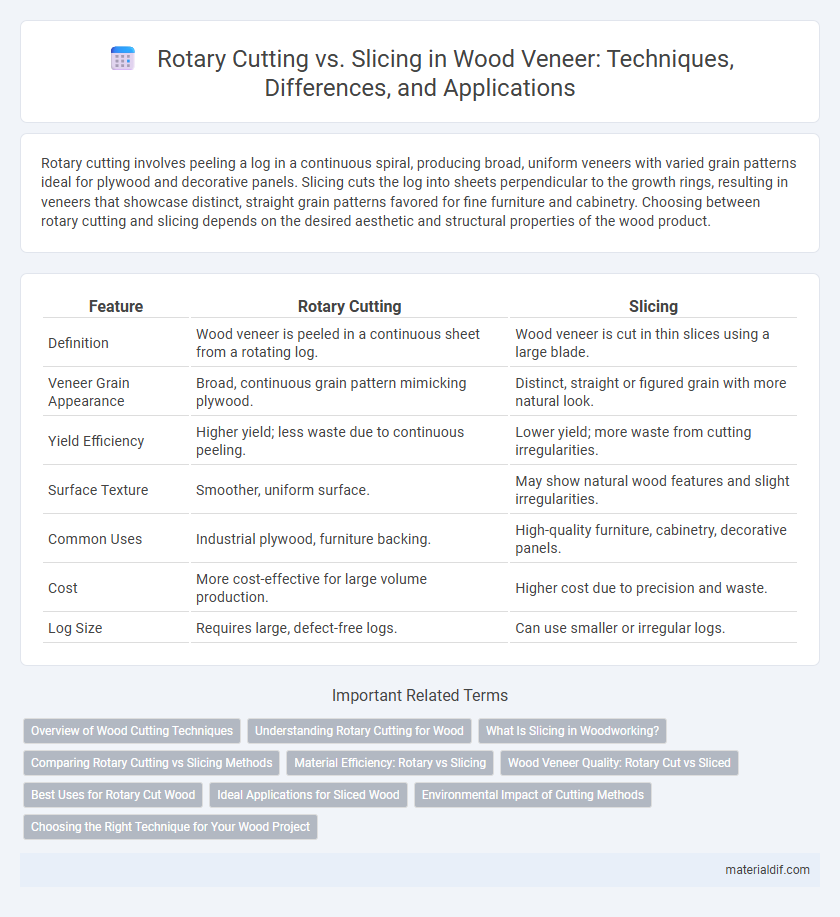
Rotary cutting involves peeling a log in a continuous spiral, producing broad, uniform veneers with varied grain patterns ideal for plywood and decorative panels. Slicing cuts the log into sheets perpendicular to the growth rings, resulting in veneers that showcase distinct, straight grain patterns favored for fine furniture and cabinetry. Choosing between rotary cutting and slicing depends on the desired aesthetic and structural properties of the wood product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rotary Cutting | Slicing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wood veneer is peeled in a continuous sheet from a rotating log. | Wood veneer is cut in thin slices using a large blade. |
| Veneer Grain Appearance | Broad, continuous grain pattern mimicking plywood. | Distinct, straight or figured grain with more natural look. |
| Yield Efficiency | Higher yield; less waste due to continuous peeling. | Lower yield; more waste from cutting irregularities. |
| Surface Texture | Smoother, uniform surface. | May show natural wood features and slight irregularities. |
| Common Uses | Industrial plywood, furniture backing. | High-quality furniture, cabinetry, decorative panels. |
| Cost | More cost-effective for large volume production. | Higher cost due to precision and waste. |
| Log Size | Requires large, defect-free logs. | Can use smaller or irregular logs. |
Overview of Wood Cutting Techniques
Rotary cutting involves peeling the log in a continuous motion to produce large veneer sheets, maximizing yield and minimizing waste. Slicing cuts the wood perpendicularly with a blade, creating veneers that highlight the natural grain pattern and texture. Both techniques serve distinct purposes in wood manufacturing, influencing aesthetics, cost, and material efficiency.
