Birch plywood and Baltic birch plywood differ primarily in construction quality and core layers, with Baltic birch featuring multiple thin plies that provide superior strength, stability, and resistance to warping. Birch plywood typically has thicker plies and may contain voids in the core, which makes it less durable and less suitable for load-bearing applications. Baltic birch plywood is ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and projects requiring high precision and a smooth finish due to its consistent density and balanced structure.
Table of Comparison
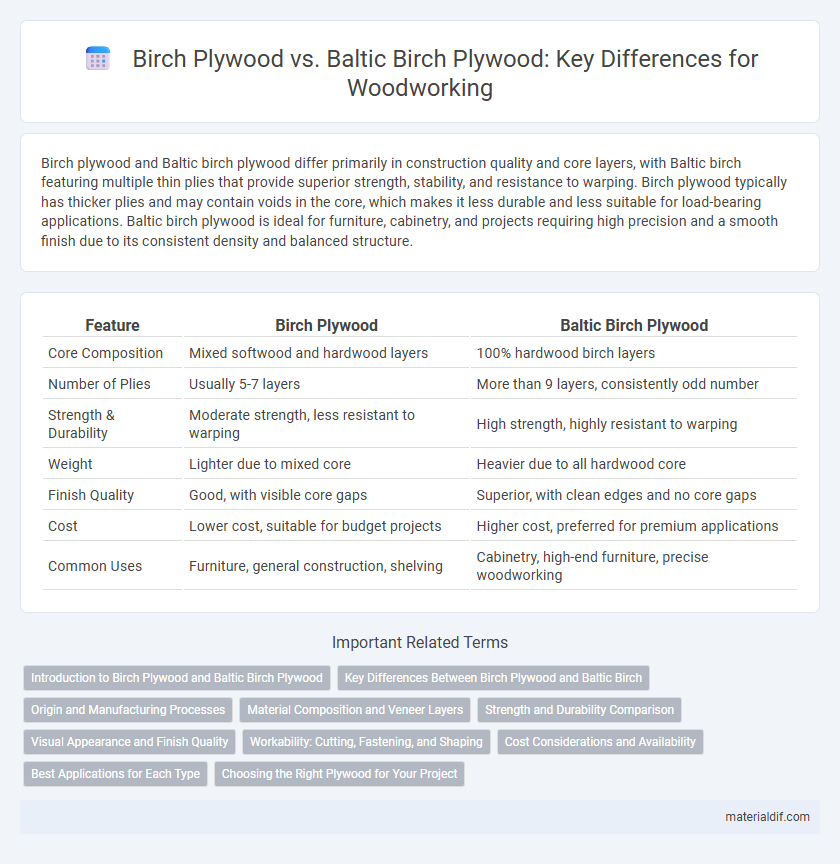
| Feature | Birch Plywood | Baltic Birch Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Core Composition | Mixed softwood and hardwood layers | 100% hardwood birch layers |
| Number of Plies | Usually 5-7 layers | More than 9 layers, consistently odd number |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate strength, less resistant to warping | High strength, highly resistant to warping |
| Weight | Lighter due to mixed core | Heavier due to all hardwood core |
| Finish Quality | Good, with visible core gaps | Superior, with clean edges and no core gaps |
| Cost | Lower cost, suitable for budget projects | Higher cost, preferred for premium applications |
| Common Uses | Furniture, general construction, shelving | Cabinetry, high-end furniture, precise woodworking |
Introduction to Birch Plywood and Baltic Birch Plywood
Birch plywood is a versatile engineered wood product made from thin layers of birch veneer glued together, known for its strength and smooth finish. Baltic birch plywood originates from the Baltic region and features multiple thin, uniform plies, offering superior durability and a consistent edge appearance. Both types are prized in woodworking, but Baltic birch plywood is often preferred for cabinetry and precision projects due to its higher ply count and minimal voids.
Key Differences Between Birch Plywood and Baltic Birch
Birch plywood is made from birch veneers and varies in quality depending on the number of plies and type of adhesives used, offering good strength and smooth finish for general woodworking. Baltic birch plywood, sourced primarily from Finland, features a higher ply count with consistent, void-free cores, providing superior durability, stability, and a finer, more uniform appearance. Key differences include Baltic birch's enhanced structural integrity, more layers for increased resistance to warping, and typically higher cost compared to standard birch plywood.
