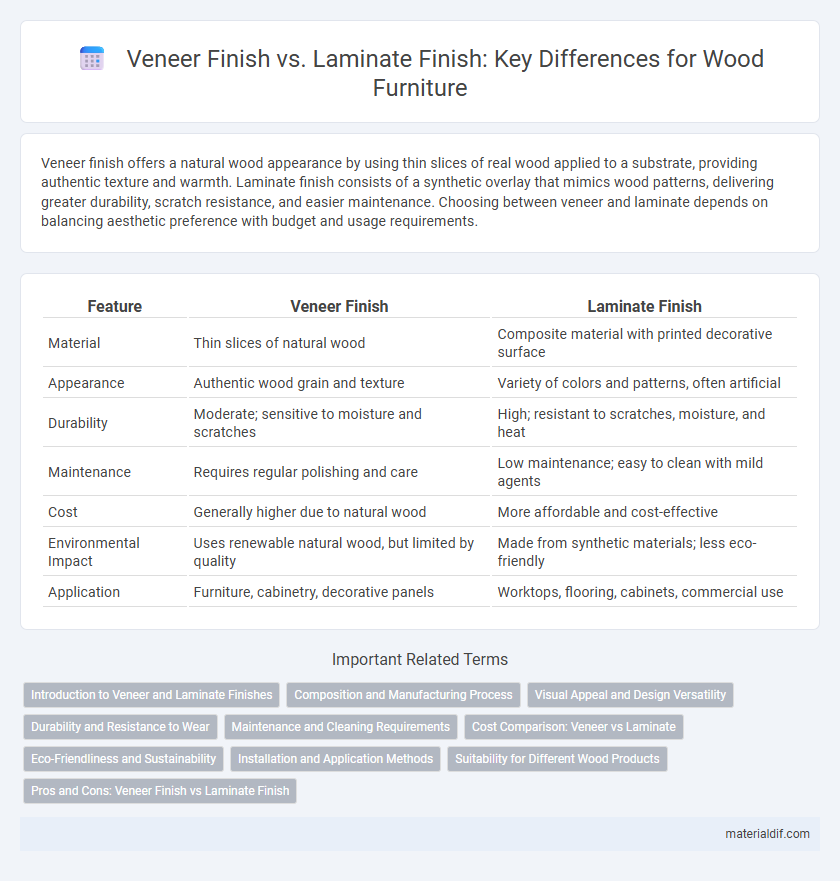
Veneer finish offers a natural wood appearance by using thin slices of real wood applied to a substrate, providing authentic texture and warmth. Laminate finish consists of a synthetic overlay that mimics wood patterns, delivering greater durability, scratch resistance, and easier maintenance. Choosing between veneer and laminate depends on balancing aesthetic preference with budget and usage requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Veneer Finish | Laminate Finish |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thin slices of natural wood | Composite material with printed decorative surface |
| Appearance | Authentic wood grain and texture | Variety of colors and patterns, often artificial |
| Durability | Moderate; sensitive to moisture and scratches | High; resistant to scratches, moisture, and heat |
| Maintenance | Requires regular polishing and care | Low maintenance; easy to clean with mild agents |
| Cost | Generally higher due to natural wood | More affordable and cost-effective |
| Environmental Impact | Uses renewable natural wood, but limited by quality | Made from synthetic materials; less eco-friendly |
| Application | Furniture, cabinetry, decorative panels | Worktops, flooring, cabinets, commercial use |
Introduction to Veneer and Laminate Finishes
Veneer finish involves applying a thin layer of natural wood to a substrate, offering the authentic texture and grain patterns of hardwood at a lower cost. Laminate finish consists of a printed decorative surface sealed with a protective overlay, providing durable, easy-to-clean options with a wide range of designs and colors. Both finishes enhance furniture and cabinetry, with veneer emphasizing natural beauty and laminate prioritizing versatility and resistance.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Veneer finish consists of a thin layer of natural wood sliced from logs, applied to plywood or MDF substrates through pressing and gluing, preserving the authentic grain and texture. Laminate finish uses a synthetic overlay composed of cellulose fibers impregnated with melamine resin, fused under high heat and pressure onto particleboard or MDF for durability and uniformity. The manufacturing of veneer maintains the wood's organic patterns, whereas laminate relies on printed designs and robust surface seals for resistance to scratches and moisture.
