Butyl rubber is renowned for its excellent airtightness and resistance to heat, chemicals, and ozone, making it ideal for inner tubes and sealants. Halobutyl rubber, a halogenated derivative of butyl, enhances these properties with improved cure rates and compatibility with other rubbers, perfect for tire inner liners and pharmaceutical stoppers. Both materials offer superior impermeability, but halobutyl rubber provides greater chemical resistance and durability in demanding applications.
Table of Comparison
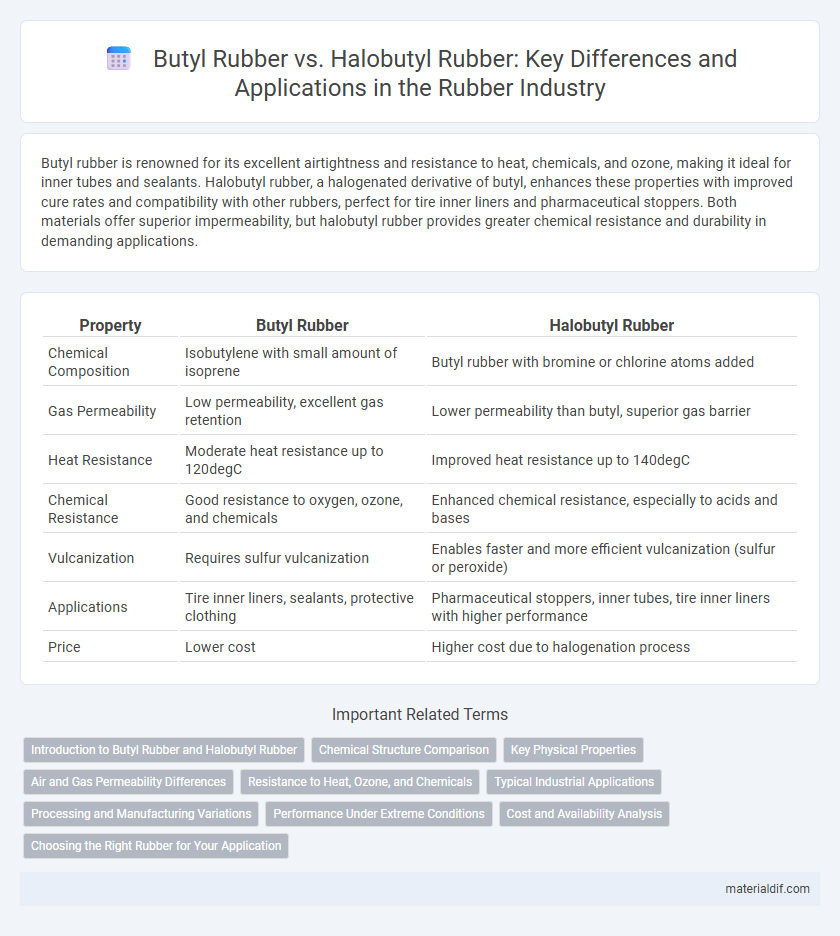
| Property | Butyl Rubber | Halobutyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Isobutylene with small amount of isoprene | Butyl rubber with bromine or chlorine atoms added |
| Gas Permeability | Low permeability, excellent gas retention | Lower permeability than butyl, superior gas barrier |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance up to 120degC | Improved heat resistance up to 140degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oxygen, ozone, and chemicals | Enhanced chemical resistance, especially to acids and bases |
| Vulcanization | Requires sulfur vulcanization | Enables faster and more efficient vulcanization (sulfur or peroxide) |
| Applications | Tire inner liners, sealants, protective clothing | Pharmaceutical stoppers, inner tubes, tire inner liners with higher performance |
| Price | Lower cost | Higher cost due to halogenation process |
Introduction to Butyl Rubber and Halobutyl Rubber
Butyl rubber is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent impermeability to gases, making it ideal for tire inner linings and pharmaceutical stoppers. Halobutyl rubber, a chlorinated or brominated derivative of butyl rubber, offers enhanced curing speed and improved resistance to ozone and aging. Both materials exhibit superior elasticity and chemical stability, but halobutyl rubber provides better performance in harsh environmental conditions.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Butyl rubber is a copolymer of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, featuring a saturated hydrocarbon backbone that provides excellent chemical and ozone resistance. Halobutyl rubber, derived from butyl rubber through halogenation with chlorine or bromine, contains reactive halogen atoms that enhance vulcanization speed and compatibility with other elastomers. The presence of halogen atoms in halobutyl rubber's chemical structure improves its curing efficiency and adhesive properties compared to the non-halogenated butyl rubber.
