Tin sheets provide a uniform, corrosion-resistant surface ideal for packaging and food storage, offering excellent durability and flexibility. Tin-coated copper combines the conductivity and strength of copper with a protective tin layer to prevent oxidation, making it suitable for electrical components and plumbing. Choosing between tin sheet and tin-coated copper depends on the application requirements for conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength.
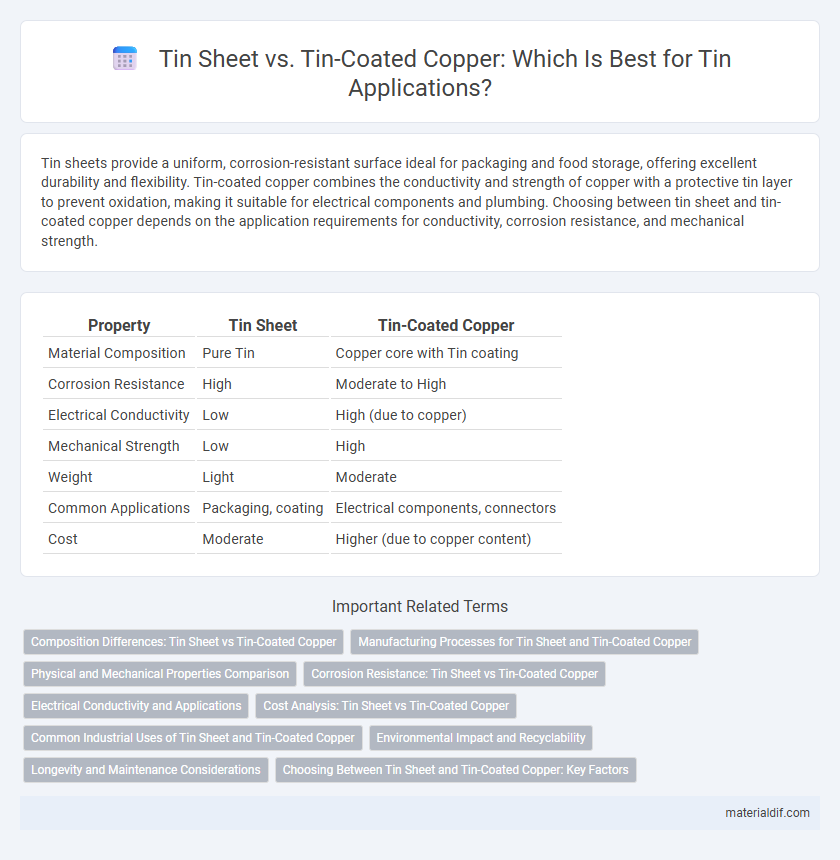
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tin Sheet | Tin-Coated Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure Tin | Copper core with Tin coating |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate to High |
| Electrical Conductivity | Low | High (due to copper) |
| Mechanical Strength | Low | High |
| Weight | Light | Moderate |
| Common Applications | Packaging, coating | Electrical components, connectors |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher (due to copper content) |
Composition Differences: Tin Sheet vs Tin-Coated Copper
Tin sheets consist primarily of pure tin or tin alloys, offering excellent corrosion resistance, malleability, and non-toxicity, making them ideal for food packaging and protective applications. In contrast, tin-coated copper features a copper core coated with a thin layer of tin to combine copper's high electrical conductivity and mechanical strength with tin's corrosion and oxidation resistance. The key composition difference lies in the pure tin surface of tin sheets versus the dual-metal structure of tin-coated copper, optimizing each material for distinct industrial uses.
Manufacturing Processes for Tin Sheet and Tin-Coated Copper
Tin sheet manufacturing involves melting high-purity tin followed by casting, rolling, and annealing to achieve a uniform thickness and enhanced mechanical properties. Tin-coated copper production requires electroplating or hot-dipping processes where a thin layer of tin is deposited onto copper substrates to improve corrosion resistance and solderability. Both methods demand precise temperature control and surface preparation to ensure optimal adhesion and finish quality.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Tin sheets exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and are highly malleable, making them ideal for applications requiring flexibility and surface protection. Tin-coated copper combines the superior electrical conductivity and mechanical strength of copper with the corrosion resistance of tin, resulting in enhanced durability and reduced oxidation in electrical components. The tin layer improves solderability and wear resistance, while the copper core maintains structural integrity, offering a balanced performance in mechanical and physical properties.
Corrosion Resistance: Tin Sheet vs Tin-Coated Copper
Tin sheets offer excellent corrosion resistance due to their uniform composition, creating a stable and protective barrier against oxidation. Tin-coated copper combines the conductivity of copper with tin's corrosion resistance, but the underlying copper is vulnerable if the tin layer is compromised. The durability of corrosion protection in tin-coated copper depends heavily on the integrity of the tin coating to prevent exposure of the reactive copper substrate.
Electrical Conductivity and Applications
Tin sheets offer moderate electrical conductivity suitable for corrosion-resistant applications, while tin-coated copper combines the excellent conductivity of copper with the protective properties of tin plating. Tin-coated copper is commonly used in electrical wiring and connectors where high conductivity and resistance to oxidation are crucial. Tin sheets find applications in packaging, roofing, and corrosion protection, where conductivity is less critical.
Cost Analysis: Tin Sheet vs Tin-Coated Copper
Tin sheets generally offer a lower initial cost compared to tin-coated copper due to simpler manufacturing processes and cheaper raw materials. Tin-coated copper provides enhanced corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, justifying its higher price in applications requiring durability and performance. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, including maintenance and replacement, reveals tin-coated copper as a cost-effective option for long-term investments despite the upfront expense.
Common Industrial Uses of Tin Sheet and Tin-Coated Copper
Tin sheets are widely used for corrosion-resistant packaging, roofing, and manufacturing of electronic components due to their malleability and solderability. Tin-coated copper combines the excellent conductivity of copper with tin's corrosion resistance, making it essential for electrical wiring, automotive connectors, and circuit board fabrication. Both materials serve critical roles in industrial applications where durability and reliable electrical performance are required.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Tin sheets exhibit higher environmental sustainability due to their pure metal composition, which facilitates straightforward recycling with minimal waste generation. Tin-coated copper, while providing enhanced electrical conductivity, leads to more complex recycling processes because the composite materials require separation to recover both metals efficiently. The environmental impact of tin sheets is lower overall, as their recyclability reduces the need for new resource extraction and lowers carbon emissions associated with metal refinement.
Longevity and Maintenance Considerations
Tin sheets offer excellent corrosion resistance and require minimal maintenance, making them ideal for long-term applications exposed to moisture or chemicals. Tin-coated copper combines the electrical conductivity of copper with a protective tin layer, extending the lifespan of copper components by preventing oxidation and reducing maintenance frequency. While tin sheets provide uniform durability, tin-coated copper is preferred in electrical and plumbing industries due to its balance of longevity and operational efficiency.
Choosing Between Tin Sheet and Tin-Coated Copper: Key Factors
Tin sheets offer excellent corrosion resistance and are highly ductile, making them ideal for applications requiring easy fabrication and superior surface protection. Tin-coated copper combines the electrical conductivity of copper with the corrosion resistance of tin, making it suitable for electrical and thermal applications. Key factors to consider include mechanical strength, conductivity requirements, environmental exposure, and cost efficiency to determine the optimal material for your specific use case.
Tin sheet vs Tin-coated copper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com