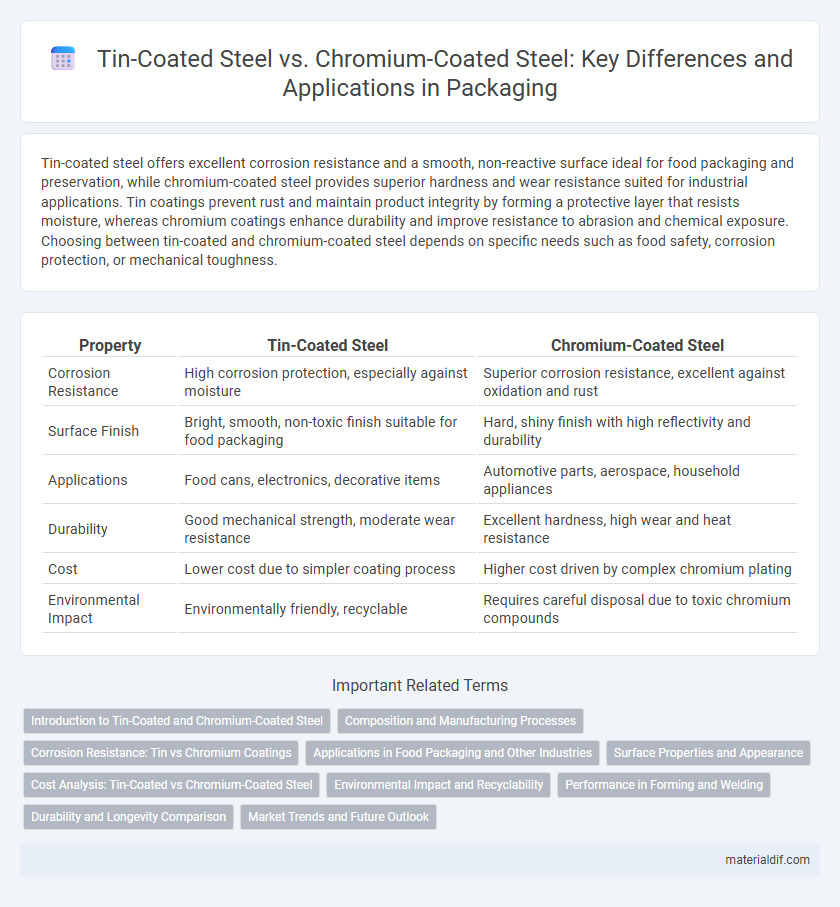
Tin-coated steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and a smooth, non-reactive surface ideal for food packaging and preservation, while chromium-coated steel provides superior hardness and wear resistance suited for industrial applications. Tin coatings prevent rust and maintain product integrity by forming a protective layer that resists moisture, whereas chromium coatings enhance durability and improve resistance to abrasion and chemical exposure. Choosing between tin-coated and chromium-coated steel depends on specific needs such as food safety, corrosion protection, or mechanical toughness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tin-Coated Steel | Chromium-Coated Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High corrosion protection, especially against moisture | Superior corrosion resistance, excellent against oxidation and rust |
| Surface Finish | Bright, smooth, non-toxic finish suitable for food packaging | Hard, shiny finish with high reflectivity and durability |
| Applications | Food cans, electronics, decorative items | Automotive parts, aerospace, household appliances |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, moderate wear resistance | Excellent hardness, high wear and heat resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost due to simpler coating process | Higher cost driven by complex chromium plating |
| Environmental Impact | Environmentally friendly, recyclable | Requires careful disposal due to toxic chromium compounds |
Introduction to Tin-Coated and Chromium-Coated Steel
Tin-coated steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and enhanced solderability, making it ideal for food packaging and electrical applications. Chromium-coated steel provides superior surface hardness and resistance to wear, commonly used in automotive and appliance manufacturing. Both coatings contribute unique protective properties that extend the lifespan of steel substrates across various industries.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Tin-coated steel features a thin layer of pure tin applied through electrolytic or hot-dip plating, enhancing corrosion resistance and solderability. Chromium-coated steel, produced via physical vapor deposition or electroplating, incorporates a chromium layer that provides superior hardness and wear resistance with improved surface luster. The manufacturing process for tin coating emphasizes controlled tin bath temperatures and degreasing, while chromium coating requires precise vacuum conditions or chromium bath chemistry to ensure uniform deposition.
