Welded steel pipes are made by rolling steel plates and welding the seam, offering cost-efficiency and versatility for various applications. Seamless steel pipes are manufactured by extrusion, providing superior strength and resistance to high pressure and temperature. Choosing between welded and seamless steel depends on the specific requirements of durability, strength, and budget for the project.
Table of Comparison
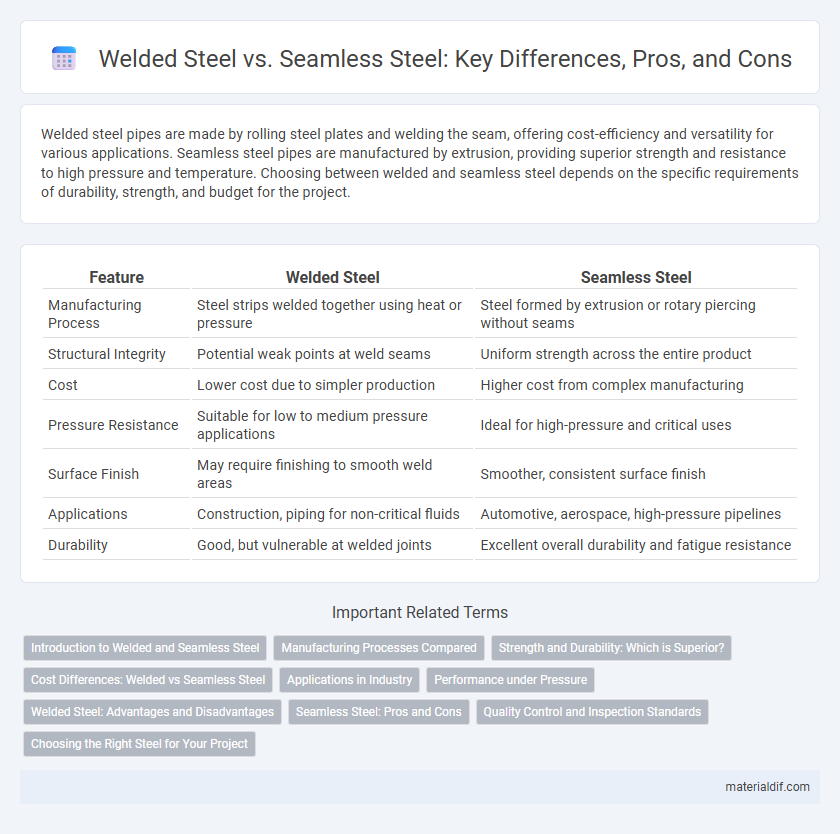
| Feature | Welded Steel | Seamless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Steel strips welded together using heat or pressure | Steel formed by extrusion or rotary piercing without seams |
| Structural Integrity | Potential weak points at weld seams | Uniform strength across the entire product |
| Cost | Lower cost due to simpler production | Higher cost from complex manufacturing |
| Pressure Resistance | Suitable for low to medium pressure applications | Ideal for high-pressure and critical uses |
| Surface Finish | May require finishing to smooth weld areas | Smoother, consistent surface finish |
| Applications | Construction, piping for non-critical fluids | Automotive, aerospace, high-pressure pipelines |
| Durability | Good, but vulnerable at welded joints | Excellent overall durability and fatigue resistance |
Introduction to Welded and Seamless Steel
Welded steel is produced by joining steel plates or strips through heat or pressure, creating a strong bond ideal for large-diameter pipes and structural applications. Seamless steel is manufactured by extruding a solid billet to form a hollow tube without any joints, offering superior strength and resistance to pressure for critical applications like pipelines and high-pressure vessels. Both types provide distinct advantages depending on the required mechanical properties and intended use in industries such as construction, oil and gas, and automotive.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Welded steel is produced by fusing steel plates or coils through processes like electric resistance welding (ERW) or submerged arc welding (SAW), allowing for cost-effective and versatile manufacturing of pipes and structural components. Seamless steel, manufactured via rotary piercing and hot rolling, involves extruding a solid billet to create a hollow tube without joints, resulting in superior strength and uniformity for high-pressure applications. The key manufacturing distinctions affect mechanical properties, with welded steel offering customization and seam integrity challenges, while seamless steel provides enhanced durability and resistance to stress and corrosion.
