Thermoplastic rubber offers greater flexibility and can be melted and reshaped multiple times, making it ideal for manufacturing processes that require recyclability and design versatility. Thermoset rubber, once cured, forms a rigid, cross-linked structure that provides superior heat resistance and durability but cannot be remolded or recycled. Choosing between thermoplastic and thermoset rubber depends on application needs, balancing ease of processing against performance under stress and temperature.
Table of Comparison
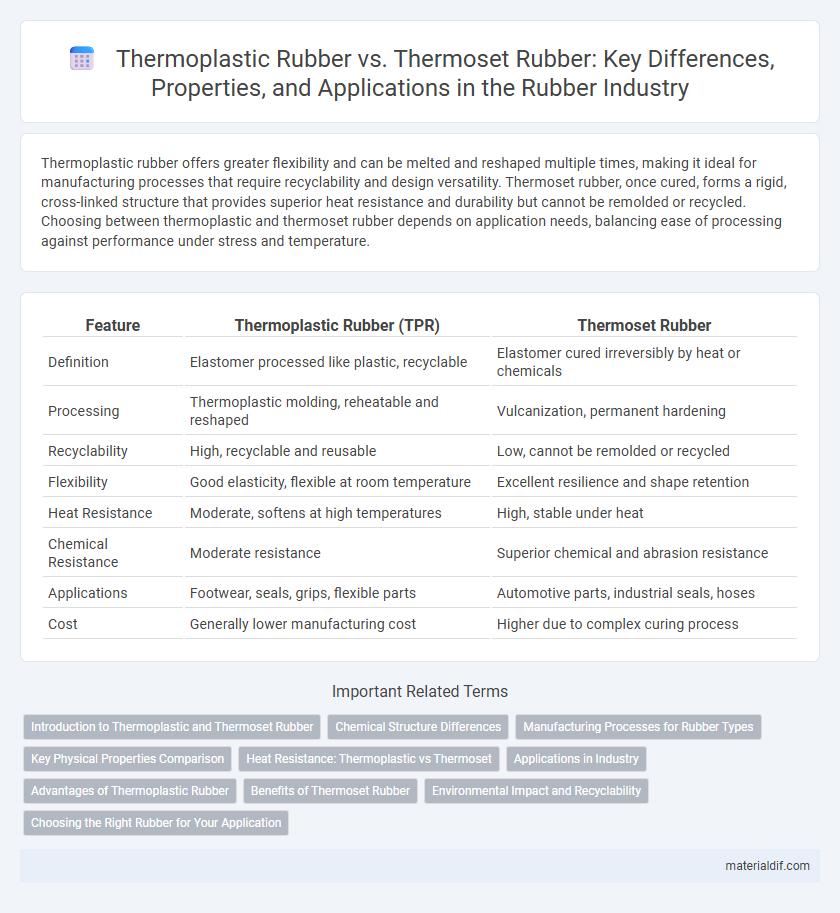
| Feature | Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) | Thermoset Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Elastomer processed like plastic, recyclable | Elastomer cured irreversibly by heat or chemicals |
| Processing | Thermoplastic molding, reheatable and reshaped | Vulcanization, permanent hardening |
| Recyclability | High, recyclable and reusable | Low, cannot be remolded or recycled |
| Flexibility | Good elasticity, flexible at room temperature | Excellent resilience and shape retention |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, softens at high temperatures | High, stable under heat |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance | Superior chemical and abrasion resistance |
| Applications | Footwear, seals, grips, flexible parts | Automotive parts, industrial seals, hoses |
| Cost | Generally lower manufacturing cost | Higher due to complex curing process |
Introduction to Thermoplastic and Thermoset Rubber
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) is a class of elastomers that combines the properties of rubber with the ease of thermoplastics, allowing it to be melted and reshaped multiple times without significant chemical change. Thermoset rubber, in contrast, undergoes a curing process that creates irreversible chemical bonds, resulting in a rigid structure that cannot be remelted or reshaped. The distinct molecular architecture of thermoplastic versus thermoset rubber defines their processing methods, mechanical properties, and applications across industries such as automotive, footwear, and consumer goods.
