Garnet sand is prized for its hardness and sharp edges, making it ideal for abrasive blasting and waterjet cutting, while chromite sand is valued primarily for its high specific gravity and resistance to heat, often used in foundry molds and refractory applications. Garnet sand's chemical stability and non-toxic nature contrast with chromite sand's metallic composition and magnetic properties, influencing their suitability for different industrial processes. Choosing between garnet and chromite sand depends on factors like abrasion resistance, heat tolerance, and the specific demands of the manufacturing or finishing task.
Table of Comparison
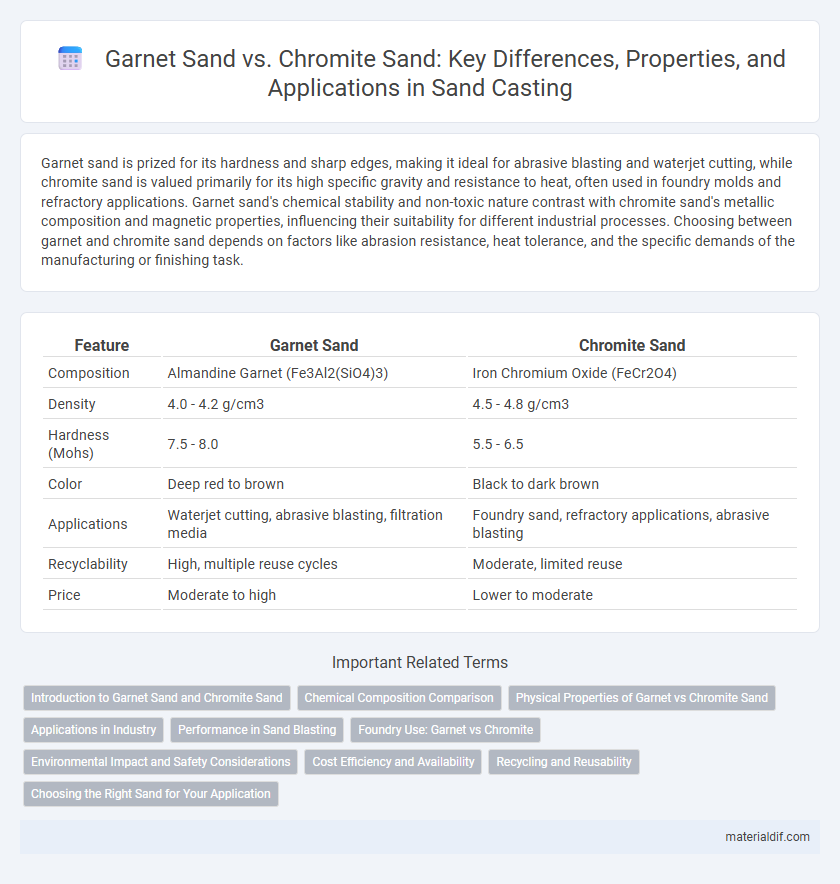
| Feature | Garnet Sand | Chromite Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Almandine Garnet (Fe3Al2(SiO4)3) | Iron Chromium Oxide (FeCr2O4) |
| Density | 4.0 - 4.2 g/cm3 | 4.5 - 4.8 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 7.5 - 8.0 | 5.5 - 6.5 |
| Color | Deep red to brown | Black to dark brown |
| Applications | Waterjet cutting, abrasive blasting, filtration media | Foundry sand, refractory applications, abrasive blasting |
| Recyclability | High, multiple reuse cycles | Moderate, limited reuse |
| Price | Moderate to high | Lower to moderate |
Introduction to Garnet Sand and Chromite Sand
Garnet sand, composed primarily of almandine and pyrope minerals, exhibits high hardness and chemical inertness, making it ideal for abrasive blasting and waterjet cutting applications. Chromite sand, rich in iron chromium oxide, offers excellent heat resistance and thermal conductivity, often utilized in foundry molds and refractory linings. Both sands are valued for their unique physical properties, with garnet providing superior abrasion resistance and chromite excelling in high-temperature environments.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Garnet sand primarily consists of iron aluminum silicate (Fe3Al2(SiO4)3), offering a high hardness and chemical resistance ideal for abrasive applications. Chromite sand contains iron chromium oxide (FeCr2O4), characterized by its high density and thermal stability, making it suitable for foundry molds and refractory uses. The significant difference in chemical composition influences their physical properties and industrial applications, with garnet providing superior abrasion resistance while chromite excels in heat resistance and density.
