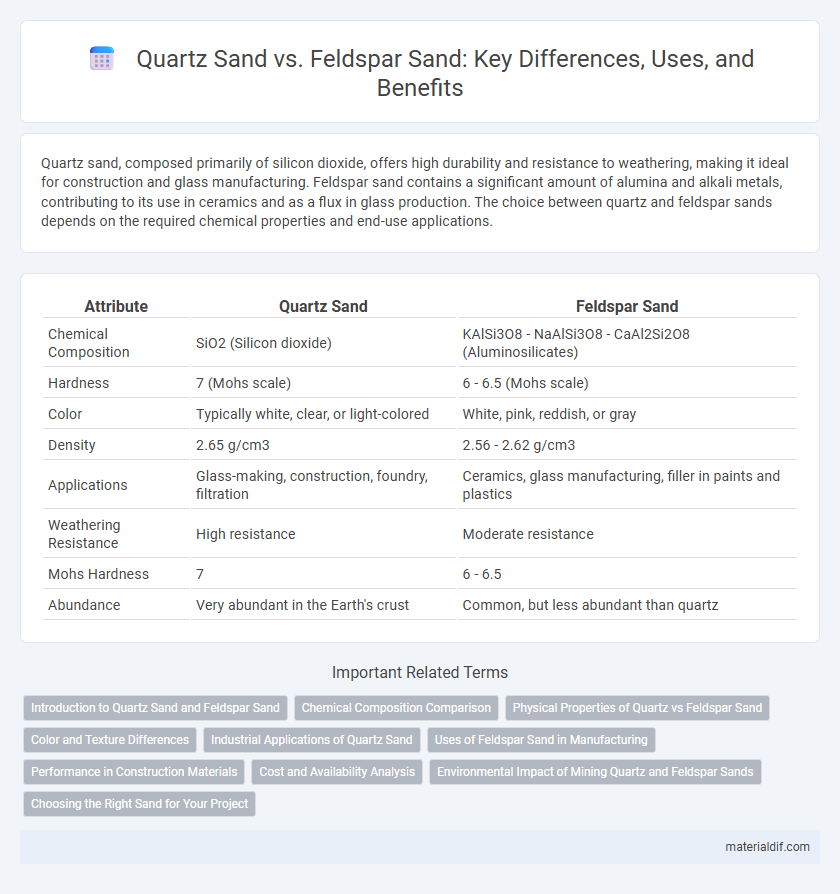
Quartz sand, composed primarily of silicon dioxide, offers high durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for construction and glass manufacturing. Feldspar sand contains a significant amount of alumina and alkali metals, contributing to its use in ceramics and as a flux in glass production. The choice between quartz and feldspar sands depends on the required chemical properties and end-use applications.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Quartz Sand | Feldspar Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | SiO2 (Silicon dioxide) | KAlSi3O8 - NaAlSi3O8 - CaAl2Si2O8 (Aluminosilicates) |
| Hardness | 7 (Mohs scale) | 6 - 6.5 (Mohs scale) |
| Color | Typically white, clear, or light-colored | White, pink, reddish, or gray |
| Density | 2.65 g/cm3 | 2.56 - 2.62 g/cm3 |
| Applications | Glass-making, construction, foundry, filtration | Ceramics, glass manufacturing, filler in paints and plastics |
| Weathering Resistance | High resistance | Moderate resistance |
| Mohs Hardness | 7 | 6 - 6.5 |
| Abundance | Very abundant in the Earth's crust | Common, but less abundant than quartz |
Introduction to Quartz Sand and Feldspar Sand
Quartz sand consists primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2) and is renowned for its hardness, chemical inertness, and high melting point, making it essential in glass manufacturing, foundry molds, and construction. Feldspar sand, composed of aluminosilicate minerals, contains potassium, sodium, and calcium, offering fluxing properties that reduce melting temperatures in ceramics and glass production. The differing mineral compositions of quartz and feldspar sands influence their industrial applications and performance characteristics in manufacturing processes.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Quartz sand primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2), offering high purity and chemical inertness that makes it ideal for glassmaking and foundry applications. Feldspar sand contains a significant proportion of alumina (Al2O3) and alkali metals like potassium (K) and sodium (Na), which contribute to its fluxing properties in ceramics and glass industries. The chemical composition difference between quartz and feldspar sands directly influences their thermal and mechanical behavior in industrial processing.