Visual Appeal and Design Versatility
Veneer finish showcases the natural grain and texture of real wood, offering a rich, authentic visual appeal ideal for high-end furniture and cabinetry. Laminate finish provides a broader range of design versatility with customizable patterns, colors, and textures, allowing for consistent and durable aesthetics suitable for modern, budget-friendly projects. Both finishes enhance interiors differently, with veneer emphasizing natural beauty and laminate emphasizing design flexibility.
Durability and Resistance to Wear
Veneer finish offers natural wood grain with moderate durability, suitable for light to medium wear environments but prone to scratches and moisture damage over time. Laminate finish provides superior resistance to wear, scratches, and stains due to its multi-layer synthetic construction, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and heavy use. Choosing laminate ensures long-lasting surface protection, while veneer emphasizes authentic wood appearance with less resilience.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Veneer finish requires gentle cleaning with mild soap and a soft cloth to preserve its natural wood grain and prevent damage, with occasional polishing to maintain its luster. Laminate finish is more durable and resistant to scratches and stains, allowing for easier maintenance through regular wiping with water or household cleaners. Both finishes demand prompt removal of spills to avoid surface degradation, but veneer is more sensitive to moisture and harsh chemicals compared to laminate.
Cost Comparison: Veneer vs Laminate
Veneer finish typically costs more than laminate due to the use of real wood layers, which require careful cutting and application, whereas laminate is made from synthetic materials that are cheaper to produce. The price difference can range from 20% to 50%, influenced by wood species and veneer thickness, making laminate a budget-friendly option for large projects. Laminate finishes also offer lower maintenance costs over time, while veneer may need refinishing, increasing long-term expenses.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Veneer finishes, derived from thin slices of natural wood, offer a more eco-friendly and sustainable option compared to laminate finishes, which are typically made from synthetic materials and resins. The production of veneer uses less raw timber and generates lower carbon emissions, supporting responsible forestry practices when sourced from certified suppliers. In contrast, laminate finishes often involve plastics and adhesives that are less biodegradable and contribute to environmental pollution during manufacturing and disposal.
Installation and Application Methods
Veneer finish installation requires careful handling and precise cutting since it involves thin slices of natural wood applied over substrates, often using adhesives and presses for a seamless look. Laminate finish installation is quicker and more straightforward, using high-pressure layers bonded to particleboard or MDF with click-lock systems or adhesives, suitable for DIY projects. Veneer is preferred for refined applications like cabinetry and furniture, while laminate suits high-traffic areas due to its durability and ease of replacement.
Suitability for Different Wood Products
Veneer finishes offer a natural wood appearance, making them ideal for high-end furniture, cabinetry, and decorative panels where authentic grain patterns enhance visual appeal. Laminate finishes provide durability and resistance to scratches and moisture, suitable for countertops, office furniture, and areas with high wear and tear. Choosing between veneer and laminate depends on the desired aesthetic, budget, and functional requirements of the wood product.
Pros and Cons: Veneer Finish vs Laminate Finish
Veneer finish offers a natural wood appearance with authentic grain patterns, making it ideal for high-end furniture and decor, but it is more susceptible to scratches and moisture damage. Laminate finish provides superior durability, resistance to stains and wear, and requires minimal maintenance, yet it lacks the depth and warmth of real wood grain. Choosing between veneer and laminate depends on the desired aesthetic value versus the need for heavy-duty performance in various environments.
Veneer Finish vs Laminate Finish Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com