Understanding Rotary Cutting for Wood
Rotary cutting involves peeling a log in a continuous sheet by rotating it against a blade, producing large, wide veneer panels ideal for plywood manufacturing. This method maximizes yield from each log and highlights the wood's natural grain patterns in broad, sweeping designs. Rotary-cut veneers are generally more uniform and less costly compared to slicing, making them preferred for applications requiring large surface coverage.
What Is Slicing in Woodworking?
Slicing in woodworking refers to cutting a log into thin, flat sheets or veneers by slicing the wood tangentially to the growth rings, producing broad grain patterns and a decorative appearance. This method differs from rotary cutting, where the log is peeled in a continuous spiral, resulting in more uniform grain but less distinctive patterns. Sliced veneers are prized for their aesthetic value in furniture and cabinetry due to their unique and varied wood grain that enhances visual appeal.
Comparing Rotary Cutting vs Slicing Methods
Rotary cutting produces a continuous veneer by peeling the log around its circumference, resulting in wider sheets with a more uniform grain pattern ideal for plywood production. Slicing simulates a saw blade, creating veneers with a natural, varied grain appearance preferred for decorative wood surfaces and fine furniture. Rotary cutting offers efficiency and yield, while slicing emphasizes aesthetic quality and texture detail.
Material Efficiency: Rotary vs Slicing
Rotary cutting maximizes material efficiency by producing wide veneer sheets from the entire log circumference, minimizing waste and yielding higher volume output per log. Slicing, in contrast, involves cutting thin sheets with a blade, which can result in more waste due to irregular grain match and trimming. Choosing rotary cutting over slicing significantly enhances yield and cost-effectiveness in veneer production.
Wood Veneer Quality: Rotary Cut vs Sliced
Rotary cutting produces wood veneer by peeling a log in a continuous sheet, resulting in a more uniform grain pattern but lower overall quality due to frequent imperfections. Slicing wood veneer involves slicing thin sheets from a flatted log, preserving the natural grain and offering higher aesthetic quality with a more refined texture. This makes sliced veneer preferable for premium woodworking projects where detailed grain patterns and superior finish are essential.
Best Uses for Rotary Cut Wood
Rotary cut wood offers a unique grain pattern that is ideal for large veneer panels, cabinetry, and plywood because the continuous slicing around the log maximizes surface area and creates broad, uniform sheets. This cutting method excels in applications requiring cost-effective, visually striking wood with bold, circular grain patterns, making it a preferred choice for interior paneling and furniture veneers. Unlike slicing, rotary cutting produces less waste and enables the efficient use of less expensive timber species without sacrificing aesthetic appeal.
Ideal Applications for Sliced Wood
Sliced wood is ideal for decorative applications such as furniture veneers, paneling, and cabinetry, where a natural wood grain appearance is essential. This method produces consistent, flat sheets with minimal waste, enhancing aesthetic value in interior design. It is best suited for hardwood species that showcase intricate grain patterns when sliced thinly.
Environmental Impact of Cutting Methods
Rotary cutting consumes less wood by producing thinner veneers from a log, minimizing waste and maximizing material use. Slicing generates higher-quality, thicker slices but results in more wood waste and increased energy consumption during processing. Choosing rotary cutting supports sustainable forestry by reducing raw material demand and lowering the environmental footprint of wood production.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Wood Project
Rotary cutting produces large, continuous veneer sheets by rotating the log against a blade, ideal for covering large surfaces with consistent grain patterns. Slicing involves cutting thin sheets from flitches, preserving natural grain variations preferred for decorative and high-quality furniture projects. Selecting rotary cutting or slicing depends on the desired wood aesthetics, project scale, and budget constraints to achieve optimal results.
Rotary Cutting vs Slicing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com