Particle board and fiberboard are both engineered wood products, but particle board is made from wood chips and adhesive, resulting in a coarser texture and lower density, while fiberboard is composed of wood fibers that provide a smoother surface and higher density. Fiberboard typically offers better durability, moisture resistance, and is preferred for furniture and cabinetry where a fine finish is essential. Particle board is more cost-effective and commonly used in applications where strength is less critical, such as subflooring and inexpensive furniture.
Table of Comparison
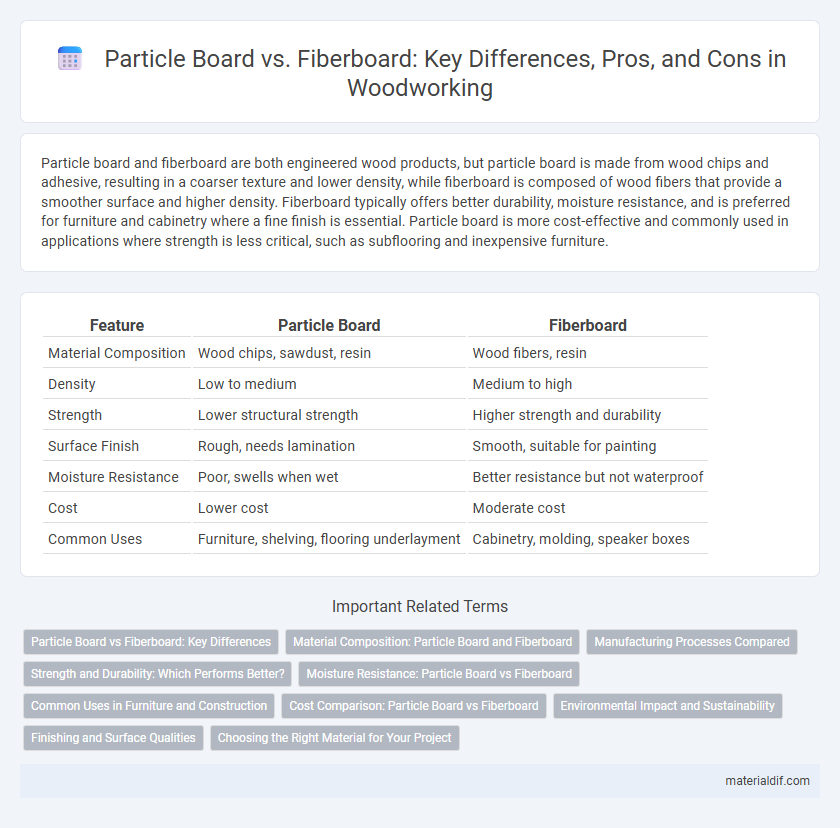
| Feature | Particle Board | Fiberboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood chips, sawdust, resin | Wood fibers, resin |
| Density | Low to medium | Medium to high |
| Strength | Lower structural strength | Higher strength and durability |
| Surface Finish | Rough, needs lamination | Smooth, suitable for painting |
| Moisture Resistance | Poor, swells when wet | Better resistance but not waterproof |
| Cost | Lower cost | Moderate cost |
| Common Uses | Furniture, shelving, flooring underlayment | Cabinetry, molding, speaker boxes |
Particle Board vs Fiberboard: Key Differences
Particle board consists of wood chips and resin pressed into dense sheets, offering affordability and moderate strength, while fiberboard, made from wood fibers, presents a smoother surface and higher density for enhanced durability and finish quality. Particle board is commonly used in inexpensive furniture and underlayment because of its cost-effectiveness, whereas fiberboard, including medium-density fiberboard (MDF), suits cabinetry and molding applications due to its superior machining properties. Moisture resistance varies significantly; fiberboard often undergoes additional treatments to improve water resistance, unlike particle board which is more prone to swelling and damage when exposed to moisture.
