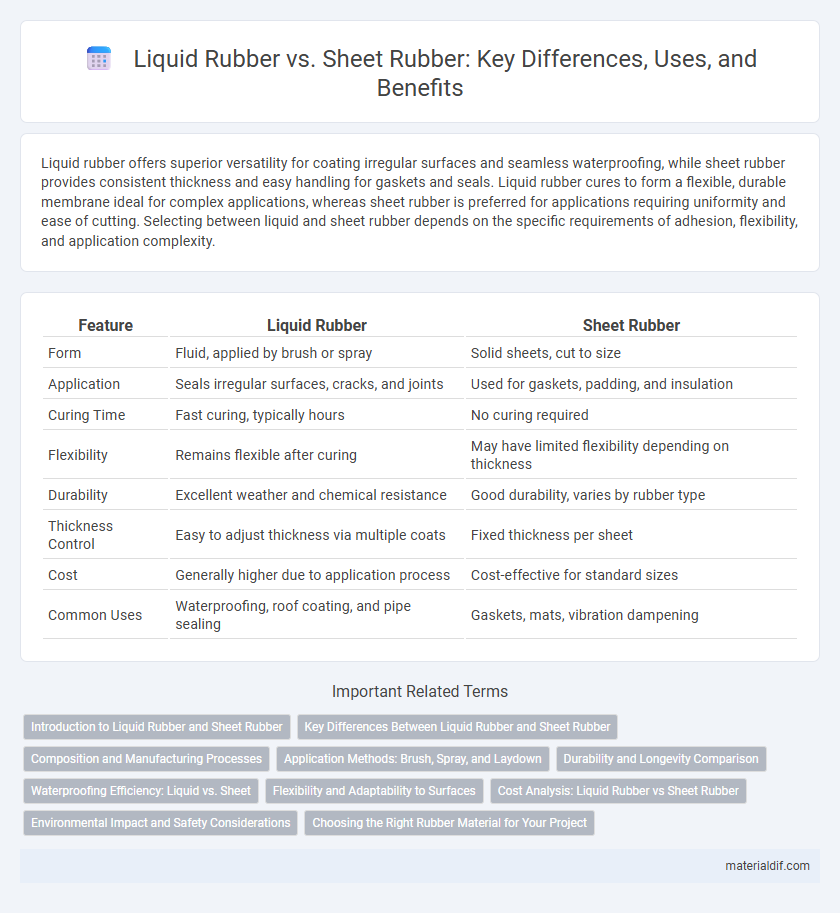
Liquid rubber offers superior versatility for coating irregular surfaces and seamless waterproofing, while sheet rubber provides consistent thickness and easy handling for gaskets and seals. Liquid rubber cures to form a flexible, durable membrane ideal for complex applications, whereas sheet rubber is preferred for applications requiring uniformity and ease of cutting. Selecting between liquid and sheet rubber depends on the specific requirements of adhesion, flexibility, and application complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Liquid Rubber | Sheet Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Fluid, applied by brush or spray | Solid sheets, cut to size |
| Application | Seals irregular surfaces, cracks, and joints | Used for gaskets, padding, and insulation |
| Curing Time | Fast curing, typically hours | No curing required |
| Flexibility | Remains flexible after curing | May have limited flexibility depending on thickness |
| Durability | Excellent weather and chemical resistance | Good durability, varies by rubber type |
| Thickness Control | Easy to adjust thickness via multiple coats | Fixed thickness per sheet |
| Cost | Generally higher due to application process | Cost-effective for standard sizes |
| Common Uses | Waterproofing, roof coating, and pipe sealing | Gaskets, mats, vibration dampening |
Introduction to Liquid Rubber and Sheet Rubber
Liquid rubber is a versatile coating material known for its seamless application and flexibility, making it ideal for waterproofing, sealing, and protective coatings on irregular surfaces. Sheet rubber, available in various thicknesses and formulations such as natural rubber and synthetic variants like EPDM, provides durable and resilient sealing and cushioning solutions in industrial and construction applications. Both forms offer unique advantages, with liquid rubber excelling in conforming to complex shapes and sheet rubber providing consistent thickness and mechanical strength.
