sustainable forestry practices.
Price Differences and Market Availability
Teak wood typically commands a higher price than mahogany due to its superior durability, natural oil content, and resistance to pests and weathering. Mahogany is more widely available in the global market, often sourced from sustainable plantations, making it a cost-effective alternative for high-quality furniture. Price fluctuations for teak are influenced by limited natural growth regions and higher demand, whereas mahogany's broader distribution supports more stable market pricing.
Workability and Finishing Techniques
Teak offers exceptional workability due to its moderate density and natural oils that enhance machining and sanding processes, while mahogany's fine grain and consistent texture allow for smooth cutting and intricate carving. Both woods respond well to finishing techniques, with teak benefiting from oil finishes that highlight its natural luster and durability against weathering, whereas mahogany excels with stains and varnishes that deepen its rich, reddish-brown hues. The choice between teak and mahogany ultimately depends on the desired balance between ease of shaping and the specific aesthetic quality of the final finish.
Choosing Between Teak and Mahogany
Teak offers exceptional durability and natural resistance to water and pests, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and marine applications. Mahogany provides a rich, deep reddish-brown color with a fine grain, favored for indoor cabinetry and fine woodworking projects. Choosing between teak and mahogany depends on the specific use case, environmental exposure, and desired aesthetic qualities.
Teak vs Mahogany Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com