Recycled rubber offers an eco-friendly alternative to virgin rubber by repurposing used materials and reducing landfill waste. While virgin rubber provides consistent purity and performance, recycled rubber supports sustainability goals without significantly compromising durability. Choosing between recycled and virgin rubber depends on balancing environmental impact with specific application requirements.
Table of Comparison
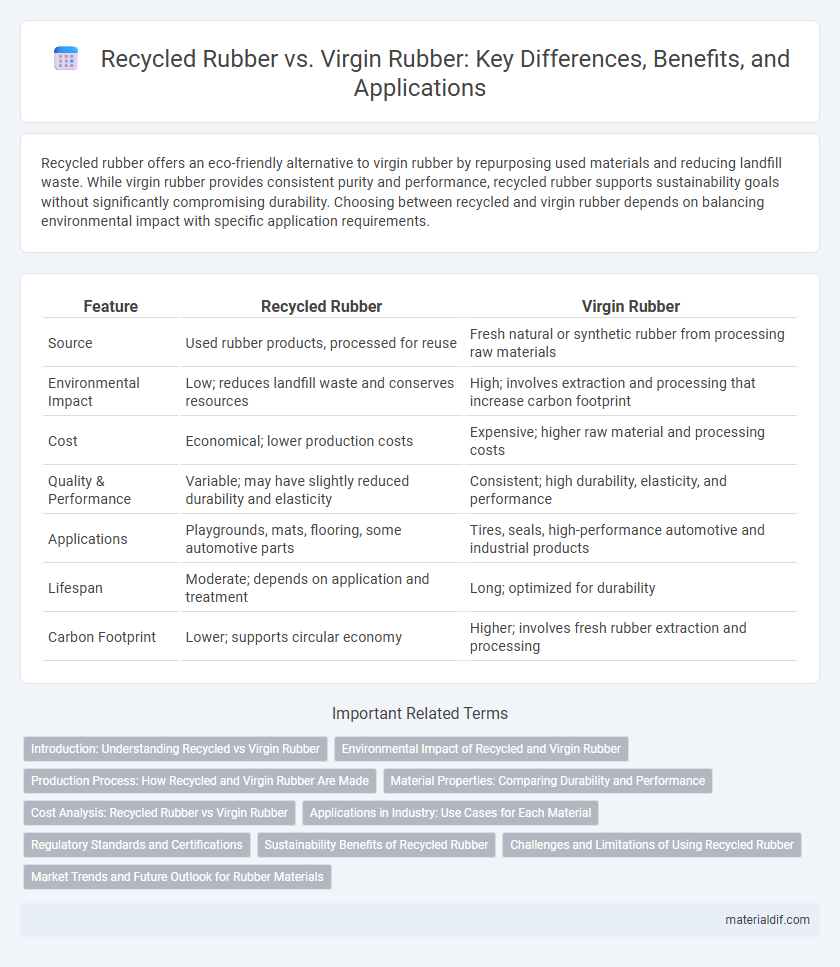
| Feature | Recycled Rubber | Virgin Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Used rubber products, processed for reuse | Fresh natural or synthetic rubber from processing raw materials |
| Environmental Impact | Low; reduces landfill waste and conserves resources | High; involves extraction and processing that increase carbon footprint |
| Cost | Economical; lower production costs | Expensive; higher raw material and processing costs |
| Quality & Performance | Variable; may have slightly reduced durability and elasticity | Consistent; high durability, elasticity, and performance |
| Applications | Playgrounds, mats, flooring, some automotive parts | Tires, seals, high-performance automotive and industrial products |
| Lifespan | Moderate; depends on application and treatment | Long; optimized for durability |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower; supports circular economy | Higher; involves fresh rubber extraction and processing |
Introduction: Understanding Recycled vs Virgin Rubber
Recycled rubber is produced by processing used rubber materials, reducing waste and conserving natural resources, while virgin rubber is derived directly from fresh latex harvested from rubber trees or synthesized chemically. The key differences lie in environmental impact, cost, and material properties, with recycled rubber offering sustainability advantages and virgin rubber providing superior purity and strength. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for industries seeking balanced performance and eco-friendly solutions.
