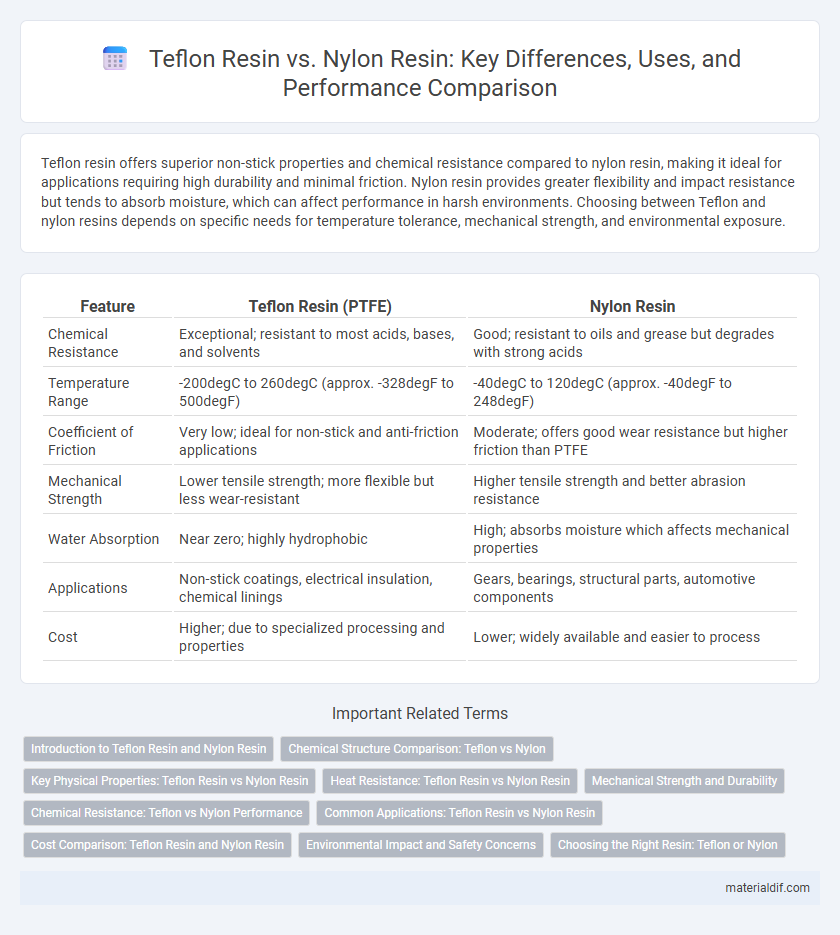
Teflon resin offers superior non-stick properties and chemical resistance compared to nylon resin, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and minimal friction. Nylon resin provides greater flexibility and impact resistance but tends to absorb moisture, which can affect performance in harsh environments. Choosing between Teflon and nylon resins depends on specific needs for temperature tolerance, mechanical strength, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Teflon Resin (PTFE) | Nylon Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional; resistant to most acids, bases, and solvents | Good; resistant to oils and grease but degrades with strong acids |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 260degC (approx. -328degF to 500degF) | -40degC to 120degC (approx. -40degF to 248degF) |
| Coefficient of Friction | Very low; ideal for non-stick and anti-friction applications | Moderate; offers good wear resistance but higher friction than PTFE |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower tensile strength; more flexible but less wear-resistant | Higher tensile strength and better abrasion resistance |
| Water Absorption | Near zero; highly hydrophobic | High; absorbs moisture which affects mechanical properties |
| Applications | Non-stick coatings, electrical insulation, chemical linings | Gears, bearings, structural parts, automotive components |
| Cost | Higher; due to specialized processing and properties | Lower; widely available and easier to process |
Introduction to Teflon Resin and Nylon Resin
Teflon resin, a brand name for polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is renowned for its exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, making it ideal for non-stick coatings and industrial applications. Nylon resin, a synthetic polymer belonging to the polyamide family, offers excellent mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and moisture absorption properties, commonly used in automotive parts and textiles. Both resins serve distinct purposes, with Teflon excelling in chemical stability and heat resistance, while nylon provides durability and flexibility in engineering components.