Corrosion Resistance: Tin vs Chromium Coatings
Tin-coated steel offers excellent corrosion resistance by forming a protective oxide layer that prevents rust and is especially effective in food packaging and mild environments. Chromium-coated steel, known as stainless steel, provides superior corrosion resistance through a passive chromium oxide film that resists oxidation and harsh chemicals, making it ideal for industrial and high-moisture applications. While tin coatings excel in preventing corrosion in low-aggressive environments, chromium coatings outperform tin in durability and resistance to severe corrosion conditions.
Applications in Food Packaging and Other Industries
Tin-coated steel is extensively used in food packaging due to its excellent corrosion resistance and food safety compliance, making it ideal for cans and other containers that preserve product freshness. Chromium-coated steel offers superior surface hardness and resistance to wear, which is beneficial in applications like automotive parts and appliances where durability is crucial. Both coatings extend the lifespan of steel in various industries, but tin-coated steel remains the preferred choice for direct food contact because of its non-toxic nature and effective barrier properties.
Surface Properties and Appearance
Tin-coated steel offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its uniform, smooth surface that enhances paint adhesion and maintains a bright, metallic appearance over time. Chromium-coated steel features a harder, more scratch-resistant surface with the characteristic reflective shine of chromium, providing superior wear resistance and a sleek, polished look. The choice between these coatings depends on the desired balance between corrosion protection, surface hardness, and aesthetic appeal in industrial applications.
Cost Analysis: Tin-Coated vs Chromium-Coated Steel
Tin-coated steel typically offers a lower cost solution compared to chromium-coated steel due to cheaper raw material prices and simpler manufacturing processes. Chromium-coated steel demands higher expenses stemming from its complex deposition techniques and the use of more costly chromium compounds. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, tin-coated steel often presents better affordability for applications requiring moderate corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Tin-coated steel offers superior recyclability due to its non-toxic nature and ease of separation during metal recovery processes, minimizing environmental contamination. Chromium-coated steel, often involving chromium VI compounds, poses environmental challenges from toxic byproducts and more complex recycling procedures. Selecting tin coatings reduces hazardous waste and supports sustainable steel lifecycle management through enhanced circular economy practices.
Performance in Forming and Welding
Tin-coated steel offers excellent formability due to its ductile tin layer, enabling easy shaping without cracking, while its solderability enhances welding processes in electronic and packaging applications. Chromium-coated steel provides superior corrosion resistance but presents challenges in forming, often requiring higher force and precision to avoid surface defects. Welding chromium coatings demands specialized techniques to prevent chromium oxides, making tin-coated steel generally more straightforward for standard forming and welding operations.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Tin-coated steel offers excellent corrosion resistance thanks to its tight, non-porous tin layer, enhancing durability in moist environments and extending product lifespan. Chromium-coated steel provides superior hardness and scratch resistance due to its chromium oxide surface, making it more durable under mechanical wear and abrasion. While tin coatings excel in preventing rust, chromium coatings offer longer-lasting protection in harsh, high-friction applications.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The market for tin-coated steel is expanding due to its superior corrosion resistance and recyclability, particularly in packaging and automotive industries where longevity and sustainability are prioritized. Chromium-coated steel maintains a strong presence in high-performance applications requiring enhanced hardness and wear resistance, with ongoing innovations aimed at reducing chromium content to meet environmental regulations. Future trends indicate a growing preference for eco-friendly coatings, driving research in alternative materials and hybrid coatings that combine the benefits of both tin and chromium to optimize performance and comply with evolving standards.
Tin-coated steel vs Chromium-coated steel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com