Maple wood is renowned for its light color, fine grain, and durability, making it a popular choice for flooring and furniture that requires a smooth, uniform surface. Walnut wood offers a rich, dark hue with intricate grain patterns, providing a luxurious appearance often favored in high-end cabinetry and decorative pieces. While maple excels in hardness and resistance to wear, walnut is prized for its aesthetic appeal and ease of carving, influencing the selection based on both functional and design priorities.
Table of Comparison
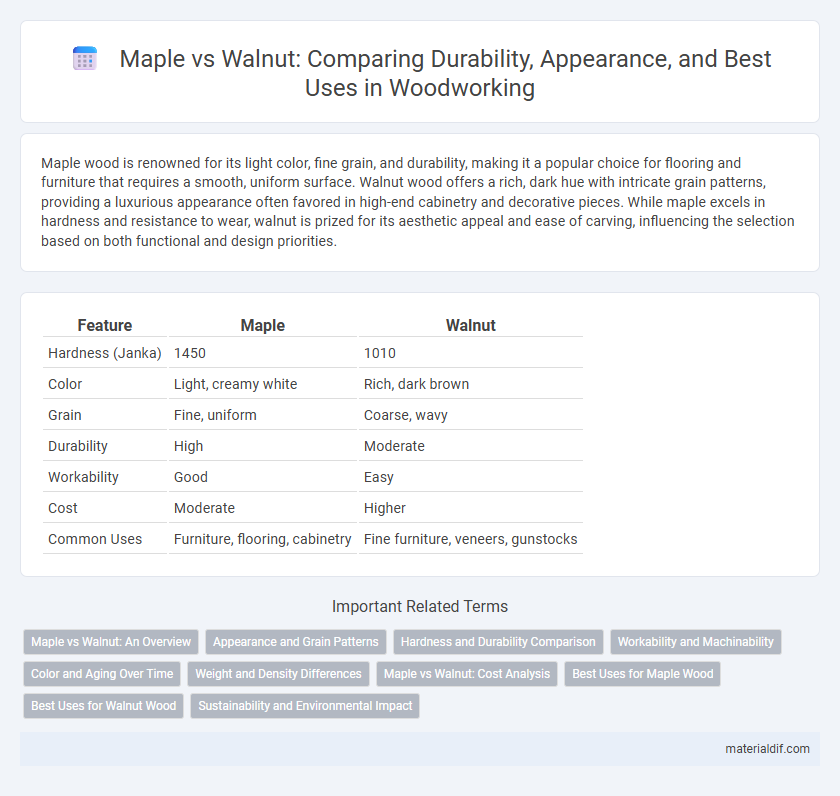
| Feature | Maple | Walnut |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Janka) | 1450 | 1010 |
| Color | Light, creamy white | Rich, dark brown |
| Grain | Fine, uniform | Coarse, wavy |
| Durability | High | Moderate |
| Workability | Good | Easy |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Common Uses | Furniture, flooring, cabinetry | Fine furniture, veneers, gunstocks |
Maple vs Walnut: An Overview
Maple and walnut are two popular hardwoods widely used in furniture and flooring due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. Maple features a lighter, creamy color with a fine, consistent grain, making it ideal for bright, modern interiors, while walnut boasts a rich, dark brown hue and complex grain patterns that add warmth and elegance. Both woods are strong and wear-resistant, but walnut is typically more expensive and prized for its luxurious look, whereas maple offers excellent hardness and a more budget-friendly option.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Maple wood showcases a light, creamy color with subtle, uniform grain patterns that range from straight to curly, providing a smooth, clean aesthetic ideal for contemporary designs. Walnut features a rich, dark brown hue with striking, bold grain patterns that include waves and swirls, offering a dramatic and luxurious appearance. The contrast in color and grain complexity makes maple suited for minimalist styles, while walnut excels in creating statement pieces with its vivid natural texture.
Hardness and Durability Comparison
Maple exhibits a Janka hardness rating of approximately 1450, making it notably harder and more resistant to dents compared to walnut, which scores around 1010. This increased hardness contributes to maple's superior durability in high-traffic flooring and heavy-use furniture applications. Walnut, while softer, offers moderate durability with excellent resistance to wear and a rich aesthetic, favored where impact resistance is less critical.
Workability and Machinability
Maple offers exceptional workability due to its fine, uniform texture and moderate hardness, making it ideal for detailed woodworking and hand tools. Walnut, while slightly softer, provides excellent machinability with smooth cutting performance and minimal tool wear, especially suited for intricate moldings and furniture components. Both woods respond well to sanding and finishing, but maple's density demands sharper tools for optimal precision.
Color and Aging Over Time
Maple wood showcases a pale, creamy color that often deepens to a rich amber hue with exposure to sunlight over time. Walnut features a deep chocolate-brown tone that can lighten slightly to a warm golden brown as it ages naturally. Both woods develop a unique patina, but maple tends to brighten while walnut maintains a darker, more consistent coloration throughout its lifespan.
Weight and Density Differences
Maple wood typically has a density of around 700 kg/m3, making it heavier and denser than walnut, which averages about 600 kg/m3. This higher density in maple contributes to its greater weight, offering increased durability and resistance to wear. Walnut's lighter weight and lower density provide easier workability and a smoother finish for fine woodworking projects.
Maple vs Walnut: Cost Analysis
Maple wood is generally more affordable than walnut, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious woodworking projects. Walnut is priced higher due to its rich color, durability, and limited availability, which increases its demand and market value. Considering cost efficiency, maple offers excellent hardness and aesthetic appeal at a lower price point compared to the premium expense of walnut.
Best Uses for Maple Wood
Maple wood excels in applications requiring durability and fine detail, making it ideal for furniture, flooring, and musical instruments. Its closed grain and hardness provide excellent resistance to wear and impact, ensuring longevity in high-traffic areas. Maple's light color and smooth texture also make it a preferred choice for kitchen cabinetry and cutting boards, where hygiene and aesthetics are key.
Best Uses for Walnut Wood
Walnut wood is prized for its rich color, fine grain, and durability, making it ideal for high-end furniture, cabinetry, and decorative veneers. Its natural resistance to wear and warping suits it well for flooring and gunstocks. Walnut's stability and workability also make it a preferred choice for musical instruments and intricate woodturning projects.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Maple wood is considered more sustainable than walnut due to its faster growth rate and higher availability, which reduces deforestation pressure. Walnut trees, being slower-growing and less abundant, often require more extensive land use and resources, leading to a higher environmental impact. Choosing maple supports sustainable forestry practices by promoting efficient resource use and minimizing habitat disruption.
Maple vs Walnut Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com