Rubber extrusion involves forcing rubber material through a shaped die to create continuous profiles, ideal for producing consistent, flexible parts like seals and tubing. Rubber molding, on the other hand, presses or injects rubber into a mold cavity, enabling complex shapes and intricate details with superior dimensional accuracy. Choosing between rubber extrusion and rubber molding depends on the desired product design, production volume, and application requirements.
Table of Comparison
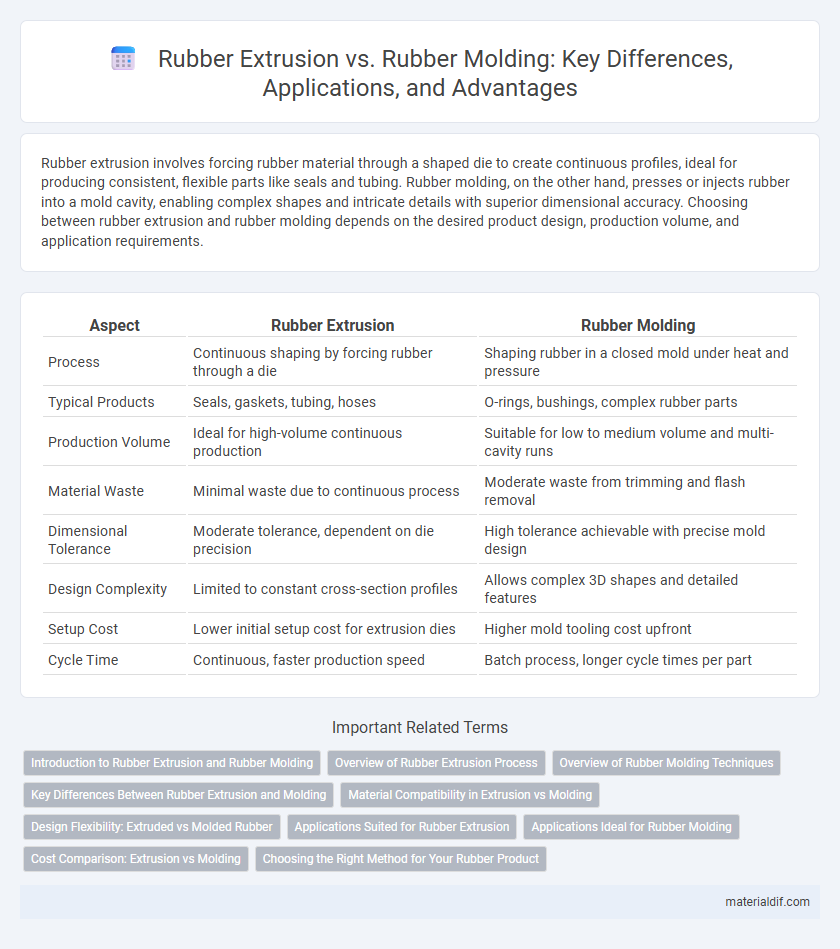
| Aspect | Rubber Extrusion | Rubber Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Continuous shaping by forcing rubber through a die | Shaping rubber in a closed mold under heat and pressure |
| Typical Products | Seals, gaskets, tubing, hoses | O-rings, bushings, complex rubber parts |
| Production Volume | Ideal for high-volume continuous production | Suitable for low to medium volume and multi-cavity runs |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste due to continuous process | Moderate waste from trimming and flash removal |
| Dimensional Tolerance | Moderate tolerance, dependent on die precision | High tolerance achievable with precise mold design |
| Design Complexity | Limited to constant cross-section profiles | Allows complex 3D shapes and detailed features |
| Setup Cost | Lower initial setup cost for extrusion dies | Higher mold tooling cost upfront |
| Cycle Time | Continuous, faster production speed | Batch process, longer cycle times per part |
Introduction to Rubber Extrusion and Rubber Molding
Rubber extrusion involves forcing uncured rubber through a shaped die to create continuous profiles like tubing, seals, or gaskets, offering consistent cross-sections and efficient production for long runs. Rubber molding, including compression, transfer, and injection molding, shapes rubber within closed molds under heat and pressure to produce complex, three-dimensional parts with precise tolerances and material properties. Both processes are essential in rubber manufacturing, with extrusion favored for uniform profiles and molding preferred for intricate designs.