Key Differences Between Liquid Rubber and Sheet Rubber
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and seamless application, making it ideal for coating irregular surfaces and waterproofing, while sheet rubber provides consistent thickness and easy handling for insulation and gasket purposes. Liquid rubber cures to form a durable, airtight membrane that adapts to complex shapes, whereas sheet rubber comes in predefined sizes and thicknesses, suited for structural and mechanical uses. The choice depends on project requirements like surface conformity, durability, and installation method efficiency.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Liquid rubber consists of polymers dissolved or dispersed in a liquid carrier, typically synthesized through emulsion or solution polymerization, allowing easy application via spraying or dipping. Sheet rubber is formed by vulcanizing solid rubber compounds into thin, uniform sheets using compression or calendaring techniques, resulting in dense, durable materials. The composition of liquid rubber often includes additives to enhance flexibility and adhesion, while sheet rubber incorporates fillers and curing agents to improve mechanical strength and resilience.
Application Methods: Brush, Spray, and Laydown
Liquid rubber offers versatile application methods including brushing, spraying, and laying down, enabling seamless coverage on irregular surfaces and intricate details. Sheet rubber, typically installed by laying down pre-formed sheets, provides uniform thickness but requires adhesive bonding and precise handling to avoid wrinkles or bubbles. Brush and spray applications of liquid rubber promote rapid curing and adaptability for waterproofing, while sheet rubber excels in heavy-duty or large-scale flooring solutions.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and seamless application, making it ideal for coating irregular surfaces while providing excellent waterproofing and UV resistance. Sheet rubber, typically made from materials like EPDM or neoprene, delivers robust tear resistance and consistent thickness, ensuring prolonged durability in high-stress environments. Both types exhibit notable longevity, but liquid rubber's ability to form a continuous membrane often results in enhanced protection against environmental wear and degradation over time.
Waterproofing Efficiency: Liquid vs. Sheet
Liquid rubber offers superior waterproofing efficiency by creating a seamless, flexible coating that adapts to irregular surfaces and expands with temperature changes. Sheet rubber provides consistent thickness and durability but may suffer from seams and joints that could allow water infiltration over time. Choosing liquid rubber ensures a more reliable waterproof barrier, especially for complex or contoured applications.
Flexibility and Adaptability to Surfaces
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility due to its ability to conform seamlessly to complex and irregular surfaces, creating a continuous, elastic membrane that resists cracking and peeling. Sheet rubber, while durable and easy to handle, often requires precise cutting and fitting, which can limit adaptability on uneven or curved surfaces. The liquid form's remarkable elasticity enhances adhesion and ensures long-lasting protection across diverse applications, outperforming sheet rubber in scenarios demanding high flexibility and surface conformity.
Cost Analysis: Liquid Rubber vs Sheet Rubber
Liquid rubber offers a cost-effective solution for large or irregular surfaces due to its ease of application and minimal labor requirements, reducing overall project expenses. Sheet rubber, while typically higher in upfront material costs, provides durability and consistent thickness that can lower long-term replacement and maintenance costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, liquid rubber excels in flexible, quick applications, whereas sheet rubber is advantageous for projects demanding uniform performance and extended lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Liquid rubber offers a lower environmental impact due to its minimal waste generation and ease of application, reducing the need for solvents and adhesives that can release harmful VOCs. Sheet rubber, while durable, often involves energy-intensive manufacturing processes and generates more offcuts leading to higher material waste. From a safety perspective, liquid rubber poses fewer handling risks because it is applied as a non-toxic, low-odor liquid, whereas sheet rubber can release dust or fumes during cutting or installation, requiring protective measures.
Choosing the Right Rubber Material for Your Project
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and seamless coverage, making it ideal for projects requiring fast application and waterproofing, such as roof coatings or protective seals. Sheet rubber provides consistent thickness and durability, suitable for gaskets, vibration dampening, and wear-resistant applications where precise dimensions are critical. Selecting the right rubber material depends on factors like project complexity, environmental exposure, and mechanical stress tolerance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Liquid Rubber vs Sheet Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com