Rubber extrusion involves forcing rubber through a shaped die to create continuous profiles such as tubing, seals, or gaskets, offering precise control over cross-sectional shapes and thickness. Rubber calendering spreads rubber into thin sheets using rollers, ideal for producing uniform rubber sheets or coatings for applications requiring consistent thickness and smooth surfaces. Choosing between rubber extrusion and calendering depends on the desired product shape, thickness uniformity, and production volume requirements.
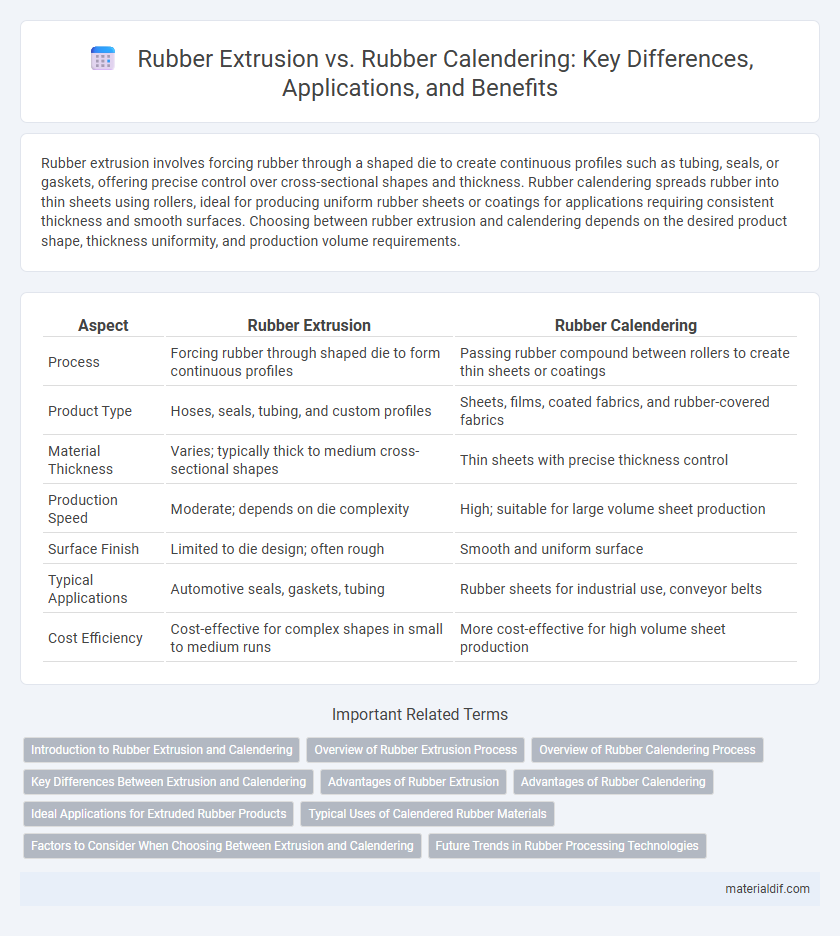
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Rubber Extrusion | Rubber Calendering |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Forcing rubber through shaped die to form continuous profiles | Passing rubber compound between rollers to create thin sheets or coatings |
| Product Type | Hoses, seals, tubing, and custom profiles | Sheets, films, coated fabrics, and rubber-covered fabrics |
| Material Thickness | Varies; typically thick to medium cross-sectional shapes | Thin sheets with precise thickness control |
| Production Speed | Moderate; depends on die complexity | High; suitable for large volume sheet production |
| Surface Finish | Limited to die design; often rough | Smooth and uniform surface |
| Typical Applications | Automotive seals, gaskets, tubing | Rubber sheets for industrial use, conveyor belts |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for complex shapes in small to medium runs | More cost-effective for high volume sheet production |
Introduction to Rubber Extrusion and Calendering
Rubber extrusion involves forcing raw rubber material through a shaped die to create continuous profiles with uniform cross-sections, ideal for producing tubes, seals, and hoses. Rubber calendering processes raw rubber by passing it through a series of heated rollers, forming thin sheets or coatings with precise thickness and smooth surface finishes suitable for tire treads and conveyor belts. Both methods are essential in rubber manufacturing, offering distinct advantages in shaping and texturing rubber products for diverse industrial applications.