Chemical Structure Comparison: Teflon vs Nylon
Teflon resin, composed of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), features a carbon backbone fully fluorinated with strong carbon-fluorine bonds, resulting in exceptional chemical inertness and heat resistance. In contrast, nylon resin consists of polyamide chains with repeating units containing amide linkages (-CONH-) that provide high mechanical strength and moderate chemical resistance but are more susceptible to hydrolysis. The fluorinated structure of Teflon offers superior non-reactivity and low friction compared to nylon's polar amide groups, influencing their respective applications in harsh chemical environments and wear-resistant components.
Key Physical Properties: Teflon Resin vs Nylon Resin
Teflon resin exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and a low coefficient of friction, making it ideal for non-stick and corrosion-resistant applications. Nylon resin offers superior mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and moisture absorption properties but has a lower maximum service temperature around 120degC. The choice between Teflon and Nylon resins depends on specific requirements for thermal stability, wear resistance, and exposure to harsh chemicals.
Heat Resistance: Teflon Resin vs Nylon Resin
Teflon resin offers superior heat resistance, maintaining stability at temperatures up to 260degC (500degF), whereas nylon resin typically withstands continuous use only up to 120degC (248degF). This significant difference makes Teflon ideal for high-temperature applications such as industrial coatings and non-stick cookware. Nylon's lower heat tolerance limits its use in environments where sustained high temperatures are common.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Teflon resin exhibits exceptional chemical resistance and low friction but has lower mechanical strength compared to nylon resin, which offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance. Nylon resin provides enhanced durability under mechanical stress, making it suitable for load-bearing applications, while Teflon's durability excels in harsh chemical environments with minimal wear. Selecting between Teflon and nylon resins depends on balancing mechanical performance requirements with environmental exposure.
Chemical Resistance: Teflon vs Nylon Performance
Teflon resin exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, withstanding exposure to aggressive acids, bases, and solvents without degradation, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments. Nylon resin, while durable and resistant to some chemicals, is susceptible to hydrolysis and degradation when exposed to strong oxidizing agents and certain solvents. This superior chemical resistance of Teflon over nylon ensures longer material lifespan and reliability in applications involving corrosive substances.
Common Applications: Teflon Resin vs Nylon Resin
Teflon resin is widely used in non-stick cookware, chemical-resistant coatings, and electrical insulation due to its exceptional chemical inertness and low friction properties. Nylon resin finds common applications in automotive parts, gears, and textiles, valued for its high mechanical strength and wear resistance. Both materials serve distinct industrial purposes, with Teflon excelling in extreme chemical and temperature environments, while Nylon is preferred for durable, load-bearing components.
Cost Comparison: Teflon Resin and Nylon Resin
Teflon resin generally commands a higher price than nylon resin due to its superior chemical resistance and non-stick properties, which make it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Nylon resin, while more affordable, offers excellent mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for cost-sensitive projects requiring durability. The cost difference is significant, with Teflon resin priced approximately two to three times higher than nylon resin, affecting material selection based on budget constraints and performance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Safety Concerns
Teflon resin, made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), has raised environmental concerns due to the persistence of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) used in its manufacturing, which is linked to water contamination and potential health risks. Nylon resin, derived from polyamides, is generally considered less harmful to the environment but can release nitrous oxide and other greenhouse gases during production, impacting air quality. Both resins require careful handling and disposal to mitigate ecological footprint and ensure safety, with Teflon demanding stricter regulatory compliance because of its chemical stability and potential bioaccumulative effects.
Choosing the Right Resin: Teflon or Nylon
Teflon resin offers exceptional chemical resistance, non-stick properties, and high-temperature tolerance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability in aggressive environments. Nylon resin provides superior mechanical strength, wear resistance, and flexibility, suitable for components subjected to mechanical stress and abrasion. Choosing between Teflon and Nylon resins depends on the specific performance requirements such as thermal stability versus toughness and resistance to friction.
Teflon Resin vs Nylon Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com