Chemical Structure Differences
Thermoplastic rubber consists of linear or branched polymer chains that can be melted and reshaped multiple times due to the absence of permanent cross-links. Thermoset rubber, conversely, features a highly cross-linked three-dimensional network formed through vulcanization, providing enhanced heat resistance and structural stability. The chemical structure difference fundamentally affects their thermal properties and recyclability, with thermoplastics being more flexible and recyclable, while thermosets offer superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance.
Manufacturing Processes for Rubber Types
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) manufacturing involves extrusion and injection molding processes that allow easy reheating and reshaping due to its repetitive softening properties. Thermoset rubber production utilizes vulcanization, where irreversible chemical cross-linking occurs under heat and pressure, resulting in a rigid, durable material. These distinct manufacturing techniques directly influence the mechanical performance and application range of each rubber type.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Thermoplastic rubber exhibits excellent flexibility, high elasticity, and superior processability, allowing it to be reshaped multiple times without degradation. Thermoset rubber, in contrast, offers superior heat resistance, higher mechanical strength, and better chemical stability due to its crosslinked polymer structure. Key physical properties such as tensile strength, elongation at break, and hardness typically favor thermoset rubber, while thermoplastic rubber excels in impact resistance and recyclability.
Heat Resistance: Thermoplastic vs Thermoset
Thermoset rubber exhibits superior heat resistance compared to thermoplastic rubber, maintaining structural integrity and mechanical properties at temperatures often exceeding 200degC. Thermoplastic rubber softens and deforms at elevated temperatures due to its reversible physical cross-links, limiting its use in high-heat applications. The irreversible chemical cross-linking in thermoset rubber provides enhanced thermal stability, making it ideal for automotive engines, electrical insulation, and industrial seals exposed to continuous heat.
Applications in Industry
Thermoplastic rubber finds extensive application in automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer goods due to its flexibility, recyclability, and ease of processing. Thermoset rubber is preferred in heavy-duty industrial seals, gaskets, and electrical insulation because of its superior heat resistance, durability, and chemical stability. Industries such as aerospace and electronics rely on thermoset rubber for components requiring long-term performance under extreme conditions.
Advantages of Thermoplastic Rubber
Thermoplastic rubber offers superior flexibility and easier processability compared to thermoset rubber, enabling efficient manufacturing with shorter cycle times. Its ability to be reshaped and recycled reduces material waste and promotes eco-friendly production. Enhanced resistance to wear, heat, and chemicals further extends the lifespan of products made with thermoplastic rubber, making it a cost-effective choice in automotive, medical, and consumer goods industries.
Benefits of Thermoset Rubber
Thermoset rubber offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength compared to thermoplastic rubber, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as automotive parts and industrial seals. Its cross-linked molecular structure provides excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability under extreme conditions. These benefits result in enhanced durability and longer service life, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Thermoplastic rubber offers superior environmental benefits due to its full recyclability and energy-efficient processing, reducing landfill waste and resource consumption. In contrast, thermoset rubber's cross-linked molecular structure prevents re-melting, resulting in limited recyclability and higher environmental impact through increased waste and energy use. Choosing thermoplastic rubber supports circular economy principles by enabling repeated recycling without significant degradation.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Application
Thermoplastic rubber offers flexibility and recyclability, making it ideal for applications requiring repeated molding and reshaping, such as automotive parts and consumer goods. Thermoset rubber provides superior chemical resistance and durability through cross-linked molecular bonds, suited for heavy-duty uses like seals and gaskets in harsh environments. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing mechanical properties, environmental exposure, and lifecycle requirements specific to the intended application.
Thermoplastic Rubber vs Thermoset Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com