Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and aging stability compared to Polybutadiene Rubber (BR), making it ideal for applications requiring durability and resilience. Polybutadiene Rubber excels in impact resistance and low-temperature flexibility, providing excellent performance in tire treads and high-impact components. Combining SBR and BR can enhance overall material properties, optimizing wear resistance and elasticity for industrial and automotive uses.
Table of Comparison
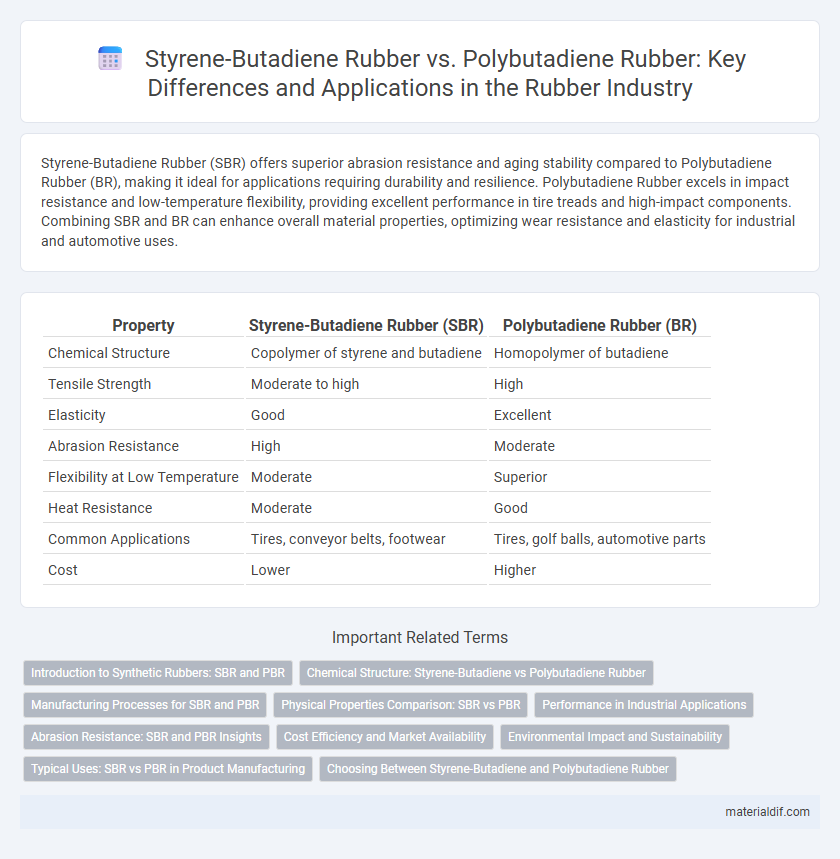
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Polybutadiene Rubber (BR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Copolymer of styrene and butadiene | Homopolymer of butadiene |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate to high | High |
| Elasticity | Good | Excellent |
| Abrasion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Flexibility at Low Temperature | Moderate | Superior |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate | Good |
| Common Applications | Tires, conveyor belts, footwear | Tires, golf balls, automotive parts |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Synthetic Rubbers: SBR and PBR
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR) are two prominent types of synthetic rubbers widely used in industrial applications. SBR offers excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it ideal for automotive tires and footwear, while PBR provides superior resilience and impact resistance, favored in tire sidewalls and golf balls. Both synthetic rubbers are produced through polymerization processes that allow customization of properties to meet specific performance requirements.
Chemical Structure: Styrene-Butadiene vs Polybutadiene Rubber
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a copolymer consisting of styrene and butadiene monomers, incorporating vinyl, trans-1,4, and cis-1,4 configurations that influence its elasticity and abrasion resistance. Polybutadiene Rubber (BR) is primarily composed of butadiene units arranged predominantly in a cis-1,4 structure, providing high resilience and low hysteresis. The presence of styrene in SBR introduces rigid phenyl groups that enhance its tensile strength and processability compared to the more flexible, highly elastic polybutadiene.
Manufacturing Processes for SBR and PBR
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) manufacturing involves emulsion polymerization using a free radical initiator, which produces a copolymer of styrene and butadiene with controlled molecular weight and microstructure. Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR) is typically synthesized through solution polymerization catalyzed by neodymium or other rare earth catalysts, resulting in high cis-1,4 content that enhances elasticity and wear resistance. Both processes require precise temperature and pressure control to optimize polymer properties for specific applications in tire manufacturing and industrial goods.
Physical Properties Comparison: SBR vs PBR
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) exhibits higher abrasion resistance and better aging stability compared to Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR), making it ideal for applications requiring durability and wear resistance. PBR offers superior elasticity and low-temperature flexibility due to its higher cis-1,4-polybutadiene content, enhancing impact toughness and resilience. Both rubbers differ significantly in mechanical strength, with SBR generally providing greater tensile strength while PBR excels in fatigue resistance and crack propagation.
Performance in Industrial Applications
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it ideal for tire treads and conveyor belts in industrial applications. Polybutadiene rubber (PBR) offers exceptional elasticity and low temperature flexibility, enhancing impact resistance in automotive parts and mechanical goods. Both rubbers deliver unique performance benefits, with SBR favored for durability and PBR for resilience in demanding industrial environments.
Abrasion Resistance: SBR and PBR Insights
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance compared to Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR) due to its enhanced toughness and wear durability, making it ideal for applications like tire treads. PBR, while offering excellent flexibility and low-temperature performance, generally shows lower resistance to surface wear under high-friction conditions. The molecular structure of SBR, incorporating styrene units, contributes to its robustness against abrasion, whereas PBR's homopolymer chain leads to reduced wear resistance.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers cost efficiency due to its lower production costs compared to Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR), making it a preferred choice in high-volume applications like tire manufacturing. SBR's widespread market availability is supported by extensive global production facilities, ensuring steady supply and competitive pricing. In contrast, Polybutadiene Rubber is more specialized with higher raw material costs, limiting its market availability but providing superior performance in products requiring enhanced wear resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) production relies heavily on petroleum feedstocks, contributing to higher carbon emissions and non-renewable resource depletion compared to Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR), which can be synthesized with fewer petrochemical inputs. PBR demonstrates greater environmental sustainability due to its longer durability and enhanced resistance to abrasion, reducing frequency of replacement and overall waste generation. Recycling initiatives for PBR show higher efficiency rates, promoting circular economy principles within the rubber industry.
Typical Uses: SBR vs PBR in Product Manufacturing
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is widely used in automotive tires, conveyor belts, and gaskets due to its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability. Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR) is preferred for manufacturing golf balls, tires, and various mechanical rubber goods because of its high resilience and low heat buildup. SBR excels in applications requiring durability and weather resistance, while PBR is favored where toughness and impact strength are critical.
Choosing Between Styrene-Butadiene and Polybutadiene Rubber
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers improved abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it ideal for automotive tires and industrial applications, while Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR) excels in low-temperature flexibility and high resilience, suitable for golf balls and mechanical goods. The choice hinges on required properties: SBR for enhanced durability and cost-effectiveness, PBR for superior wear resistance and elasticity. Analyzing specific performance needs such as abrasion resistance, heat resistance, and flexibility ensures optimal rubber selection.
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber vs Polybutadiene Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com