Wenge and teak are both prized hardwoods known for their durability and rich color, but wenge features a dark brown to black grain with a coarse texture, creating a bold and dramatic appearance. Teak, on the other hand, offers a warm golden to medium brown hue with a natural oil content that enhances its resistance to water and decay, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and marine applications. Selecting between wenge and teak depends on the desired aesthetic and functional requirements, with wenge excelling in striking indoor designs and teak providing exceptional longevity in harsh environments.
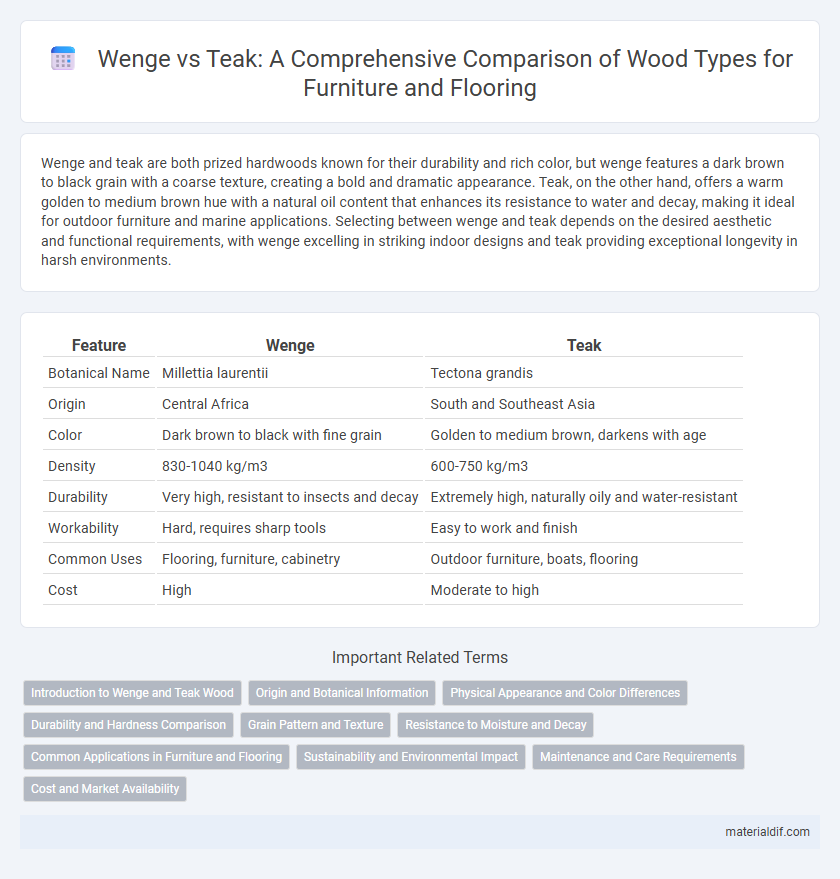
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wenge | Teak |
|---|---|---|
| Botanical Name | Millettia laurentii | Tectona grandis |
| Origin | Central Africa | South and Southeast Asia |
| Color | Dark brown to black with fine grain | Golden to medium brown, darkens with age |
| Density | 830-1040 kg/m3 | 600-750 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Very high, resistant to insects and decay | Extremely high, naturally oily and water-resistant |
| Workability | Hard, requires sharp tools | Easy to work and finish |
| Common Uses | Flooring, furniture, cabinetry | Outdoor furniture, boats, flooring |
| Cost | High | Moderate to high |
Introduction to Wenge and Teak Wood
Wenge wood, known for its dark brown to black coloration with fine, close grain, is harvested primarily from the Millettia laurentii tree native to Central Africa. Teak wood, prized for its durability and water-resistant properties, comes from the Tectona grandis tree commonly found in Southeast Asia's tropical forests. Both woods are highly valued in furniture making and flooring, with Wenge offering a more dramatic, rich aesthetic while Teak provides superior longevity and resistance to decay.
