Hardwood comes from deciduous trees and is typically denser, making it ideal for furniture and flooring due to its durability and resistance to wear. Softwood, derived from coniferous trees, is lighter and easier to work with, often used in construction and framing. The choice between hardwood and softwood depends on the project requirements for strength, appearance, and cost.
Table of Comparison
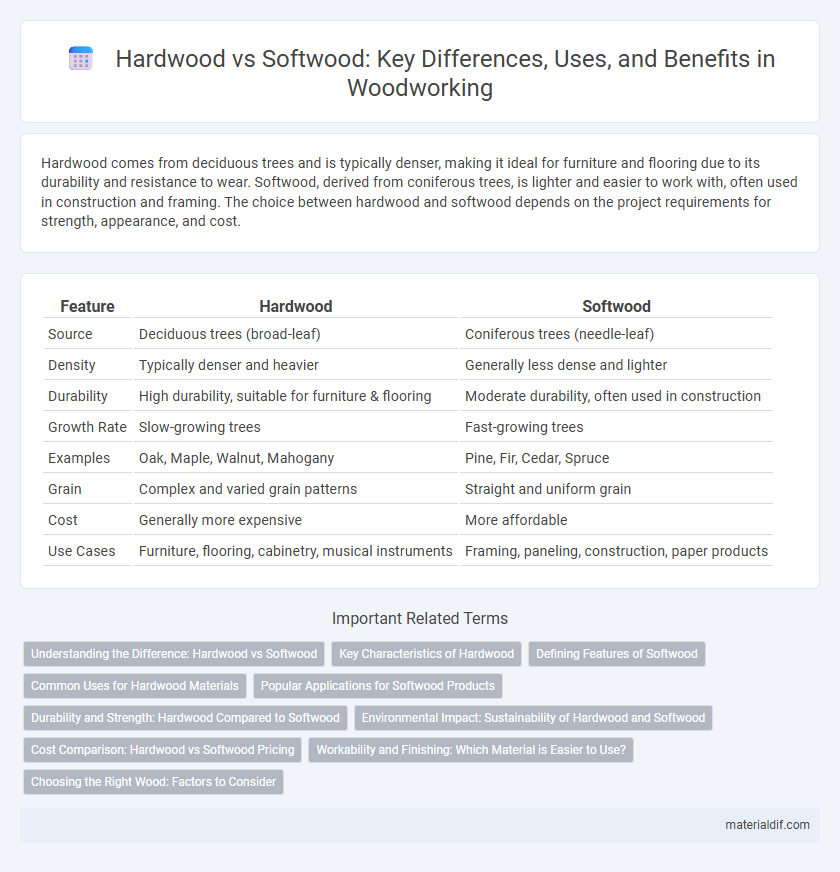
| Feature | Hardwood | Softwood |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Deciduous trees (broad-leaf) | Coniferous trees (needle-leaf) |
| Density | Typically denser and heavier | Generally less dense and lighter |
| Durability | High durability, suitable for furniture & flooring | Moderate durability, often used in construction |
| Growth Rate | Slow-growing trees | Fast-growing trees |
| Examples | Oak, Maple, Walnut, Mahogany | Pine, Fir, Cedar, Spruce |
| Grain | Complex and varied grain patterns | Straight and uniform grain |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More affordable |
| Use Cases | Furniture, flooring, cabinetry, musical instruments | Framing, paneling, construction, paper products |
Understanding the Difference: Hardwood vs Softwood
Hardwood comes from angiosperm trees with broad leaves, such as oak, maple, and walnut, known for their dense grain and durability. Softwood originates from gymnosperm trees like pine, spruce, and fir, featuring lighter, more porous wood suitable for construction and paper production. Understanding differences in cell structure and growth patterns helps determine the best use of each wood type for furniture, flooring, or building materials.
Key Characteristics of Hardwood
Hardwood derives from angiosperm trees with broad leaves, typically exhibiting a dense grain and higher durability, making it ideal for furniture and flooring. Its cellular structure contains pores that contribute to its hardness and strength, often resulting in a heavier weight compared to softwood. Common hardwood species include oak, maple, and walnut, known for their resistance to wear and ability to take stains well.
Defining Features of Softwood
Softwood primarily comes from gymnosperm trees such as pine, fir, and spruce, characterized by needle-like leaves and cones. Its cellular structure is simpler, with tracheids serving as the main water-conducting cells, resulting in a generally lighter weight and softer texture compared to hardwood. Softwood is commonly used in construction, paper production, and furniture due to its fast growth rate and ease of processing.
Common Uses for Hardwood Materials
Hardwood materials like oak, maple, and walnut are commonly used for furniture, flooring, and cabinetry due to their durability and attractive grain patterns. These woods offer superior strength, making them ideal for construction elements such as beams and staircases. Hardwood is also preferred in musical instruments and high-quality tools where precision and resilience are critical.
Popular Applications for Softwood Products
Softwood products are widely used in construction due to their strength and affordability, making them ideal for framing, roofing, and flooring. They are also popular in the manufacture of furniture, cabinetry, and interior paneling because of their ease of workability and smooth finish. Additionally, softwoods like pine and cedar are preferred for outdoor structures such as decks and fences due to their natural resistance to pests and elements.
Durability and Strength: Hardwood Compared to Softwood
Hardwood, derived from deciduous trees, generally exhibits greater density and strength than softwood from coniferous trees, making it more durable for furniture and flooring applications. The complex cellular structure of hardwoods like oak and maple contributes to superior resistance against wear, moisture, and impact compared to softer species such as pine or cedar. This inherent durability and strength make hardwood the preferred choice for construction projects requiring long-lasting, robust materials.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Hardwood and Softwood
Hardwood typically comes from deciduous trees that grow slower, resulting in denser wood but longer carbon storage, which can enhance sustainability if harvested responsibly. Softwood is sourced from fast-growing coniferous trees that enable quicker reforestation and carbon cycle regeneration, often making it more renewable for large-scale use. The environmental impact of both depends heavily on sustainable forestry practices, certification standards like FSC, and regional ecosystem management.
Cost Comparison: Hardwood vs Softwood Pricing
Hardwood generally commands a higher price than softwood due to its density, durability, and slower growth rate, which increases harvesting costs. Softwood tends to be more affordable, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious construction and furniture projects. Market prices for hardwood can be two to three times higher than softwood, reflecting the premium quality and longevity associated with woods like oak, maple, and cherry.
Workability and Finishing: Which Material is Easier to Use?
Hardwood generally offers superior workability for fine woodworking projects due to its dense grain, allowing smoother cuts and detailed finishes. Softwood is easier to manipulate with basic tools because of its lighter density, making it ideal for beginners and larger construction tasks. When it comes to finishing, hardwood absorbs stains and varnishes more evenly, resulting in a richer and more polished appearance compared to the often blotchy finish of softwood.
Choosing the Right Wood: Factors to Consider
Hardwood, sourced from deciduous trees like oak and maple, offers greater durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for furniture and flooring, while softwood from conifers such as pine and cedar is lighter and easier to work with, suited for construction and decorative uses. Factors to consider include the wood's density, grain pattern, and natural resistance to moisture and pests, which influence its longevity and maintenance requirements. Budget constraints and project-specific needs like structural support or aesthetic appeal should also guide the choice between hardwood and softwood.
Hardwood vs Softwood Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com