Quartz sand features high purity and durability, making it ideal for uses in glassmaking and construction due to its resistance to weathering. Feldspathic sand contains feldspar minerals that provide alumina and alkalies, enhancing the strength and workability of ceramics and concrete mixtures. The choice between quartz and feldspathic sand depends on the specific requirements of strength, chemical composition, and application in industrial processes.
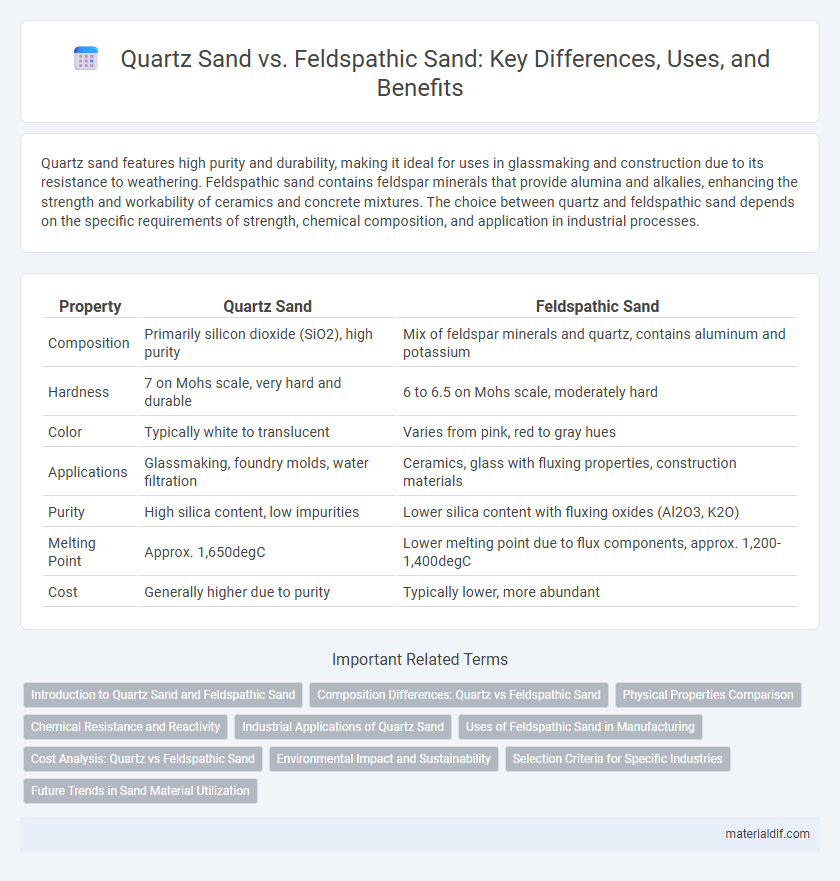
Table of Comparison
| Property | Quartz Sand | Feldspathic Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Primarily silicon dioxide (SiO2), high purity | Mix of feldspar minerals and quartz, contains aluminum and potassium |
| Hardness | 7 on Mohs scale, very hard and durable | 6 to 6.5 on Mohs scale, moderately hard |
| Color | Typically white to translucent | Varies from pink, red to gray hues |
| Applications | Glassmaking, foundry molds, water filtration | Ceramics, glass with fluxing properties, construction materials |
| Purity | High silica content, low impurities | Lower silica content with fluxing oxides (Al2O3, K2O) |
| Melting Point | Approx. 1,650degC | Lower melting point due to flux components, approx. 1,200-1,400degC |
| Cost | Generally higher due to purity | Typically lower, more abundant |
Introduction to Quartz Sand and Feldspathic Sand
Quartz sand primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2) and is known for its high purity, hardness, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for glass manufacturing and industrial applications. Feldspathic sand contains a significant proportion of feldspar minerals, such as orthoclase and plagioclase, which provide alumina and alkali content beneficial in ceramics and foundry molds. The distinct mineral composition of quartz sand and feldspathic sand influences their physical properties and suitability across various construction and manufacturing industries.
