Reclaimed wood offers a sustainable alternative to virgin wood by repurposing old timber, reducing deforestation and environmental impact. It often features unique character and weathered textures that add aesthetic value to furniture and flooring projects. Virgin wood provides consistent quality and availability but contributes significantly to habitat loss and carbon emissions.
Table of Comparison
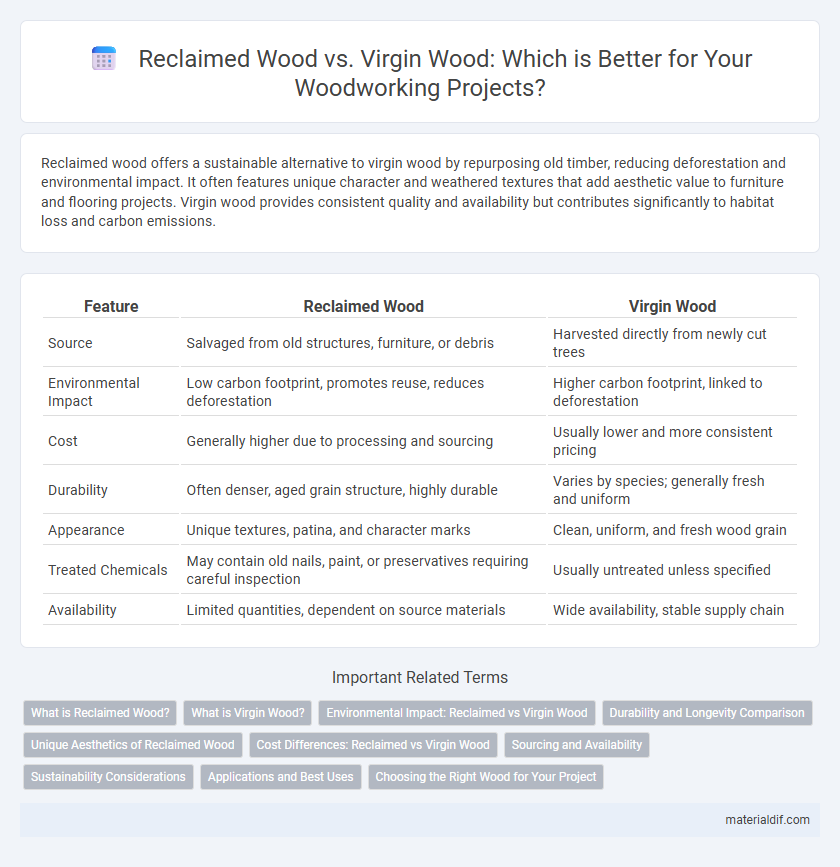
| Feature | Reclaimed Wood | Virgin Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Salvaged from old structures, furniture, or debris | Harvested directly from newly cut trees |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, promotes reuse, reduces deforestation | Higher carbon footprint, linked to deforestation |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing and sourcing | Usually lower and more consistent pricing |
| Durability | Often denser, aged grain structure, highly durable | Varies by species; generally fresh and uniform |
| Appearance | Unique textures, patina, and character marks | Clean, uniform, and fresh wood grain |
| Treated Chemicals | May contain old nails, paint, or preservatives requiring careful inspection | Usually untreated unless specified |
| Availability | Limited quantities, dependent on source materials | Wide availability, stable supply chain |
What is Reclaimed Wood?
Reclaimed wood is timber salvaged from old structures such as barns, factories, and warehouses, repurposed for new construction or furniture projects. This sustainable material offers unique character with weathered textures and historical imperfections not found in virgin wood. Using reclaimed wood reduces deforestation by recycling existing resources, making it an eco-friendly alternative to freshly harvested timber.
What is Virgin Wood?
Virgin wood refers to timber harvested directly from natural forests or plantation-grown trees that have not been previously processed or used in any form. It is characterized by its fresh, untreated state, offering pristine grain quality and structural integrity essential for construction and fine woodworking. Virgin wood typically provides higher strength and durability compared to reclaimed wood, making it suitable for applications requiring robust, long-lasting material.
Environmental Impact: Reclaimed vs Virgin Wood
Reclaimed wood significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing deforestation and lowering carbon emissions linked to logging and manufacturing processes. Virgin wood extraction involves cutting down trees, leading to habitat loss, biodiversity decline, and increased carbon footprint from intensive forestry operations. Utilizing reclaimed wood conserves natural resources, decreases landfill waste, and supports sustainable building practices crucial for mitigating climate change effects.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Reclaimed wood offers enhanced durability due to its aged and seasoned nature, which often results in tighter grain structures and increased resistance to warping and shrinking compared to virgin wood. Virgin wood, while fresh and more flexible for customization, may require additional treatments to reach similar longevity, as it contains higher moisture content and is more prone to environmental damage. Choosing reclaimed wood supports sustainability and provides a sturdy, long-lasting material ideal for construction and furniture that withstands the test of time.
Unique Aesthetics of Reclaimed Wood
Reclaimed wood offers unique aesthetics marked by its rich history, weathered textures, and distinctive color variations that virgin wood cannot replicate. The natural patina and character gained from previous use create an authentic, rustic charm highly sought after in interior design and furniture making. Each reclaimed piece tells a story through its knots, nail holes, and grain patterns, providing unparalleled visual interest and environmental sustainability.
Cost Differences: Reclaimed vs Virgin Wood
Reclaimed wood generally costs more upfront due to the labor-intensive process of sourcing, cleaning, and preparing it, while virgin wood tends to have a lower initial price because it is harvested and processed directly from forests. The long-term value of reclaimed wood often surpasses that of virgin wood due to its unique character, durability, and environmental benefits. Cost fluctuations in virgin wood are heavily influenced by logging regulations, lumber demand, and supply chain factors, whereas reclaimed wood pricing is more stable but limited by availability.
Sourcing and Availability
Reclaimed wood is sourced from old buildings, barns, and furniture, offering limited but sustainable availability due to its recycled nature. Virgin wood comes directly from logging operations in forests, ensuring a more consistent and abundant supply but with higher environmental impact. Sustainable forestry certifications like FSC help regulate virgin wood harvesting to balance availability with conservation.
Sustainability Considerations
Reclaimed wood significantly reduces deforestation by repurposing existing materials, lowering carbon emissions associated with harvesting and processing virgin wood. Virgin wood, while renewable when sourced from sustainably managed forests, often involves higher environmental costs due to logging, transportation, and replanting processes. Choosing reclaimed wood supports circular economy principles and minimizes landfill waste, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious construction and furniture projects.
Applications and Best Uses
Reclaimed wood excels in applications requiring unique character and sustainability, such as furniture, flooring, and decorative paneling, offering rich textures and weathered finishes not found in virgin wood. Virgin wood is best suited for structural uses, cabinetry, and precision woodworking projects, providing uniform strength, stability, and consistent grain quality. Selecting between reclaimed and virgin wood depends on balancing aesthetics, environmental impact, and specific project requirements.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Project
Reclaimed wood offers a sustainable and eco-friendly option with unique character from its previous use, making it ideal for projects prioritizing environmental impact and rustic aesthetics. Virgin wood provides consistent quality and structural integrity, suitable for builds requiring precise measurements and strength. Assess project requirements for durability, appearance, and sustainability to determine the optimal choice between reclaimed and virgin wood.
Reclaimed Wood vs Virgin Wood Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com