Origin and Botanical Information
Wenge wood originates from the Millettia laurentii tree, native to the Congo Basin in Central Africa, known for its dense hardwood and dark, richly textured grain. Teak wood comes from the Tectona grandis tree, primarily found in Southeast Asia, especially Myanmar, India, and Thailand, valued for its natural oil content and resistance to decay. Both woods are prized in fine woodworking, but Wenge's botanical classification places it in the legume family, while Teak belongs to the Lamiaceae family, influencing their distinct physical properties and uses.
Physical Appearance and Color Differences
Wenge wood features a dark brown to black coloration with distinctive grain patterns marked by fine, closely spaced streaks, creating a striking visual texture. Teak, on the other hand, exhibits a golden to medium brown hue that can develop a rich patina over time, with a more uniform and straight grain compared to wenge. The darker, more dramatic appearance of wenge contrasts sharply with teak's warm and lighter tones, making each wood unique for different aesthetic applications.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Wenge wood exhibits exceptional durability and hardness, with a Janka hardness rating of approximately 1630 lbf, making it highly resistant to wear and denting. Teak, while renowned for its natural oils that enhance moisture resistance, has a lower Janka hardness around 1070 lbf, making it softer but more flexible compared to Wenge. The superior hardness of Wenge makes it ideal for heavy-use flooring and furniture, whereas Teak's durability lies in its ability to withstand outdoor elements and resist decay.
Grain Pattern and Texture
Wenge wood features a distinctive dark brown to black color with pronounced, straight grain patterns and a coarse, dense texture that enhances its durability and visual depth. Teak wood exhibits a golden to medium brown hue with a more varied, interlocking grain pattern and a smoother, oily texture due to natural oils that provide excellent water resistance. The coarse texture of Wenge contrasts sharply with the fine, almost silky feel of Teak, making each ideal for different aesthetic and functional applications in woodworking.
Resistance to Moisture and Decay
Wenge wood exhibits moderate resistance to moisture and decay, making it suitable for indoor applications but less ideal for prolonged exposure to wet conditions. Teak is renowned for its exceptional resistance to moisture and decay due to its high natural oil content, making it the preferred choice for outdoor furniture and marine use. The dense grain structure of teak further enhances its durability against fungal attacks and water damage compared to the more porous wenge.
Common Applications in Furniture and Flooring
Wenge wood is commonly used in high-end furniture and flooring due to its rich dark color and durability, making it ideal for cabinetry, decorative veneers, and hardwood floors that demand a luxurious aesthetic. Teak is highly favored for outdoor furniture and flooring because of its exceptional weather resistance and natural oils that protect against moisture and decay. Both woods offer durability and beauty, with Wenge often chosen for striking interior pieces, while Teak excels in outdoor and marine environments.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Wenge wood, sourced primarily from Central African rainforests, faces sustainability challenges due to slow growth and illegal logging, while teak, native to Southeast Asia, is often cultivated in plantations that support sustainable harvesting practices. Teak plantations help reduce deforestation pressure on natural forests and offer a renewable timber source, whereas wenge's limited natural regeneration heightens its ecological risk. Choosing plantation-grown teak over wild-harvested wenge can significantly reduce environmental impact and promote responsible forestry management.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Wenge wood requires minimal maintenance due to its natural resistance to moisture and decay, making it ideal for indoor use with occasional dusting and oiling to preserve its dark, rich color. Teak demands more frequent care, including regular cleaning and oiling to maintain its golden hue and prevent surface cracks from exposure to sunlight and humidity. Both woods benefit from proper ventilation and avoiding prolonged water exposure to extend their longevity and aesthetic appeal.
Cost and Market Availability
Wenge wood is generally more expensive than teak due to its rarity and limited market availability, with prices often reflecting its exotic appeal. Teak is widely available and sustainably harvested, making it a more cost-effective option in both local and international markets. The strong demand and established supply chains for teak contribute to its stable pricing compared to the fluctuating cost of wenge.
Wenge vs Teak Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com