Composition Differences: Quartz vs Feldspathic Sand
Quartz sand primarily consists of nearly pure silicon dioxide (SiO2), characterized by its high hardness and chemical stability, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to weathering. Feldspathic sand contains significant amounts of feldspar minerals, such as orthoclase and plagioclase, which contribute alumina and alkaline elements, resulting in a more chemically reactive and softer composition compared to quartz. This difference in mineral composition affects the sand's suitability for various industrial uses, with quartz sand favored in glassmaking and foundry molds, while feldspathic sand is often used in ceramics and as a source of alumina.
Physical Properties Comparison
Quartz sand exhibits high hardness, low porosity, and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to abrasion. Feldspathic sand contains feldspar minerals that contribute to moderate hardness and slightly higher porosity, affecting its overall permeability and strength. The density of quartz sand typically ranges from 2.65 to 2.75 g/cm3, whereas feldspathic sand densities vary between 2.56 and 2.62 g/cm3, impacting their suitability for different construction and industrial uses.
Chemical Resistance and Reactivity
Quartz sand exhibits superior chemical resistance due to its high silica content (SiO2), making it highly inert and stable in acidic and alkaline environments. Feldspathic sand, containing feldspar minerals with aluminum and potassium silicates, shows greater reactivity and can alter chemically under exposure to acids or alkaline conditions. The lower reactivity and higher purity of quartz sand make it preferred for industries requiring minimal chemical interaction, such as glass manufacturing and foundry molds.
Industrial Applications of Quartz Sand
Quartz sand, rich in silica (SiO2) content above 95%, is extensively used in the glass manufacturing industry for producing clear, high-quality glass due to its purity and consistent granule size. Its high melting point and chemical inertness make it ideal for foundry molds and refractory materials, ensuring durability under extreme temperatures. Feldspathic sand, containing feldspar minerals, is primarily utilized in ceramics and as a flux to lower melting temperatures, but lacks the industrial versatility and purity quartz sand offers in sectors like glassmaking and abrasives.
Uses of Feldspathic Sand in Manufacturing
Feldspathic sand is primarily used in the manufacturing of glass and ceramics due to its high alumina and alkali content, which enhances the strength and durability of finished products. It serves as a vital fluxing agent in the production of tiles, porcelain, and various glass types, improving melting characteristics and thermal properties. This makes feldspathic sand essential for industries requiring materials with superior hardness and chemical resistance.
Cost Analysis: Quartz vs Feldspathic Sand
Quartz sand typically has a higher market price than feldspathic sand due to its superior purity and durability, making it preferred for high-quality glass and foundry applications. Feldspathic sand, with its lower silica content and higher feldspar minerals, offers a cost-effective alternative for construction and ceramic industries where high silica purity is not critical. Cost efficiency depends on application requirements, with quartz sand favored for premium projects and feldspathic sand chosen to reduce material expenses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Quartz sand extraction generally has a lower environmental impact than feldspathic sand due to its higher purity and reduced need for processing chemicals, which minimizes habitat disruption and chemical runoff. Feldspathic sand mining often involves more intensive beneficiation processes that increase energy consumption and generate more waste, posing greater sustainability challenges. Sustainable sourcing of quartz sand supports reduced carbon footprint and less ecological disturbance, aligning better with environmental conservation goals.
Selection Criteria for Specific Industries
Quartz sand is preferred in industries requiring high purity and chemical resistance, such as glass manufacturing and foundries, due to its high silica content and minimal impurities. Feldspathic sand is selected in ceramics and construction for its alumina and alkali content, which improve strength and thermal properties. Selection criteria include mineral composition, grain size, thermal stability, and impurity levels tailored to the specific industrial application.
Future Trends in Sand Material Utilization
Quartz sand, known for its high purity and durability, is increasingly favored in advanced glass manufacturing and semiconductor industries where contamination-free materials are crucial. Feldspathic sand, rich in alumina and potassium, is gaining attention for use in ceramic production and innovative construction materials due to its fluxing properties that enhance firing efficiency. Emerging trends indicate a shift towards sustainable extraction and processing techniques for both sands, driven by environmental regulations and growing demand in high-performance industrial applications.
Quartz sand vs Feldspathic sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com