Origin and Manufacturing Processes
Birch plywood commonly originates from various species of birch trees found across North America and Europe, while Baltic birch plywood is specifically sourced from birch forests in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. The manufacturing process of Baltic birch plywood involves layering multiple thin veneers of birch wood in alternating grain directions, resulting in exceptional strength and durability, whereas standard birch plywood may use fewer layers with mixed wood species or lower-grade veneers. The precise craftsmanship and consistent quality control in Baltic birch plywood production distinguish it from general birch plywood, making it highly favored for professional woodworking and cabinetry.
Material Composition and Veneer Layers
Birch plywood typically consists of multiple layers of birch veneer glued together, but the number and quality of these veneer layers can vary widely depending on the manufacturer. Baltic birch plywood is distinguished by its consistent high-quality birch veneers, often featuring 13 or more thin, solid plies with steady grain patterns, which provides superior strength and durability. The material composition of Baltic birch plywood uses higher-grade birch veneers throughout, compared to standard birch plywood that may include lower-quality filler or mixed wood species in its inner layers.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Baltic Birch plywood is known for its superior strength and durability compared to standard birch plywood due to its multiple, uniformly thin layers and fewer voids, providing enhanced stability and resistance to warping. Standard birch plywood, while strong, often contains more core gaps and inconsistent layers, resulting in lower load-bearing capacity and reduced longevity in demanding applications. The cross-banding technique in Baltic Birch plywood ensures exceptional resistance to splitting and delamination, making it the preferred choice for heavy-duty woodworking projects and structural uses.
Visual Appearance and Finish Quality
Birch plywood offers a smooth, light-colored surface with a uniform grain, ideal for clear finishes and consistent staining, while Baltic birch plywood features a distinctive multi-ply edge with visibly alternated layers that enhance visual appeal and structural integrity. The finish quality of Baltic birch is notably higher due to its void-free plies and durable hardwood faces, resulting in a premium look with minimal sanding needed. Both types provide excellent paint and varnish adhesion, but Baltic birch is preferred for projects demanding superior aesthetics and edge detail.
Workability: Cutting, Fastening, and Shaping
Birch plywood offers smooth cutting, excellent fastening with nails or screws, and good shaping abilities due to its uniform layers and fine grain. Baltic birch plywood is favored for superior workability, featuring consistently even plies that resist splintering during cutting and provide exceptional strength for fastening. Both types perform well, but Baltic birch plywood's compact core and balanced plies make it ideal for intricate shapes and precision joinery.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Birch plywood generally costs less than Baltic birch plywood due to differences in manufacturing processes and veneer quality. Baltic birch plywood, known for its consistent multi-ply construction and fewer voids, is often more expensive but offers superior durability and strength. Availability of Baltic birch plywood can be more limited and region-specific, making it pricier in areas where it is less common compared to the more widely available standard birch plywood.
Best Applications for Each Type
Birch plywood offers a smooth surface ideal for furniture making, cabinetry, and decorative projects due to its fine grain and ease of finishing. Baltic birch plywood, characterized by its numerous layers and uniform cross-banding, excels in applications requiring high strength and durability such as industrial shelving, speaker boxes, and drawer bottoms. Selecting the appropriate plywood depends on the balance between aesthetic appeal and structural integrity needed for the specific project.
Choosing the Right Plywood for Your Project
Birch plywood offers a smooth surface with fine grain, ideal for detailed finishing and light-duty applications, while Baltic Birch plywood is known for its superior strength, durability, and uniform multi-ply core, making it a preferred choice for heavy-duty construction and cabinetry. Choosing the right plywood depends on project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, aesthetic finish, and cost considerations, with Baltic Birch excelling in structural integrity and Birch plywood favored for appearance and ease of work. Understanding the specific characteristics of each can optimize material performance and longevity in woodworking projects.
Birch Plywood vs Baltic Birch Plywood Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com