Key Physical Properties
Butyl rubber is known for its excellent impermeability to gases, moderate tensile strength of around 20 MPa, and superior resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for inner tubes and sealants. Halobutyl rubber, a halogenated variant of butyl, offers enhanced cure rate, improved ozone and weather resistance, and slightly higher tensile strength, typically exceeding 22 MPa, which extends its application in tire inner liners and pharmaceutical stoppers. Both materials exhibit low permeability and excellent flexibility, but halobutyl rubber's halogen modification provides superior aging properties and enhanced compatibility with other elastomers.
Air and Gas Permeability Differences
Butyl rubber exhibits low air and gas permeability due to its saturated polyisobutylene backbone, making it ideal for applications requiring airtight seals. Halobutyl rubber, which is halogenated butyl rubber, offers slightly improved gas barrier properties and enhanced resistance to ozone and heat while maintaining low permeability. The lower gas permeability of halobutyl rubber makes it preferable in tire inner liners and pharmaceutical stoppers where superior air retention and chemical stability are critical.
Resistance to Heat, Ozone, and Chemicals
Butyl rubber exhibits excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals due to its saturated polymer backbone, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Halobutyl rubber, a halogenated variant, offers enhanced chemical resistance and superior heat stability while maintaining excellent ozone resistance, expanding its use in automotive and pharmaceutical sealing. Both materials provide durability, but halobutyl rubber's improved performance under harsh conditions makes it preferable for applications requiring extended exposure to aggressive environments.
Typical Industrial Applications
Butyl rubber is widely used in tire inner liners, pharmaceutical stoppers, and adhesives due to its excellent airtightness and chemical resistance. Halobutyl rubber, a modified form of butyl, offers superior ozone and heat resistance, making it ideal for pharmaceutical closures, fuel system components, and automotive inner tubes. Both types exhibit outstanding impermeability, but halobutyl's enhanced durability extends its applications to more demanding industrial environments.
Processing and Manufacturing Variations
Butyl rubber, primarily composed of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, undergoes conventional curing processes like sulfur vulcanization, resulting in good impermeability and elasticity. Halobutyl rubber, a halogenated derivative of butyl rubber, features enhanced curing rates and improved compatibility with other polymers due to the presence of chlorine or bromine atoms, enabling faster production cycles and better adhesion properties. These processing variations make halobutyl rubber more suitable for high-performance applications such as inner tubes and pharmaceutical closures where accelerated manufacturing and superior chemical resistance are critical.
Performance Under Extreme Conditions
Butyl rubber exhibits excellent impermeability to gases and superior elasticity, making it highly effective under extreme temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress. Halobutyl rubber, a halogenated derivative, enhances resistance to chemical degradation, ozone, and weathering, ensuring prolonged durability in harsh environments. Its improved thermal stability and slight increase in polarity provide better adhesive properties and compatibility with other materials in demanding applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Butyl rubber offers a cost-effective solution due to its widespread availability and established manufacturing processes, making it suitable for large-scale industrial applications. Halobutyl rubber, though more expensive, provides enhanced chemical resistance and permeability control, justifying the premium for specialized uses in automotive and medical industries. Market availability for halobutyl rubber remains limited compared to butyl rubber, impacting procurement strategies and overall project budgeting.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Application
Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability and resistance to chemicals, making it ideal for tire inner liners and pharmaceutical stoppers. Halobutyl rubber enhances these properties with improved heat stability and aging resistance, suitable for high-performance automotive and industrial applications. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific requirements such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress.
Butyl Rubber vs Halobutyl Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com