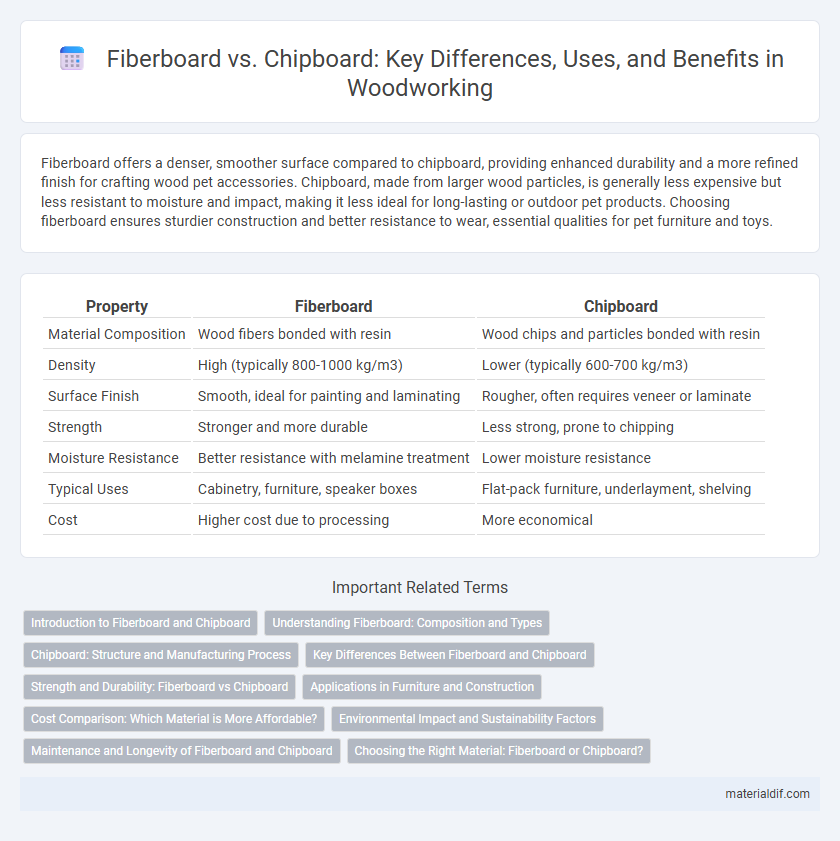
Fiberboard offers a denser, smoother surface compared to chipboard, providing enhanced durability and a more refined finish for crafting wood pet accessories. Chipboard, made from larger wood particles, is generally less expensive but less resistant to moisture and impact, making it less ideal for long-lasting or outdoor pet products. Choosing fiberboard ensures sturdier construction and better resistance to wear, essential qualities for pet furniture and toys.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fiberboard | Chipboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood fibers bonded with resin | Wood chips and particles bonded with resin |
| Density | High (typically 800-1000 kg/m3) | Lower (typically 600-700 kg/m3) |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, ideal for painting and laminating | Rougher, often requires veneer or laminate |
| Strength | Stronger and more durable | Less strong, prone to chipping |
| Moisture Resistance | Better resistance with melamine treatment | Lower moisture resistance |
| Typical Uses | Cabinetry, furniture, speaker boxes | Flat-pack furniture, underlayment, shelving |
| Cost | Higher cost due to processing | More economical |
Introduction to Fiberboard and Chipboard
Fiberboard is an engineered wood product made from wood fibers combined with resin, offering uniform density and smooth surfaces ideal for cabinetry and furniture. Chipboard, also known as particleboard, consists of wood chips and particles bonded with adhesive, making it a cost-effective material commonly used for shelving and inexpensive furniture. Both materials provide versatile solutions in woodworking but differ significantly in strength, density, and finish quality.