Strength and Durability: Which is Superior?
Welded steel offers high tensile strength due to the fusion of metal pieces but may have potential weaknesses along the weld seam under extreme stress. Seamless steel, manufactured without any joints or seams, provides uniform strength and better resistance to pressure and fatigue, making it more durable in demanding applications. For maximum strength and durability in critical conditions, seamless steel typically outperforms welded steel.
Cost Differences: Welded vs Seamless Steel
Welded steel is generally more cost-effective than seamless steel due to its simpler manufacturing process, which involves joining steel plates or strips through welding, reducing material waste and production time. Seamless steel, produced by extruding or rotary piercing solid billets, demands higher energy consumption and more complex machinery, resulting in elevated costs. While seamless steel offers superior pressure resistance and durability, the substantial price difference often makes welded steel the preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications.
Applications in Industry
Welded steel is extensively used in structural applications, such as bridges, pipelines, and automotive frames, due to its cost-effectiveness and suitability for large diameter pipes. Seamless steel finds critical applications in high-pressure environments like oil and gas drilling, power plants, and hydraulic systems, where uniform strength and resistance to extreme conditions are essential. Industrial sectors prioritize welded steel for fabrication versatility, while seamless steel is preferred for safety-critical components requiring superior integrity and durability.
Performance under Pressure
Welded steel pipes typically offer consistent strength and can handle high-pressure applications but may exhibit slightly lower pressure tolerance due to seam welds prone to potential weak points. Seamless steel pipes provide superior performance under pressure, as their uniform molecular structure eliminates weld seams, resulting in higher resistance to stress and reduced risk of leakage. For critical high-pressure environments such as oil and gas or hydraulic systems, seamless steel ensures enhanced reliability and safety compared to welded alternatives.
Welded Steel: Advantages and Disadvantages
Welded steel offers cost efficiency and faster production compared to seamless steel, making it ideal for large-scale applications like pipelines and structural components. Its uniform joint strength and flexibility allow for various diameters and custom shapes, enhancing design versatility. However, welded steel may experience reduced corrosion resistance and potential weaknesses at the weld seams, requiring careful inspection and maintenance.
Seamless Steel: Pros and Cons
Seamless steel pipes are manufactured without any welding or joints, offering superior strength, corrosion resistance, and the ability to handle high pressure and temperature conditions, making them ideal for critical applications in oil and gas, aerospace, and power generation. However, seamless steel tends to be more expensive due to complex production processes and limited availability compared to welded steel, and its size range is often more restricted. The absence of weld seams reduces failure risks but requires strict quality control measures to ensure consistent material integrity throughout the pipe.
Quality Control and Inspection Standards
Welded steel undergoes rigorous quality control measures including ultrasonic testing and radiographic inspection to detect weld defects, ensuring structural integrity and uniformity. Seamless steel, produced without welds, is subjected to strict dimensional checks and non-destructive testing methods such as magnetic particle and hydrostatic tests to verify the absence of internal flaws. Both types adhere to industry standards like ASTM A513 for welded steel and ASTM A106 for seamless steel, emphasizing precise inspection protocols to guarantee performance and safety.
Choosing the Right Steel for Your Project
Welded steel offers cost efficiency and flexibility, making it ideal for large-diameter pipes and custom structural components, while seamless steel provides superior strength and durability, essential for high-pressure applications or environments demanding corrosion resistance. Evaluating project requirements such as pressure ratings, environmental conditions, and budget constraints ensures the selection of the optimal steel type. Prioritizing the appropriate steel enhances structural integrity and longevity in construction, manufacturing, or infrastructure projects.
Welded Steel vs Seamless Steel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com