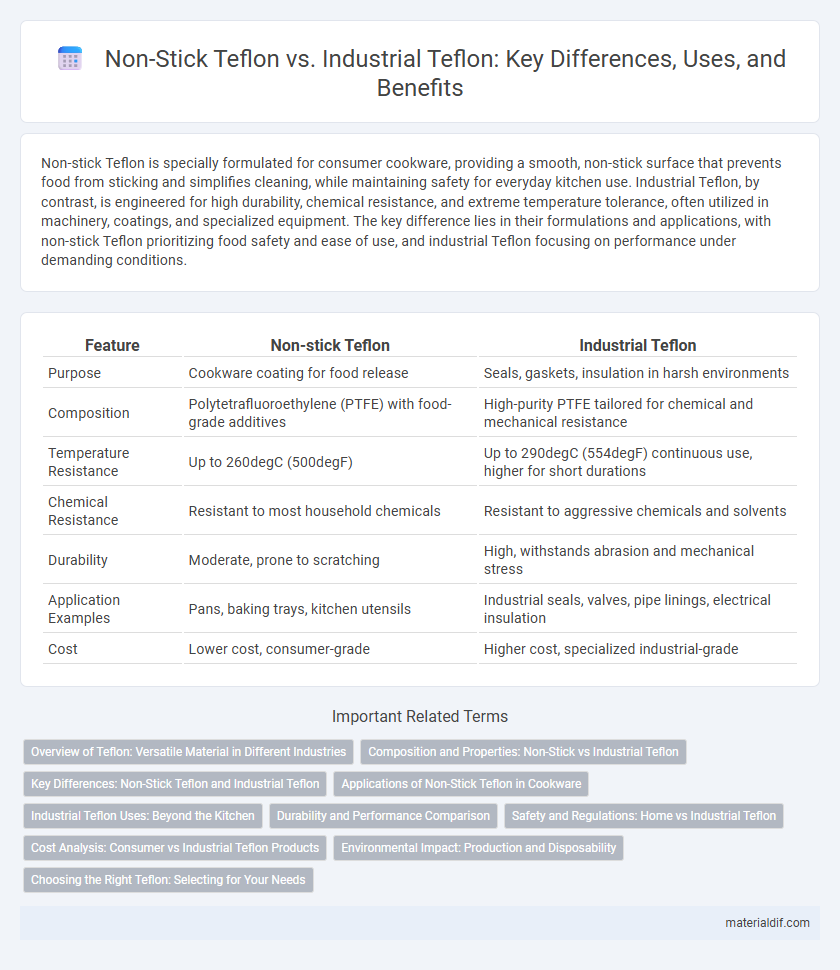
Non-stick Teflon is specially formulated for consumer cookware, providing a smooth, non-stick surface that prevents food from sticking and simplifies cleaning, while maintaining safety for everyday kitchen use. Industrial Teflon, by contrast, is engineered for high durability, chemical resistance, and extreme temperature tolerance, often utilized in machinery, coatings, and specialized equipment. The key difference lies in their formulations and applications, with non-stick Teflon prioritizing food safety and ease of use, and industrial Teflon focusing on performance under demanding conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Non-stick Teflon | Industrial Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Cookware coating for food release | Seals, gaskets, insulation in harsh environments |
| Composition | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) with food-grade additives | High-purity PTFE tailored for chemical and mechanical resistance |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260degC (500degF) | Up to 290degC (554degF) continuous use, higher for short durations |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most household chemicals | Resistant to aggressive chemicals and solvents |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to scratching | High, withstands abrasion and mechanical stress |
| Application Examples | Pans, baking trays, kitchen utensils | Industrial seals, valves, pipe linings, electrical insulation |
| Cost | Lower cost, consumer-grade | Higher cost, specialized industrial-grade |
Overview of Teflon: Versatile Material in Different Industries
Teflon, a brand name for polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), exhibits exceptional chemical resistance and low friction, making it essential in both non-stick cookware and industrial applications. Non-stick Teflon coatings provide a durable, heat-resistant surface ideal for kitchenware, while industrial Teflon is engineered for use in gaskets, seals, and insulating materials across automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing industries. The versatility of Teflon arises from its unique molecular structure, enabling diverse formulations tailored to specific performance requirements in various sectors.
