Maple offers a dense and hard surface with a fine, uniform grain, making it ideal for flooring and furniture that require durability and a smooth finish. Birch wood, slightly softer and lighter in color, features a subtle grain pattern that enhances its appeal for cabinetry and decorative veneers. Both woods provide excellent strength and versatility, but maple stands out for wear resistance while birch is favored for its ease of staining and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
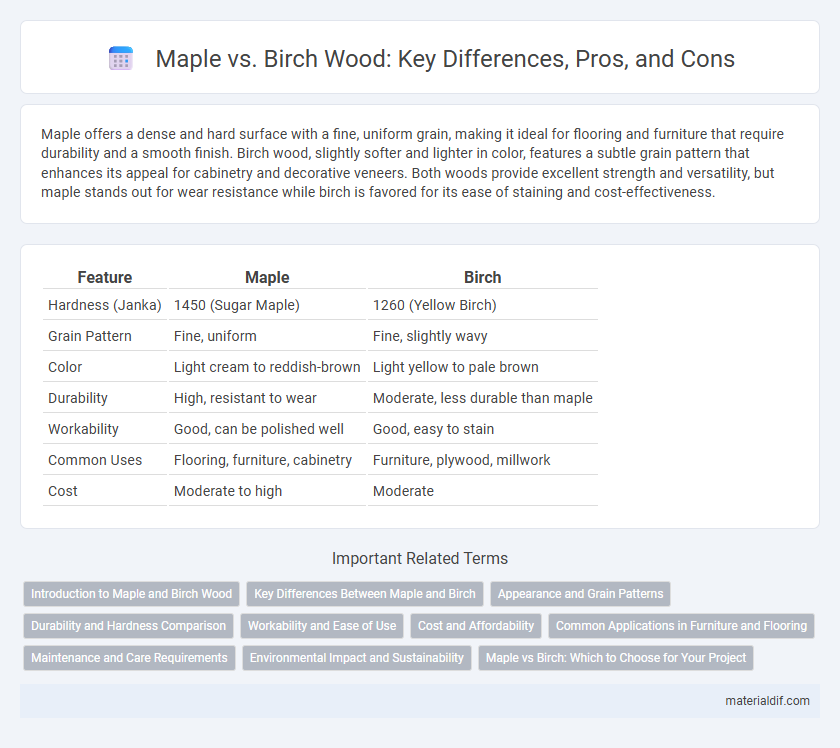
| Feature | Maple | Birch |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Janka) | 1450 (Sugar Maple) | 1260 (Yellow Birch) |
| Grain Pattern | Fine, uniform | Fine, slightly wavy |
| Color | Light cream to reddish-brown | Light yellow to pale brown |
| Durability | High, resistant to wear | Moderate, less durable than maple |
| Workability | Good, can be polished well | Good, easy to stain |
| Common Uses | Flooring, furniture, cabinetry | Furniture, plywood, millwork |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction to Maple and Birch Wood
Maple wood is known for its fine, uniform texture and high durability, making it ideal for furniture, flooring, and cabinetry. Birch wood offers a pale color with a smooth grain and excellent strength, often used in plywood, veneers, and interior trim. Both hardwoods are valued for their workability and resistance to wear, but maple tends to be harder and heavier than birch.
Key Differences Between Maple and Birch
Maple wood features a dense, fine grain with a creamy white to light reddish-brown color, offering high hardness and durability ideal for flooring and furniture. Birch wood displays a lighter color with a smooth, even texture and is slightly softer, making it easier to work with but less resistant to wear compared to maple. The key differences include maple's superior strength and tighter grain pattern, while birch provides better machining properties and a more uniform appearance.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Maple wood features a light, creamy color with a fine, consistent grain pattern that often exhibits subtle waves or curls, making it ideal for a smooth and elegant finish. Birch wood displays a slightly darker hue with a more pronounced, straight grain and occasional knots, providing a rustic and textured aesthetic. Both woods offer distinctive visual characteristics suited for cabinetry, furniture, and flooring, with maple favored for uniformity and birch valued for its unique, natural patterns.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Maple wood is generally harder and more durable than birch, making it a preferred choice for high-traffic areas and furniture that requires resistance to dents and scratches. On the Janka hardness scale, hard maple rates around 1450, whereas birch typically scores between 1260 and 1400, indicating slightly less hardness. Birch is still durable but more prone to wear and denting compared to the denser and more resilient maple.
Workability and Ease of Use
Maple wood is highly regarded for its excellent workability, offering a smooth finish and bending easily without splintering, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry. Birch wood, while also workable, is denser and can be slightly more challenging to cut and shape, requiring sharper tools and more effort. Both woods respond well to finishes, but maple is often preferred for precision woodworking due to its consistent grain and resistance to warping.
Cost and Affordability
Maple wood tends to be more expensive than birch due to its density and durability, making it a premium choice for furniture and flooring. Birch offers greater affordability while maintaining decent strength and workability, appealing to budget-conscious projects. Choosing birch over maple can significantly reduce costs without compromising basic structural integrity.
Common Applications in Furniture and Flooring
Maple is frequently used in furniture making for its durability and fine, uniform grain, making it ideal for cabinets, chairs, and dressers. Birch offers similar strength but features a slightly coarser texture, commonly applied in flooring and plywood due to its affordability and smooth finish. Both woods provide excellent wear resistance and aesthetic appeal, with maple often preferred for high-end furniture and birch favored in cost-effective flooring solutions.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Maple requires minimal maintenance due to its dense grain, which resists scratches and stains better than birch. Birch, while durable, demands more frequent sealing and refinishing to protect its softer wood from dents and moisture damage. Proper care for maple includes regular cleaning with mild soap, whereas birch needs more attentive moisture control to prevent warping.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Maple exhibits a lower environmental impact compared to birch due to its greater carbon sequestration capacity and longer forest growth cycles, which contribute to enhanced ecosystem stability. Birch trees, while faster-growing and thus more rapidly renewable, often require more intensive management practices that can disrupt soil health and biodiversity. Sustainable forestry certifications such as FSC or PEFC are essential for both woods to ensure responsible harvesting and minimize ecological footprints.
Maple vs Birch: Which to Choose for Your Project
Maple offers a dense, hard grain ideal for flooring and furniture requiring durability, while birch provides a smoother texture perfect for cabinetry with a lighter color palette. Both woods excel in workability and finishing, but maple's resistance to wear suits high-traffic areas better. Choose maple for strength and longevity, and birch for affordability and aesthetic versatility in your woodworking project.
Maple vs Birch Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com