Electro-galvanized steel offers a smooth, uniform coating ideal for indoor applications where corrosion resistance is moderate. Hot-dip galvanized steel provides a thicker, more durable zinc layer that excels in harsh outdoor environments with high exposure to moisture and chemicals. Choosing between them depends on the specific durability requirements and environmental conditions for the steel pet's intended use.
Table of Comparison
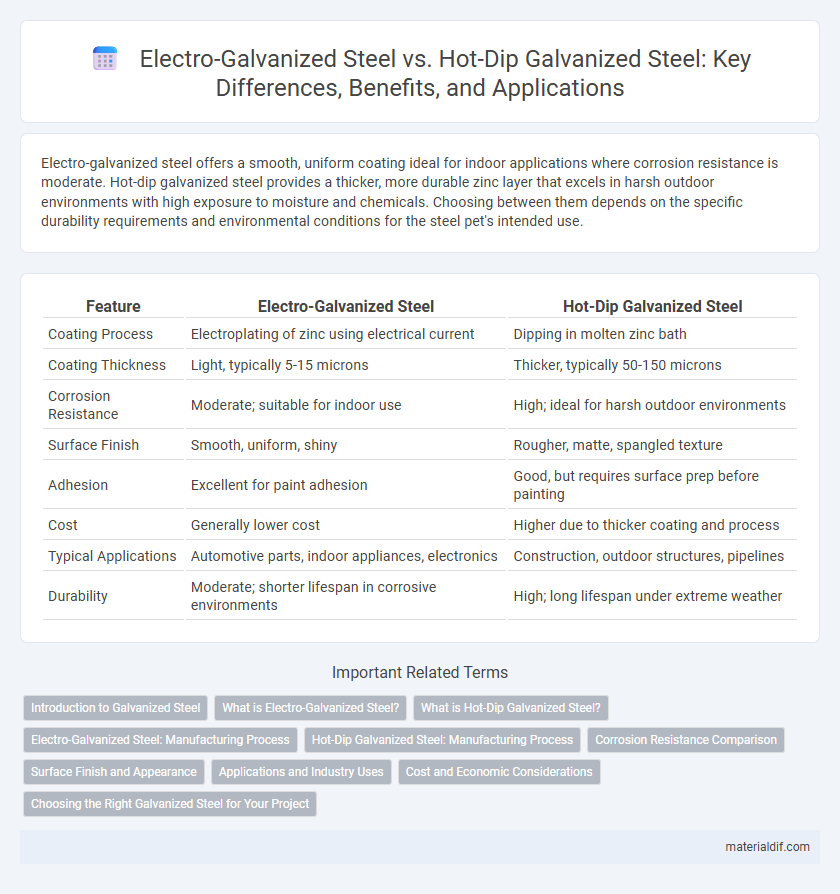
| Feature | Electro-Galvanized Steel | Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Process | Electroplating of zinc using electrical current | Dipping in molten zinc bath |
| Coating Thickness | Light, typically 5-15 microns | Thicker, typically 50-150 microns |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; suitable for indoor use | High; ideal for harsh outdoor environments |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, uniform, shiny | Rougher, matte, spangled texture |
| Adhesion | Excellent for paint adhesion | Good, but requires surface prep before painting |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher due to thicker coating and process |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, indoor appliances, electronics | Construction, outdoor structures, pipelines |
| Durability | Moderate; shorter lifespan in corrosive environments | High; long lifespan under extreme weather |
Introduction to Galvanized Steel
Electro-galvanized steel features a thin, uniform zinc coating applied through an electroplating process, offering excellent surface smoothness and precise thickness control ideal for automotive and appliance manufacturing. Hot-dip galvanized steel undergoes immersion in molten zinc, producing a thicker, more durable coating with enhanced corrosion resistance suited for construction and outdoor applications. Both methods provide essential protection against rust, extending steel longevity by forming a barrier that prevents oxidation.
What is Electro-Galvanized Steel?
Electro-galvanized steel is a type of steel coated with a thin layer of zinc through an electroplating process, providing corrosion resistance and a smooth, uniform finish. This method deposits zinc ions onto the steel surface using an electric current, resulting in precise control over coating thickness and enhanced surface quality. It is commonly used in automotive components, appliances, and electrical enclosures due to its excellent paint adhesion and aesthetic appeal.
