Duplex steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and high strength due to its balanced austenitic and ferritic microstructure, making it ideal for moderately aggressive environments. Super duplex steel enhances these properties by increasing chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen content, resulting in superior resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking and pitting in highly corrosive conditions. Both materials are favored in the oil and gas industry, but super duplex steel is preferred for more demanding applications requiring greater durability and longevity.
Table of Comparison
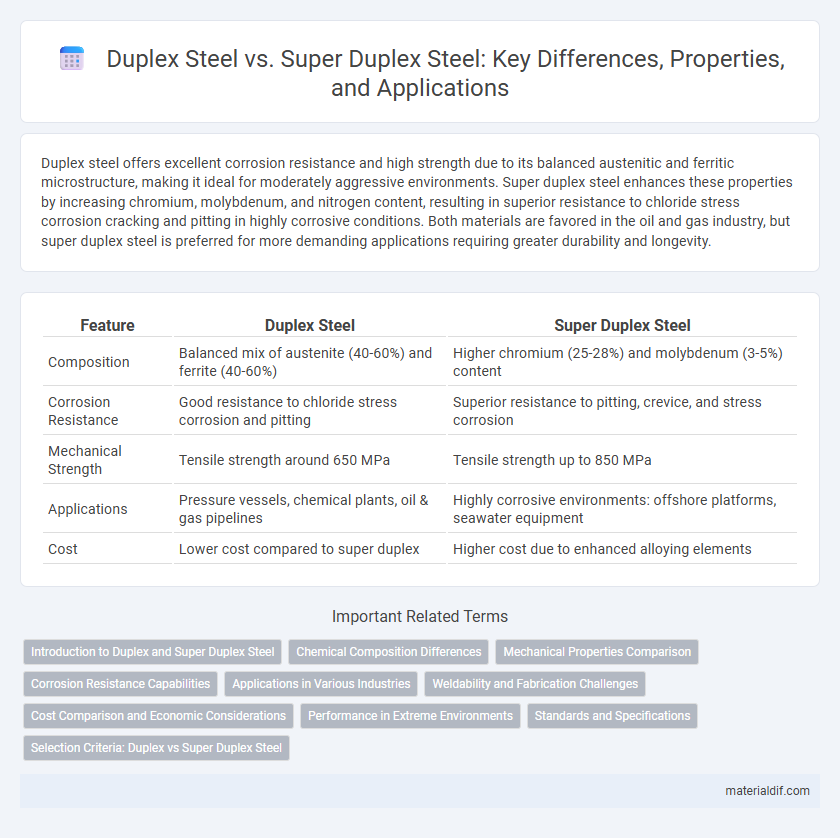
| Feature | Duplex Steel | Super Duplex Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Balanced mix of austenite (40-60%) and ferrite (40-60%) | Higher chromium (25-28%) and molybdenum (3-5%) content |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good resistance to chloride stress corrosion and pitting | Superior resistance to pitting, crevice, and stress corrosion |
| Mechanical Strength | Tensile strength around 650 MPa | Tensile strength up to 850 MPa |
| Applications | Pressure vessels, chemical plants, oil & gas pipelines | Highly corrosive environments: offshore platforms, seawater equipment |
| Cost | Lower cost compared to super duplex | Higher cost due to enhanced alloying elements |
Introduction to Duplex and Super Duplex Steel
Duplex steel combines austenitic and ferritic microstructures, delivering enhanced strength and corrosion resistance compared to standard stainless steels. Super duplex steel offers higher chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen content, boosting its resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking in aggressive environments. These steels are widely utilized in offshore oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine applications due to their superior durability and mechanical properties.
Chemical Composition Differences
Duplex steel typically contains 18-28% chromium, 4-6.5% nickel, and up to 3% molybdenum, providing a balanced microstructure of austenite and ferrite for enhanced corrosion resistance. Super duplex steel increases chromium content to 24-26%, nickel to 6-8%, and molybdenum to 3-5%, resulting in superior resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking. The higher alloying elements in super duplex steel improve mechanical strength and chemical stability, making it ideal for aggressive environments in oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Duplex steel typically offers tensile strengths of 550-750 MPa, while super duplex steel exhibits higher tensile strength in the range of 800-1,100 MPa, making it more suitable for demanding mechanical applications. The yield strength of super duplex steel is generally around 690-1,000 MPa, surpassing that of standard duplex steel, which ranges between 400-600 MPa, enhancing resistance to deformation under load. Both materials provide excellent corrosion resistance, but super duplex steel's superior mechanical properties make it ideal for harsh environments requiring higher performance and durability.
Corrosion Resistance Capabilities
Duplex steel offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its balanced microstructure of austenite and ferrite, making it highly effective against stress corrosion cracking and chloride-induced pitting. Super duplex steel enhances these properties with increased chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen content, providing superior resistance in highly aggressive environments like seawater and chemical processing. The improved corrosion resistance capabilities of super duplex steel make it ideal for offshore oil and gas applications and marine engineering where durability is critical.
Applications in Various Industries
Duplex steel, known for its balanced austenitic-ferritic microstructure, excels in chemical processing, oil and gas pipelines, and marine environments due to its corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. Super duplex steel, with higher chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen content, offers enhanced resistance to chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking, making it ideal for offshore drilling, desalination plants, and petrochemical industries. Both materials serve critical roles in industries requiring durability and corrosion resistance under harsh conditions.
Weldability and Fabrication Challenges
Duplex steel offers good weldability with balanced ferritic-austenitic microstructure that reduces cracking risk, but requires precise control of heat input and interpass temperature to maintain mechanical properties. Super duplex steel, with higher alloy content and increased corrosion resistance, presents greater fabrication challenges including susceptibility to phase imbalances and sigma phase formation during welding, demanding specialized welding techniques and post-weld heat treatment. Both steels require skilled welding procedures to prevent sensitization and ensure structural integrity in aggressive environments.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Duplex steel offers a cost-effective solution with moderate strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for many industrial applications. Super duplex steel, while more expensive due to higher nickel and molybdenum content, provides enhanced durability and resistance to harsh environments, reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs. Economic considerations favor duplex steel for projects with budget constraints, but super duplex steel justifies its higher initial investment through superior performance in aggressive conditions, leading to lower overall lifecycle expenses.
Performance in Extreme Environments
Duplex steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength in moderately aggressive environments, making it suitable for chemical processing and marine applications. Super duplex steel provides superior chloride stress corrosion cracking resistance and higher mechanical strength, enabling it to perform reliably in highly corrosive and extreme temperature conditions such as offshore oil and gas extraction. The enhanced nickel and molybdenum content in super duplex steel results in better durability against pitting and crevice corrosion compared to standard duplex steel.
Standards and Specifications
Duplex steel and super duplex steel are distinguished by their chemical composition and corrosion resistance, with super duplex offering higher chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen content for enhanced performance. Standards such as ASTM A790 and UNS S31803 apply to duplex steel, while super duplex steel complies with stricter specifications like ASTM A890 Grade 5A and UNS S32750, reflecting increased alloying elements and toughness requirements. These standards ensure material properties meet the demands of aggressive environments in industries like oil and gas, seawater desalination, and chemical processing.
Selection Criteria: Duplex vs Super Duplex Steel
Selection criteria for Duplex vs Super Duplex steel depend on corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and environmental conditions. Duplex steel offers excellent resistance to stress corrosion cracking and moderate chloride environments, making it suitable for general chemical processing and seawater applications. Super Duplex steel provides superior resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking, ideal for harsh offshore oil and gas, marine, and chemical industries requiring higher strength and durability.
Duplex Steel vs Super Duplex Steel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com