Physical Properties of Quartz vs Feldspar Sand
Quartz sand exhibits higher hardness and greater chemical stability compared to feldspar sand, making it more resistant to weathering and abrasion. Quartz grains tend to be more angular and have a higher specific gravity, while feldspar sand particles often display a more blocky shape with lower density. The lower cleavage in quartz contributes to its durability, whereas feldspar's perfect cleavage planes render it more prone to fragmentation under mechanical stress.
Color and Texture Differences
Quartz sand typically appears in a wide range of colors, from clear and white to light pink or gray, characterized by its smooth, glassy texture due to high silica content. Feldspar sand often exhibits a more varied color palette, including shades of pink, orange, red, and white, with a slightly rougher, grainier texture caused by its aluminum and potassium content. The distinct color and texture differences between quartz and feldspar sands impact their suitability for various industrial and decorative applications.
Industrial Applications of Quartz Sand
Quartz sand is highly valued in industrial applications due to its high silica content, hardness, and chemical purity, making it essential for glass manufacturing, foundry molds, and hydraulic fracturing. Its consistent grain size and resistance to weathering enhance the quality and durability of products in construction and ceramics industries. In contrast, feldspar sand, with a lower silica percentage and higher alkali content, is primarily used as a flux in ceramics and glass production rather than as a primary raw material.
Uses of Feldspar Sand in Manufacturing
Feldspar sand is extensively used in the manufacturing of glass, ceramics, and enamel due to its high alumina and alkali content, which improve the strength and durability of finished products. It serves as a fluxing agent in glassmaking, lowering melting temperatures and enhancing product quality, while in ceramics, feldspar sand aids in vitrification and hardness. Compared to quartz sand, feldspar's unique chemical properties make it essential for producing specialized industrial materials requiring thermal and chemical resistance.
Performance in Construction Materials
Quartz sand exhibits superior durability and hardness compared to feldspar sand, making it ideal for high-strength concrete and abrasive-resistant construction materials. Feldspar sand, with its higher alumina and alkali content, enhances the workability and low shrinkage characteristics of cement mixtures but offers less abrasion resistance. The choice between quartz and feldspar sand critically influences the structural integrity and longevity of construction projects, with quartz favored for wear-resistance and feldspar for improved composite bonding.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Quartz sand is typically more abundant and cost-effective compared to feldspar sand, making it a preferred choice in large-scale industrial applications. Feldspar sand, though less readily available, often commands a higher price due to its specialized use in ceramics and glass manufacturing. Market trends indicate that quartz sand offers more competitive pricing and wider geographic availability, while feldspar sand's scarcity can drive up logistical and procurement costs.
Environmental Impact of Mining Quartz and Feldspar Sands
Mining quartz sand often results in significant landscape disruption and increased silica dust emissions, posing health risks to workers and local communities. Feldspar sand extraction typically involves less intensive processing but can lead to soil erosion and habitat loss, impacting biodiversity. Sustainable mining practices and reclamation efforts are crucial to minimize the environmental footprint of both quartz and feldspar sand industries.
Choosing the Right Sand for Your Project
Quartz sand offers superior durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring high stability and strength, such as glass manufacturing and water filtration. Feldspar sand contains higher levels of aluminum and potassium, which enhance its use in ceramics and as a flux in industrial processes. Selecting between quartz and feldspar sand depends on project requirements for hardness, chemical reactivity, and thermal properties.
Quartz sand vs Feldspar sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com