Industrial sand, characterized by its high silica content and uniform grain size, is primarily used in manufacturing processes such as glassmaking, foundry molds, and hydraulic fracturing. Building sand, on the other hand, contains a mix of finer particles and impurities, making it ideal for construction purposes like mortar, plaster, and concrete production. The distinct properties of these sands determine their specific applications, ensuring performance efficiency and structural integrity in their respective industries.
Table of Comparison
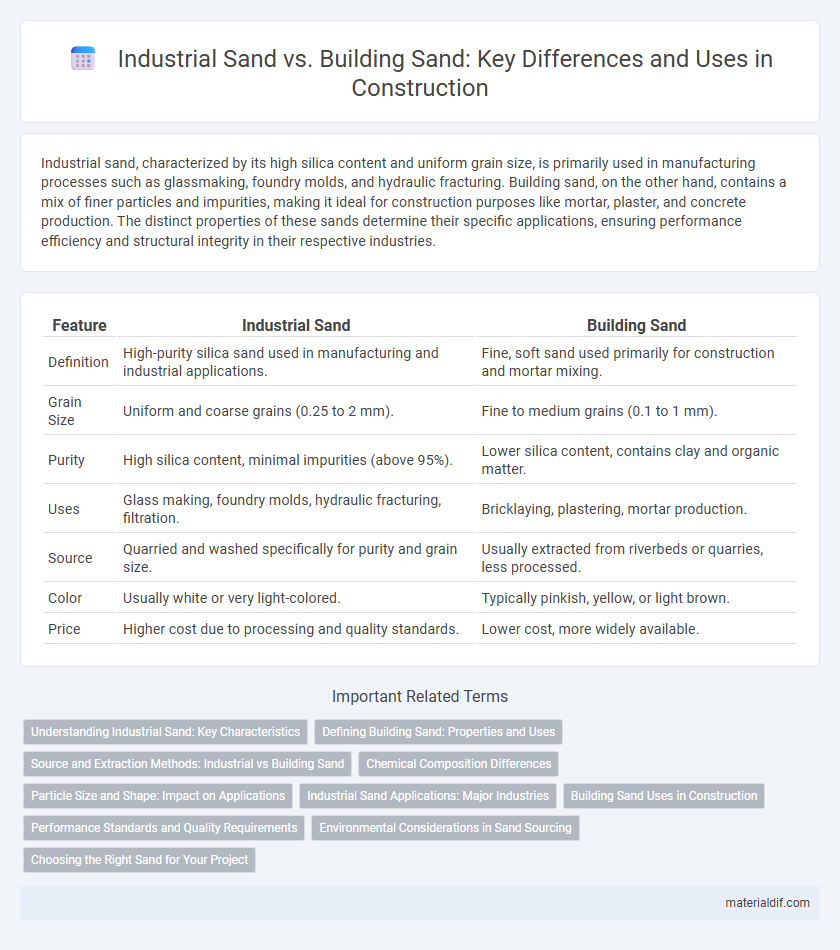
| Feature | Industrial Sand | Building Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High-purity silica sand used in manufacturing and industrial applications. | Fine, soft sand used primarily for construction and mortar mixing. |
| Grain Size | Uniform and coarse grains (0.25 to 2 mm). | Fine to medium grains (0.1 to 1 mm). |
| Purity | High silica content, minimal impurities (above 95%). | Lower silica content, contains clay and organic matter. |
| Uses | Glass making, foundry molds, hydraulic fracturing, filtration. | Bricklaying, plastering, mortar production. |
| Source | Quarried and washed specifically for purity and grain size. | Usually extracted from riverbeds or quarries, less processed. |
| Color | Usually white or very light-colored. | Typically pinkish, yellow, or light brown. |
| Price | Higher cost due to processing and quality standards. | Lower cost, more widely available. |
Understanding Industrial Sand: Key Characteristics
Industrial sand, also known as silica sand, is characterized by its high purity, uniform particle size, and angular grain shape, making it essential for specialized applications such as glass manufacturing, foundry molds, and hydraulic fracturing. Unlike building sand, which contains a mix of finer particles and impurities suited for construction and masonry work, industrial sand undergoes rigorous processing to meet strict chemical and physical specifications. The high silica content, consistent grain size distribution, and low levels of contaminants are critical attributes that define industrial sand's performance and value in industrial sectors.
