Chloroprene rubber offers superior weather resistance and chemical stability compared to SBR rubber, making it ideal for applications exposed to harsh environments. SBR rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in tires and general-purpose rubber goods. Choosing between chloroprene and SBR depends on the specific performance requirements, such as durability versus flexibility.
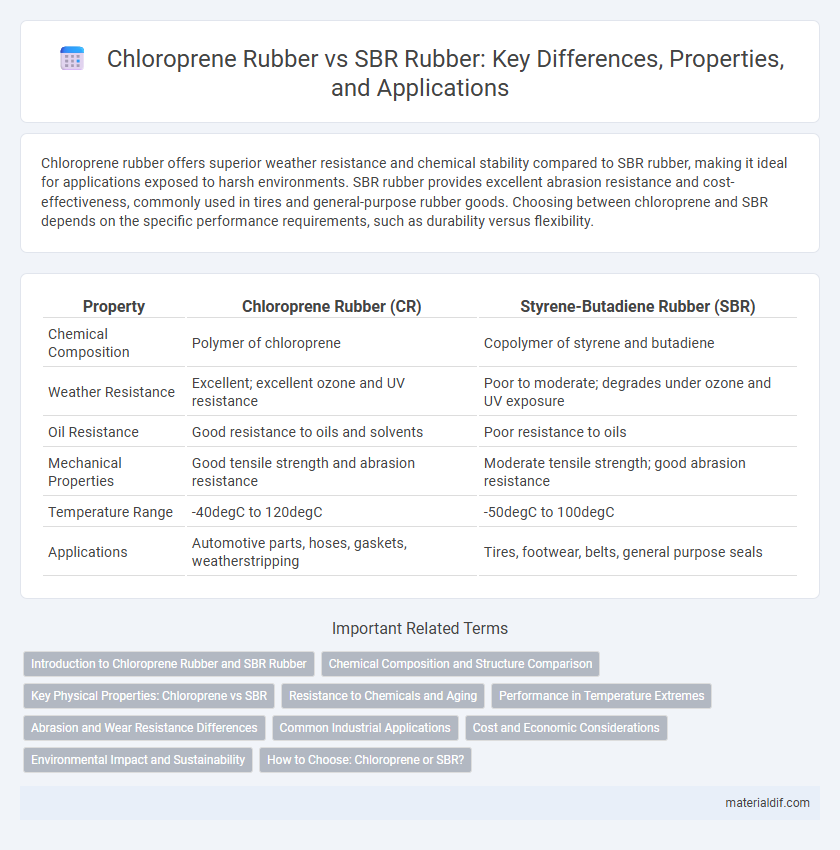
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Polymer of chloroprene | Copolymer of styrene and butadiene |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent; excellent ozone and UV resistance | Poor to moderate; degrades under ozone and UV exposure |
| Oil Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Poor resistance to oils |
| Mechanical Properties | Good tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength; good abrasion resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 100degC |
| Applications | Automotive parts, hoses, gaskets, weatherstripping | Tires, footwear, belts, general purpose seals |
Introduction to Chloroprene Rubber and SBR Rubber
Chloroprene rubber (CR) is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent chemical stability, oil resistance, and durability in harsh environments, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers good abrasion resistance and aging stability, commonly used in tire manufacturing and footwear due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility. Both CR and SBR exhibit unique properties tailored to specific performance requirements in the rubber industry.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Chloroprene rubber (CR) is a synthetic rubber composed primarily of chloroprene monomers (2-chloro-1,3-butadiene) which provide its characteristic chlorine atoms that enhance resistance to oil, weather, and flame. In contrast, styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a copolymer made from styrene and butadiene monomers, featuring a structure that balances flexibility with abrasion resistance but lacks chlorine atoms, making it less resistant to chemical attack. The presence of chlorine in CR's molecular structure confers superior chemical stability and durability in harsh environments compared to the hydrocarbon-based SBR polymer.
Key Physical Properties: Chloroprene vs SBR
Chloroprene rubber exhibits superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance compared to SBR rubber, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions. SBR rubber offers better abrasion resistance and tensile strength but has lower resilience to oil and heat. Both types differ distinctly in elasticity and durability, influencing their suitability for specific industrial applications.
Resistance to Chemicals and Aging
Chloroprene rubber exhibits superior resistance to oils, ozone, and weather aging compared to SBR rubber, making it ideal for applications in harsh chemical environments and outdoor use. SBR rubber offers moderate chemical resistance but degrades faster when exposed to ozone and UV radiation, limiting its lifespan in aging conditions. The enhanced molecular structure of chloroprene rubber provides better stability and durability against chemical exposure and environmental factors than SBR.
Performance in Temperature Extremes
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior performance in temperature extremes, maintaining flexibility and resilience from -40degC to 120degC, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications exposed to harsh environments. Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) typically performs well between -50degC and 70degC but deteriorates faster under prolonged heat exposure, limiting its use in high-temperature conditions. The enhanced thermal stability and ozone resistance of chloroprene rubber provide significant advantages over SBR in demanding temperature cycles.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance Differences
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior abrasion and wear resistance compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for applications requiring durability under frictional stress. CR's molecular structure provides enhanced resilience against mechanical wear, while SBR offers moderate resistance but tends to degrade faster in high-abrasion environments. This makes CR the preferred choice for industrial belts, gaskets, and automotive parts exposed to harsh conditions.
Common Industrial Applications
Chloroprene rubber, also known as neoprene, is widely used in industrial applications requiring chemical resistance, such as gaskets, hoses, and conveyor belts in automotive and chemical manufacturing industries. SBR rubber (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) is predominantly employed in the production of tires, shoe soles, and industrial rollers due to its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability. Both rubbers serve critical roles in industrial settings, with Chloroprene favored for environmental resistance and SBR for wear and tear durability.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Chloroprene rubber generally has higher production costs compared to SBR (styrene-butadiene rubber) due to its complex polymerization process and superior chemical resistance properties. SBR rubber offers a more cost-effective solution for applications requiring good abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it economically favorable for mass production in automotive and industrial sectors. The choice between chloroprene and SBR hinges on balancing higher upfront material costs against long-term performance benefits and application-specific requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chloroprene Rubber (CR) has a higher environmental footprint due to its energy-intensive production process and the release of toxic byproducts, whereas Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is considered more sustainable because it can be synthesized using less energy and incorporates more recyclable materials. SBR's biodegradability and lower emissions during manufacturing contribute to reduced ecological impact compared to CR, which contains chlorine compounds that pose disposal challenges and potential environmental hazards. Innovations in bio-based SBR production further enhance its sustainability profile, making it a preferred choice for eco-friendly rubber applications.
How to Choose: Chloroprene or SBR?
Choosing between Chloroprene Rubber (CR) and Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) depends on the specific application requirements and environmental exposure. Chloroprene Rubber offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive seals, gaskets, and industrial applications requiring durability against harsh conditions. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability at a lower cost, often preferred in tire manufacturing and general-purpose rubber goods where heavy chemical exposure is limited.
Chloroprene Rubber vs SBR Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com