Overview of Rubber Extrusion Process
Rubber extrusion is a continuous process where raw rubber compounds are forced through a shaped die to produce long, uniform profiles with consistent cross-sections, commonly used for tubing, seals, and gaskets. This method enables precise control over dimensions and surface finish while allowing for various shapes and sizes, ensuring high production efficiency. Compared to calendering, extrusion is ideal for creating complex, hollow, or solid profiles with enhanced mechanical properties and reduced material waste.
Overview of Rubber Calendering Process
Rubber calendering is a manufacturing process that involves passing raw rubber compound through a series of heated rollers to form thin sheets with precise thickness and smooth surface finish. This technique offers high production efficiency and uniformity, making it ideal for producing rubber sheets, conveyor belts, and automotive components. The controlled temperature and roller pressure ensure consistent material properties, enhancing the overall quality of calendered rubber products.
Key Differences Between Extrusion and Calendering
Rubber extrusion involves forcing rubber compound through a shaped die to create continuous profiles, ideal for tubes, seals, and gaskets, while rubber calendering presses rubber between rollers to form sheets or films with uniform thickness. Extrusion offers precise cross-sectional shapes and is suited for complex profiles, whereas calendering provides broad, flat materials with controlled thickness and surface texture. Temperature control and compound viscosity play critical roles in extrusion, whereas roller speed and pressure are key parameters in calendering.
Advantages of Rubber Extrusion
Rubber extrusion offers precise shaping and continuous production, enabling the creation of complex cross-sectional profiles with consistent quality. This process enhances material efficiency by minimizing waste compared to rubber calendering, which is better suited for flat sheets and films. Extrusion also allows for faster production speeds, making it ideal for manufacturing hoses, seals, and tubing with uniform thickness and superior mechanical properties.
Advantages of Rubber Calendering
Rubber calendering offers superior thickness control and uniformity compared to rubber extrusion, producing consistent rubber sheets ideal for high-precision applications. The process enables smooth surface finishes and enhanced dimensional accuracy, crucial for automotive and industrial rubber products. Its ability to integrate textile or metal reinforcements within the rubber layers increases material strength and durability.
Ideal Applications for Extruded Rubber Products
Extruded rubber products are ideal for applications requiring complex cross-sectional shapes, such as seals, gaskets, tubing, and weatherstripping, where continuous lengths and uniformity are essential. This process excels in producing consistent profiles used in automotive, construction, and aerospace industries, offering superior flexibility and durability. Rubber extrusion is preferred for custom designs needing precision dimensional control and efficient high-volume manufacturing.
Typical Uses of Calendered Rubber Materials
Calendered rubber materials are commonly used in the manufacturing of conveyor belts, automotive parts, and liners due to their uniform thickness and smooth finish. The calendering process enables the production of rubber sheets with precise dimensions, ideal for applications requiring consistent surface properties and enhanced mechanical strength. Typical uses also include seals, gaskets, and hoses where flexibility and durability are critical.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Extrusion and Calendering
Rubber extrusion excels in producing continuous profiles with complex cross-sections, making it ideal for sealing components, tubing, and hoses, while rubber calendering offers superior control over sheet thickness and surface finish, beneficial for manufacturing rubber sheets and coated fabrics. Factors such as required product geometry, desired dimensional tolerances, production volume, and material type significantly influence the choice between extrusion and calendering. Evaluating these parameters alongside equipment capabilities and cost considerations ensures optimal processing method selection for specific rubber applications.
Future Trends in Rubber Processing Technologies
Rubber extrusion and rubber calendering technologies are evolving with advancements in automation, precision control, and sustainable materials integration, driving enhanced production efficiency and product consistency. Future trends emphasize the adoption of Industry 4.0 principles, including IoT-enabled monitoring and AI-powered process optimization, to reduce waste and energy consumption in rubber processing. Innovations in polymer formulations and eco-friendly additives are set to revolutionize extrusion and calendering methods, addressing environmental regulations and market demand for high-performance, sustainable rubber products.
Rubber Extrusion vs Rubber Calendering Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com