What is Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel?
Hot-dip galvanized steel is steel coated with a layer of zinc by immersing it in a molten zinc bath, providing enhanced corrosion resistance. This process creates a metallurgical bond between the steel and zinc, resulting in a thicker and more durable coating compared to electro-galvanized steel. Hot-dip galvanized steel is widely used in construction, automotive, and outdoor applications due to its superior protection against rust and environmental damage.
Electro-Galvanized Steel: Manufacturing Process
Electro-galvanized steel undergoes a manufacturing process where a thin layer of zinc is electrically deposited onto the steel surface in a controlled electrolyte bath, ensuring uniform coating thickness and smooth finish. This electroplating technique allows for precise corrosion resistance and improved paint adhesion compared to hot-dip galvanized steel. The process operates at ambient temperatures, reducing thermal distortion and maintaining tight dimensional tolerances ideal for automotive and appliance applications.
Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel: Manufacturing Process
Hot-dip galvanized steel is produced by immersing steel sheets or components into a bath of molten zinc at approximately 450degC, creating a robust metallurgical bond that provides superior corrosion resistance. The process forms a series of zinc-iron alloy layers that enhance durability and abrasion resistance compared to electro-galvanized steel. This method is widely used in industries requiring long-lasting protection in harsh environments, such as construction, automotive, and infrastructure.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Electro-galvanized steel features a thin, uniform zinc coating applied through an electrolytic process, offering moderate corrosion resistance ideal for indoor applications with minimal exposure to moisture. Hot-dip galvanized steel undergoes immersion in molten zinc, creating a thicker, metallurgically bonded coating that provides superior corrosion protection in harsh outdoor environments and extends service life under aggressive weather conditions. The enhanced durability of hot-dip galvanizing makes it the preferred choice for structural steel components, while electro-galvanized steel suits applications requiring a smoother finish and light corrosion resistance.
Surface Finish and Appearance
Electro-galvanized steel offers a smooth, uniform surface finish with a brighter and more aesthetically appealing appearance due to its precise electroplating process. Hot-dip galvanized steel features a thicker, rougher coating with a matte, spangled finish that provides superior corrosion resistance but a less polished look. Surface texture and visual consistency are key factors influencing the choice between electro-galvanizing for decorative applications and hot-dip galvanizing for heavy-duty protection.
Applications and Industry Uses
Electro-galvanized steel is commonly used in automotive panels, household appliances, and electronic enclosures due to its smooth surface finish and precise coating thickness, providing excellent corrosion resistance in controlled environments. Hot-dip galvanized steel finds extensive application in construction, infrastructure, and outdoor equipment, offering robust protection against harsh weather conditions and industrial pollutants. Industries such as automotive manufacturing, construction, and electrical equipment production favor these steel types based on specific durability and environmental requirements.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Electro-galvanized steel typically incurs higher production costs due to its precise coating process, resulting in a thinner and more uniform zinc layer that provides moderate corrosion resistance suitable for indoor applications. Hot-dip galvanized steel offers a thicker zinc coating through immersion in molten zinc, ensuring enhanced durability and superior protection in harsh environments at a generally lower cost per unit of protection. Economic considerations favor hot-dip galvanizing for large-scale, outdoor infrastructure projects, while electro-galvanizing is cost-effective for automotive and electronics industries requiring fine surface finishes.
Choosing the Right Galvanized Steel for Your Project
Electro-galvanized steel offers a smooth, uniform zinc coating ideal for indoor applications requiring precision and aesthetics, while hot-dip galvanized steel provides a thicker, more durable zinc layer suited for harsh outdoor environments and heavy corrosion resistance. Selecting the right galvanized steel depends on factors like exposure conditions, mechanical stress, and desired surface finish, with electro-galvanized steel favored for light-duty and aesthetic projects, and hot-dip galvanized steel preferred for structural or industrial uses. Understanding project requirements and environmental challenges ensures optimal protection and longevity of galvanized steel components.
Electro-galvanized steel vs Hot-dip galvanized steel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com