Overview of Rubber Extrusion Process
Rubber extrusion is a manufacturing process where raw rubber material is forced through a shaped die to create continuous profiles such as tubes, seals, or gaskets. This method allows for consistent cross-sectional shapes with high precision and is ideal for producing long lengths of rubber components. The extrusion process is efficient for scaling production while maintaining uniformity in dimensions and physical properties.
Overview of Rubber Molding Techniques
Rubber molding techniques include compression molding, transfer molding, and injection molding, each offering distinct advantages in shaping rubber components with precision and efficiency. Compression molding involves placing raw rubber into a heated mold cavity, ideal for simpler shapes and lower production volumes. Injection molding forces heated rubber into molds under pressure, enabling high-volume production of complex parts with tight tolerances, while transfer molding provides a balance by allowing more intricate designs without the high costs of injection molding.
Key Differences Between Rubber Extrusion and Molding
Rubber extrusion involves forcing heated rubber through a shaped die to create continuous profiles like seals and tubes, optimizing production speed and uniformity. Rubber molding, including compression, transfer, and injection methods, shapes rubber into complex, three-dimensional parts such as gaskets and automotive components, offering higher precision but longer cycle times. Key differences lie in the complexity of shapes achievable, production volume efficiency, and the mechanical properties influenced by the curing process.
Material Compatibility in Extrusion vs Molding
Rubber extrusion excels in processing thermoplastic elastomers and specific silicone rubbers due to continuous shaping capabilities, while rubber molding techniques like compression and injection molding accommodate a broader range of elastomers including natural rubber, EPDM, and neoprene. Material compatibility in extrusion is limited by rheological properties requiring uniform viscosity for smooth flow, whereas molding allows for greater versatility in compound formulations and complex geometries. Selecting between extrusion and molding hinges on the elastomer type, with molding favored for intricate shapes and diverse rubber formulations, and extrusion preferred for long, consistent profiles.
Design Flexibility: Extruded vs Molded Rubber
Rubber extrusion offers greater design flexibility for creating continuous profiles with uniform cross-sections, ideal for seals, tubing, and gaskets requiring consistent shapes along their length. Molded rubber provides superior complexity, enabling intricate geometries, undercuts, and detailed features that extrusion cannot achieve, making it suitable for custom parts with precise dimensional requirements. Selecting between extruded and molded rubber depends on the part's design complexity, production volume, and the specific mechanical properties needed.
Applications Suited for Rubber Extrusion
Rubber extrusion is ideal for continuous profiles such as seals, gaskets, tubing, and weatherstripping, where uniform cross-sections are essential. This process excels in producing flexible, long-length products with consistent shape and tight dimensional tolerances. Applications in automotive weather seals, construction caulking, and electrical wire insulation benefit significantly from the cost-efficiency and scalability of rubber extrusion.
Applications Ideal for Rubber Molding
Rubber molding is ideal for producing complex, high-precision parts used in automotive seals, medical devices, and aerospace components due to its ability to create intricate shapes with consistent quality. It excels in applications requiring superior mechanical properties, such as high thermal resistance and durability, making it suitable for industrial gaskets and vibration dampening components. Unlike rubber extrusion, molding allows for efficient mass production of detailed parts with tight tolerances essential for sealing and insulating applications.
Cost Comparison: Extrusion vs Molding
Rubber extrusion typically offers lower initial tooling costs and faster production times, making it cost-effective for continuous shapes and high-volume runs. In contrast, rubber molding requires higher upfront investment due to complex molds but provides more precision and versatility for intricate designs, which can reduce material waste and post-processing expenses. For large production volumes with simpler geometries, extrusion is generally more economical, whereas molding becomes cost-efficient for customized parts and lower quantities despite higher initial costs.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Rubber Product
Rubber extrusion excels in creating continuous profiles with consistent cross-sections, ideal for seals, gaskets, and tubing requiring uniformity and long lengths. Rubber molding, including compression, transfer, and injection methods, provides versatility for complex shapes, tight tolerances, and high-volume production with excellent surface finish. Selecting the right method depends on product design complexity, volume requirements, and dimensional precision necessary for your specific rubber application.
Rubber Extrusion vs Rubber Molding Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com