Environmental Impact of Recycled and Virgin Rubber
Recycled rubber significantly reduces landfill waste and lowers carbon emissions compared to virgin rubber, which requires intensive resource extraction and energy consumption from natural rubber trees or petroleum-based sources. The environmental footprint of recycled rubber includes decreased reliance on non-renewable resources and diminished greenhouse gas emissions throughout its lifecycle. In contrast, virgin rubber production contributes to deforestation and habitat loss, making recycled rubber a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly manufacturing and product applications.
Production Process: How Recycled and Virgin Rubber Are Made
Virgin rubber is extracted directly from rubber trees through a process called tapping, where latex sap is collected and then coagulated, purified, and dried to produce natural rubber sheets. Recycled rubber is manufactured by collecting used rubber products, such as tires, which are shredded, cleaned, and processed through methods like devulcanization to restore elasticity and reshape the material for new uses. The production of recycled rubber reduces environmental impact by minimizing raw material extraction and energy consumption compared to the virgin rubber manufacturing process.
Material Properties: Comparing Durability and Performance
Recycled rubber exhibits slightly lower tensile strength and elasticity compared to virgin rubber, affecting its overall durability in high-stress applications. Virgin rubber maintains superior consistency in molecular structure, resulting in enhanced resistance to wear, tear, and environmental degradation. Performance trade-offs often lead to recycled rubber being favored in eco-friendly products where moderate durability suffices, while virgin rubber is preferred for demanding industrial uses requiring maximum resilience.
Cost Analysis: Recycled Rubber vs Virgin Rubber
Recycled rubber offers significant cost savings compared to virgin rubber due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during processing. Virgin rubber, derived directly from natural latex or synthetic polymers, incurs higher costs linked to extraction, refinement, and supply chain factors. Overall, recycled rubber presents a more economical option for manufacturers aiming to balance performance with budget constraints.
Applications in Industry: Use Cases for Each Material
Recycled rubber is widely used in applications such as playground surfaces, sports tracks, and molded mats due to its cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits. Virgin rubber offers superior elasticity and durability, making it ideal for high-performance automotive tires, industrial seals, and medical devices. Industries prioritize recycled rubber for sustainability projects while relying on virgin rubber where material integrity and longevity are critical.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Recycled rubber must comply with stringent regulatory standards such as the EU REACH and U.S. EPA guidelines, ensuring it meets environmental and health safety criteria comparable to virgin rubber. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and Oeko-Tex Standard 100 for chemical safety often apply to both recycled and virgin rubber, though recycled materials may face additional scrutiny due to variability in source materials. Compliance with these standards guarantees recycled rubber products maintain quality and performance while supporting sustainability goals.
Sustainability Benefits of Recycled Rubber
Recycled rubber significantly reduces environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and lowering the demand for raw materials, conserving natural resources like rubber trees and petroleum. Its production requires less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases compared to virgin rubber manufacturing, supporting carbon footprint reduction goals. Recycled rubber products also promote circular economy principles, enhancing sustainability in industries such as automotive, construction, and footwear.
Challenges and Limitations of Using Recycled Rubber
Recycled rubber faces challenges such as inconsistent material quality and reduced elasticity compared to virgin rubber, limiting its application in high-performance products. Contaminants and degradation during the recycling process can compromise durability, affecting the integrity of final goods. Supply chain variability and higher processing costs also hinder widespread adoption in industries requiring precise material specifications.
Market Trends and Future Outlook for Rubber Materials
The market for recycled rubber is expanding rapidly due to increasing environmental regulations and growing demand for sustainable materials in automotive and construction industries. Virgin rubber continues to hold a significant share driven by its superior performance characteristics, but its market growth is slower compared to recycled alternatives. Future outlook suggests a rising preference for recycled rubber driven by cost benefits, advancements in processing technology, and consumer awareness on eco-friendly products.
Recycled Rubber vs Virgin Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com