Material Composition: Particle Board and Fiberboard
Particle board consists of wood particles, such as chips, shavings, and sawdust, bonded together with synthetic resin adhesives under heat and pressure. Fiberboard is made from wood fibers that are broken down and reconstituted, typically with additive bonds like wax and resin, resulting in a denser, smoother panel. The differing compositions influence their density, durability, and applications in furniture and construction.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Particle board is produced by compressing wood chips, sawmill shavings, and sawdust with synthetic resin binders under heat and pressure, resulting in a dense, uniform sheet. Fiberboard manufacturing involves breaking wood fibers down into a pulp, which is then combined with adhesives and bonded using steam, heat, and pressure to create a smoother, more homogeneous panel. The primary distinction lies in particle board using larger wood particles whereas fiberboard uses fine wood fibers, impacting the board's density, strength, and surface finish.
Strength and Durability: Which Performs Better?
Particle board exhibits moderate strength and durability, making it suitable for lightweight furniture and interior applications, but it tends to be less resistant to moisture and impact compared to fiberboard. Fiberboard, particularly medium-density fiberboard (MDF) and high-density fiberboard (HDF), offers superior strength and durability due to its denser composition and improved resistance to warping, moisture, and wear. Overall, fiberboard outperforms particle board in structural stability and longevity, especially in environments with fluctuating humidity levels.
Moisture Resistance: Particle Board vs Fiberboard
Fiberboard exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to particle board due to its denser composition and refined wood fibers that reduce water absorption. Particle board tends to swell and deteriorate when exposed to high humidity or moisture, limiting its use in damp environments. Enhanced moisture resistance in fiberboard makes it ideal for applications like cabinetry and flooring where durability against humidity is critical.
Common Uses in Furniture and Construction
Particle board is widely utilized in affordable furniture, cabinetry, and underlayment due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of machining. Fiberboard, especially medium-density fiberboard (MDF), is preferred for detailed molding, decorative panels, and veneer bases because of its smooth surface and versatility. In construction, particle board often serves as subflooring or wall sheathing, while fiberboard is used for insulation and soundproofing applications.
Cost Comparison: Particle Board vs Fiberboard
Particle board generally costs less than fiberboard due to its lower density and simpler manufacturing process, making it a budget-friendly option for furniture and cabinetry. Fiberboard, including MDF (medium-density fiberboard), tends to be more expensive as it offers better strength, smoothness, and durability, which justify the higher price for quality-sensitive projects. Cost differences between these materials can vary based on thickness, size, and supplier, but particle board remains the economical choice for cost-conscious applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Particle board and fiberboard differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with particle board often made from wood chips, sawdust, and resin, which can release formaldehyde emissions during production and use. Fiberboard, especially medium-density fiberboard (MDF), utilizes finer wood fibers and may contain synthetic adhesives but advancements in low-formaldehyde and no-added formaldehyde resins improve its eco-friendliness. Both materials contribute to wood waste recycling, yet fiberboard's denser composition allows for longer product lifespans, enhancing sustainability in furniture and construction applications.
Finishing and Surface Qualities
Particle board typically features a rougher surface that requires extensive sanding and sealing to achieve a smooth finish, making it less ideal for high-end furniture without veneer or laminate overlays. Fiberboard, especially medium-density fiberboard (MDF), offers a smoother, more uniform surface that absorbs paint and finishes evenly, resulting in a sleek appearance with minimal prep work. The denser composition of fiberboard enhances its ability to hold detailed paint finishes and veneers, providing superior aesthetic qualities compared to particle board.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Particle board offers affordability and stability, making it suitable for furniture projects that require cost-effectiveness and basic durability. Fiberboard, especially medium-density fiberboard (MDF), provides a smoother surface and better strength, ideal for detailed finishing and cabinetry. Evaluate your project's demands for strength, finish, and budget to select between particle board's economical benefits and fiberboard's refined quality.
Particle Board vs Fiberboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com