Physical Properties of Garnet vs Chromite Sand
Garnet sand exhibits a higher specific gravity, typically ranging from 4.0 to 4.3, compared to chromite sand's specific gravity of approximately 4.5 to 4.8, indicating chromite's greater density. Garnet particles are harder, ranking 6.5 to 7.5 on the Mohs scale, while chromite has a hardness of about 5.5 to 6.0, affecting abrasion resistance during industrial applications. The angularity of garnet sand grains is more pronounced, resulting in better cutting efficiency for waterjet and abrasive blasting, whereas chromite sand's rounded grains provide superior thermal conductivity for foundry molds.
Applications in Industry
Garnet sand is extensively used in abrasive blasting, waterjet cutting, and filtration due to its hardness and chemical stability, making it ideal for surface preparation and water purification industries. Chromite sand, valued for its high thermal stability and density, is predominantly employed in foundry applications for metal casting molds and cores, enhancing mold strength and surface finish. Both sands serve critical roles in industrial processes, with garnet sand favored for abrasive tasks and chromite sand essential in high-temperature metal casting.
Performance in Sand Blasting
Garnet sand offers superior hardness and angularity, enabling efficient removal of coatings and rust with minimal dust generation during sand blasting. Chromite sand provides excellent heat resistance and recyclability, maintaining consistent performance in high-temperature applications but produces more dust compared to garnet. The choice between garnet and chromite sand depends on project-specific requirements such as surface finish quality, abrasive longevity, and environmental considerations.
Foundry Use: Garnet vs Chromite
Garnet sand offers superior hardness and chemical inertness, making it ideal for foundry use where high-quality surface finishes and minimal contamination are critical. Chromite sand provides excellent thermal stability and refractoriness, which enhances mold strength and reduces metal penetration during casting processes. Foundry operators often choose garnet for precision castings, while chromite is preferred for ferrous metal castings requiring enhanced heat resistance.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Garnet sand, primarily composed of almandine and pyrope minerals, offers a lower environmental footprint due to its natural abundance and minimal chemical processing compared to chromite sand, which contains heavy metals like chromium that can pose toxicity risks. Chromite sand's environmental impact is heightened by potential leaching of hexavalent chromium compounds, requiring stringent handling and disposal protocols to mitigate groundwater contamination. Safety considerations prioritize garnet sand for abrasive blasting and filtration applications due to its non-toxic nature, whereas chromite sand necessitates specialized protective equipment and regulatory compliance to prevent occupational exposure to carcinogenic substances.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Garnet sand generally offers higher cost efficiency due to its abundant availability and lower extraction costs compared to chromite sand, which is rarer and more expensive to source. Chromite sand provides superior heat resistance and durability but commands a premium price, making it less economically viable for large-scale projects. Industries requiring cost-effective abrasives often prefer garnet sand for its balanced performance and widespread accessibility.
Recycling and Reusability
Garnet sand exhibits superior recycling and reusability compared to chromite sand due to its hardness and resistance to abrasion, which allows multiple reuse cycles in abrasive blasting and waterjet cutting. Chromite sand, while dense and effective for high-temperature applications, tends to degrade faster under repetitive use, limiting its recycling potential. Efficient recycling of garnet sand reduces operational costs and environmental impact, making it a preferred choice in sustainable industrial processes.
Choosing the Right Sand for Your Application
Garnet sand offers high hardness and chemical inertness, making it ideal for abrasive blasting and waterjet cutting where precision and surface finish are critical. Chromite sand provides excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for foundry molding and casting applications. Selecting between garnet and chromite sand depends on factors like application type, temperature tolerance, and desired surface texture.
Garnet Sand vs Chromite Sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com