Composition and Properties: Non-Stick vs Industrial Teflon
Non-stick Teflon primarily consists of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) with a focus on low surface energy to prevent food adhesion, characterized by excellent chemical resistance and a smooth, non-reactive surface. Industrial Teflon also uses PTFE but often incorporates fillers like glass fibers or graphite to enhance mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and wear durability for demanding applications. These compositional variations directly influence their properties, with non-stick Teflon optimized for easy cleaning and food safety, while industrial Teflon excels in high-temperature stability and mechanical performance.
Key Differences: Non-Stick Teflon and Industrial Teflon
Non-stick Teflon, primarily used in cookware, features a smooth polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) coating that prevents food from adhering to surfaces, ensuring easy cleaning and enhanced cooking performance. Industrial Teflon incorporates a broader range of PTFE applications, including gaskets, seals, and insulation, prized for its chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low friction properties. Key differences lie in their formulations and surface textures, with non-stick variants optimized for food safety and cooking efficiency, while industrial Teflon prioritizes durability and performance in harsh environments.
Applications of Non-Stick Teflon in Cookware
Non-stick Teflon, primarily polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is widely used in cookware due to its exceptional heat resistance and ultra-low friction properties, preventing food from adhering to surfaces. This variant of Teflon is specifically engineered to withstand temperatures up to 260degC without degrading, making it ideal for frying pans, baking trays, and griddles. In contrast, industrial Teflon grades are formulated for applications requiring enhanced chemical resistance and mechanical strength, often used in sealing, coatings, and insulation rather than culinary uses.
Industrial Teflon Uses: Beyond the Kitchen
Industrial Teflon, known for its exceptional chemical resistance and low friction properties, is widely used in applications such as manufacturing seals, gaskets, and linings in chemical processing equipment. Unlike non-stick Teflon coatings commonly found in cookware, industrial-grade Teflon withstands extreme temperatures and aggressive chemicals, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. Its versatility extends to insulating electrical wires, preventing corrosion, and reducing wear in heavy machinery, highlighting its critical role beyond kitchen use.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Non-stick Teflon is engineered for cookware, emphasizing easy food release and moderate heat resistance, while Industrial Teflon offers superior durability and chemical resistance for harsh environments. The performance of Industrial Teflon excels in abrasive and high-temperature applications, maintaining stability beyond 260degC, unlike non-stick variants that degrade faster under intense conditions. Durability in Industrial Teflon makes it ideal for machinery coatings and sealing applications, whereas non-stick Teflon prioritizes user convenience and safety during typical cooking processes.
Safety and Regulations: Home vs Industrial Teflon
Non-stick Teflon used in cookware is formulated with strict safety standards regulated by the FDA, ensuring it is free from harmful substances like PFOA in compliant products. Industrial Teflon, often applied in manufacturing and chemical processing, may contain stronger formulations that require adherence to OSHA and EPA regulations to manage potential exposure risks. Home-use Teflon coatings prioritize consumer safety with rigorous testing, while industrial Teflon focuses on operational durability under regulatory oversight to prevent environmental and worker hazards.
Cost Analysis: Consumer vs Industrial Teflon Products
Non-stick Teflon products targeted at consumers typically incur lower manufacturing costs due to thinner coatings and simpler application processes, resulting in more affordable pricing. Industrial Teflon, designed for high-performance applications, involves thicker, more durable coatings and specialized formulations, significantly increasing production expenses. The cost disparity reflects the enhanced chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and longevity required in industrial settings compared to everyday consumer use.
Environmental Impact: Production and Disposability
Non-stick Teflon, widely used in cookware, involves polymerization of PTFE that releases harmful perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), contributing to persistent environmental pollution and bioaccumulation in wildlife. Industrial Teflon applications require more robust formulations with higher molecular weight PTFE, often involving energy-intensive manufacturing processes and complex waste management to minimize soil and water contamination. Disposal of both types poses significant challenges due to Teflon's chemical stability, resulting in long degradation times and potential release of toxic fluorinated compounds if incinerated improperly.
Choosing the Right Teflon: Selecting for Your Needs
Non-stick Teflon coatings are engineered primarily for cookware, providing easy food release and wear resistance at moderate temperatures. Industrial Teflon variants, such as PTFE sheets and rods, offer enhanced chemical resistance, higher temperature tolerance, and electrical insulation suited for engineering applications. Choosing the right Teflon requires evaluating factors like temperature range, mechanical stress, and exposure to chemicals to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Non-stick Teflon vs Industrial Teflon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com