Understanding Fiberboard: Composition and Types
Fiberboard is engineered wood made from wood fibers bonded with resin under heat and pressure, resulting in a dense and uniform panel. Common types include Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF), High-Density Fiberboard (HDF), and Low-Density Fiberboard (LDF), each varying in density and strength for specific applications. MDF offers smooth surfaces ideal for painting and cabinetry, while HDF is denser and used for flooring and heavy-duty furniture components.
Chipboard: Structure and Manufacturing Process
Chipboard consists of wood chips, sawmill shavings, and resin bonded under heat and pressure, creating a dense, rigid panel commonly used in furniture and construction. Its manufacturing process involves crushing wood into small chips, mixing with synthetic resin adhesives, then hot-pressing layers into sheets that offer structural stability and moisture resistance. Unlike fiberboard, chipboard's coarser texture and lower density make it less smooth but ideal for strength-focused applications.
Key Differences Between Fiberboard and Chipboard
Fiberboard is made from wood fibers bonded under heat and pressure, resulting in a denser, smoother surface ideal for painting and cabinetry, while chipboard is produced by compressing wood chips and resin, offering a more porous texture often used in furniture backing and particleboard flooring. Fiberboard typically has higher strength and durability, making it suitable for structural applications, whereas chipboard is generally less dense, more affordable, and better for lightweight, non-load-bearing uses. Moisture resistance in fiberboard can be enhanced through treatments, unlike standard chipboard which tends to swell and degrade when exposed to water.
Strength and Durability: Fiberboard vs Chipboard
Fiberboard offers higher strength and durability compared to chipboard due to its dense, uniform composition made from tightly compressed wood fibers. Chipboard, composed of larger wood chips bonded with resin, has lower resistance to impact and moisture, making it less durable in heavy-use environments. For structural applications where load-bearing capacity and longevity are critical, fiberboard is the preferred choice over chipboard.
Applications in Furniture and Construction
Fiberboard offers superior strength and smoothness, making it ideal for high-quality furniture like cabinets and decorative panels, while chipboard is commonly used in budget-friendly furniture, flooring, and underlayment due to its cost-effectiveness. In construction, fiberboard excels in insulation and soundproofing applications, whereas chipboard serves well for subflooring and structural sheathing where moisture exposure is minimal. Selection depends on specific requirements for durability, finish, and environmental resistance, with fiberboard generally providing enhanced performance in demanding furniture and construction uses.
Cost Comparison: Which Material is More Affordable?
Fiberboard generally costs more than chipboard due to its higher density and smoother finish, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry. Chipboard, composed of compressed wood chips and resin, is more affordable and commonly used in budget-friendly applications such as shelving and subflooring. The price difference often reflects durability and appearance, with chipboard offering a cost-effective option for projects with lower aesthetic demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Fiberboard often has a lower environmental impact than chipboard due to its production from finer wood fibers, including recycled wood waste, which reduces deforestation and landfill use. Chipboard, typically made from larger wood chips and bonded with synthetic resins, can emit higher levels of formaldehyde, raising concerns about indoor air quality and sustainability. Both materials benefit from certifications like FSC or PEFC, but fiberboard's potential for higher recycled content and lower emissions generally makes it a more sustainable choice in wood-based panel products.
Maintenance and Longevity of Fiberboard and Chipboard
Fiberboard offers superior durability and resistance to moisture compared to chipboard, resulting in easier maintenance and a longer lifespan in environments prone to humidity or wear. Chipboard tends to absorb moisture, causing swelling and weakening over time, which necessitates more frequent repairs or replacement. Proper sealing and finishing can enhance the longevity of both materials, but fiberboard remains the preferred choice for long-term performance and minimal upkeep.
Choosing the Right Material: Fiberboard or Chipboard?
Fiberboard offers a smooth, dense surface ideal for painting and fine cabinetry, making it suitable for projects requiring a polished finish and greater strength. Chipboard, made from larger wood particles, is more cost-effective and best for applications like shelving or furniture backing where structural integrity is less critical. Selecting between fiberboard and chipboard depends on budget constraints, desired durability, and the finish quality required for the woodworking project.
Fiberboard vs Chipboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com