Defining Building Sand: Properties and Uses
Building sand is a fine, smooth sand typically composed of quartz and feldspar, distinguished by its softness and rounded particles that enhance workability and cohesion in mortar mixes. Its properties include excellent water retention, moderate plasticity, and minimal impurities, making it ideal for masonry, plastering, and rendering applications. Commonly sourced from riverbeds or pits, building sand facilitates strong, durable bonds in bricklaying and construction projects where surface finish and structural integrity are crucial.
Source and Extraction Methods: Industrial vs Building Sand
Industrial sand is primarily sourced from high-purity quartz deposits extracted through open-pit mining techniques to ensure consistent grain size and chemical composition necessary for manufacturing applications. Building sand, commonly derived from naturally occurring riverbeds and glacial deposits, is typically obtained via dredging or excavation methods that preserve its mixed grain sizes and mineral diversity suitable for construction tasks. The extraction of industrial sand involves rigorous processing to remove impurities, whereas building sand undergoes minimal refinement to retain its natural properties.
Chemical Composition Differences
Industrial sand is primarily composed of high-purity silica (SiO2) with minimal impurities such as iron oxides, alumina, and other minerals, making it suitable for applications requiring chemical inertness and specific grain sizes. Building sand contains a more varied chemical composition including higher levels of clay, silt, and organic matter, which affect its workability and bonding properties in construction materials. The distinct chemical compositions impact their respective uses, with industrial sand favored in glassmaking and foundry molds, while building sand is preferred for concrete and mortar mixtures.
Particle Size and Shape: Impact on Applications
Industrial sand typically features uniform particle size and angular shape, optimizing it for applications in manufacturing, such as glassmaking and foundry molds, where consistent grain structure enhances product quality. Building sand exhibits more variable particle sizes and rounded shapes, improving workability and cohesion in mortar and concrete mixes for construction purposes. The distinct particle characteristics directly influence the sand's suitability, affecting factors like strength, texture, and material bonding in their respective industries.
Industrial Sand Applications: Major Industries
Industrial sand, also known as silica sand, is crucial in industries such as glass manufacturing, foundries, and hydraulic fracturing. High-purity quartz grains provide the strength and chemical stability required for glass production, casting molds, and proppants in oil and gas extraction. The demand for industrial sand is driven by its specific grain size, shape, and mineral composition that optimize performance in these specialized applications.
Building Sand Uses in Construction
Building sand, often referred to as masonry or bricklayer's sand, is primarily used in construction for creating mortar and plaster due to its fine, smooth texture that enhances workability and adhesion. It is essential in bricklaying, block laying, and rendering, providing a strong bond between materials while maintaining workability and aesthetic finish. Unlike industrial sand, which is coarser and used in applications like glass manufacturing and foundry work, building sand is refined to ensure consistency and durability in structural and decorative elements.
Performance Standards and Quality Requirements
Industrial sand must meet strict performance standards for high silica content, uniform grain size, and minimal impurities to ensure optimal strength and durability in manufacturing processes. Building sand requires lower specifications, focusing on particle shape and size for workability and bonding in construction masonry. Quality requirements for industrial sand include certification for chemical purity and abrasion resistance, whereas building sand emphasizes grading consistency and contamination absence.
Environmental Considerations in Sand Sourcing
Industrial sand extraction often involves large-scale mining operations that can disrupt local ecosystems and groundwater levels, necessitating careful environmental impact assessments and sustainable management practices. Building sand, typically sourced from riverbeds or quarries, requires consideration of sediment runoff and habitat preservation to minimize soil erosion and protect aquatic biodiversity. Both types of sand demand adherence to regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing environmental degradation and promoting responsible resource use.
Choosing the Right Sand for Your Project
Industrial sand offers high purity and uniform grain size, making it ideal for manufacturing processes such as glassmaking and foundry work. Building sand, characterized by its coarser texture and greater variability, provides excellent strength and binding properties necessary for construction and mortar applications. Selecting the right sand depends on the project requirements, where industrial sand ensures precision and performance, while building sand supports structural integrity.
Industrial Sand vs Building Sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com