EPDM rubber excels in weather, ozone, and UV resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications and sealing systems exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it the preferred choice for automotive and industrial seals, hoses, and gaskets where contact with hydrocarbons is frequent. Selecting between EPDM and nitrile depends on the operating environment, chemical exposure, and temperature requirements to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Table of Comparison
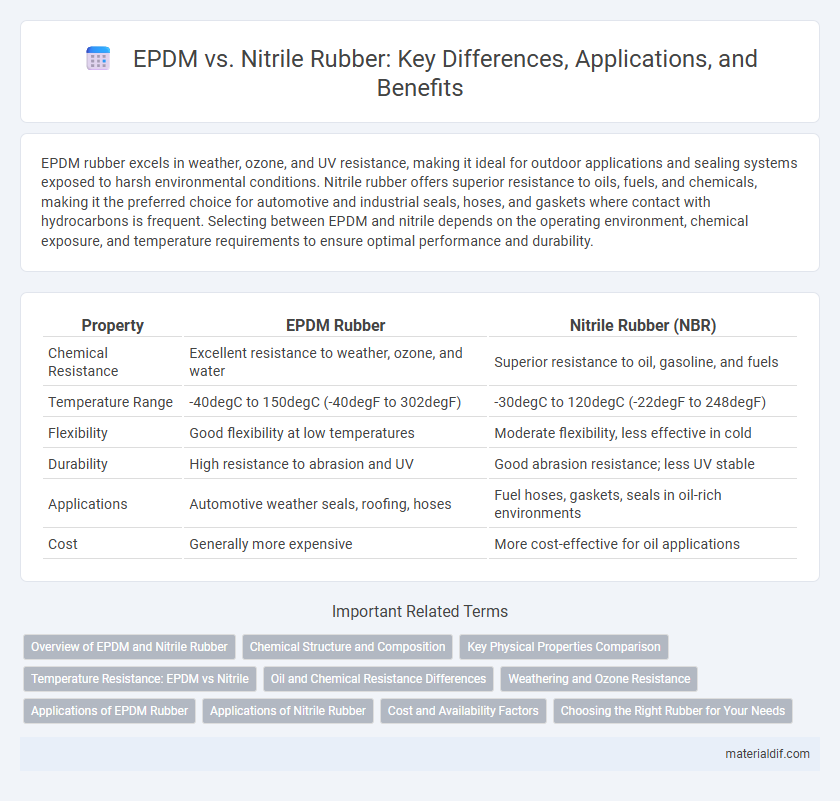
| Property | EPDM Rubber | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to weather, ozone, and water | Superior resistance to oil, gasoline, and fuels |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (-40degF to 302degF) | -30degC to 120degC (-22degF to 248degF) |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility, less effective in cold |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and UV | Good abrasion resistance; less UV stable |
| Applications | Automotive weather seals, roofing, hoses | Fuel hoses, gaskets, seals in oil-rich environments |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More cost-effective for oil applications |
Overview of EPDM and Nitrile Rubber
EPDM rubber, known for its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV exposure, is widely used in automotive seals and roofing membranes. Nitrile rubber, or NBR, offers superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for gaskets, hoses, and fuel system components. Both elastomers differ significantly in their chemical properties and applications, with EPDM excelling in outdoor durability and NBR favored in oil-related environments.
Chemical Structure and Composition
EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber features a saturated hydrocarbon backbone with unsaturated diene monomers that enable vulcanization, providing excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering. Nitrile rubber (NBR) contains copolymers of butadiene and acrylonitrile, with polar nitrile groups that offer superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals. The distinct chemical structures influence their performance, where EPDM's saturated backbone enhances environmental durability, and NBR's polar composition improves hydrocarbon compatibility.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
EPDM rubber excels in weather, ozone, and heat resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and automotive sealing applications, while nitrile rubber offers superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance suited for industrial and automotive fuel system components. EPDM has a temperature tolerance range from -40degC to 150degC, whereas nitrile performs best between -30degC and 120degC. Tensile strength for EPDM typically ranges from 7 to 14 MPa, slightly lower than nitrile's 10 to 25 MPa, influencing their suitability based on mechanical stress requirements.
Temperature Resistance: EPDM vs Nitrile
EPDM rubber offers superior temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and performance in extreme heat environments up to 150degC, while nitrile rubber typically withstands temperatures only up to 100degC before degrading. EPDM's exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, and steam enables its use in automotive cooling systems and outdoor applications exposed to temperature fluctuations. Nitrile rubber excels in oil resistance but performs poorly in high-temperature conditions compared to EPDM, making EPDM the preferred choice for heat-intensive applications.
Oil and Chemical Resistance Differences
EPDM rubber exhibits excellent resistance to heat, weathering, and ozone but has poor resistance to oils and hydrocarbons, making it unsuitable for applications involving prolonged exposure to petroleum-based fluids. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and many chemicals due to its polar nitrile groups, which enhance compatibility with hydrocarbons and reduce swelling. Selecting EPDM or Nitrile depends on the specific chemical environment, with Nitrile preferred for oil-based applications and EPDM favored where weather and ozone resistance are critical.
Weathering and Ozone Resistance
EPDM rubber exhibits superior weathering and ozone resistance compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for outdoor applications exposed to sunlight and harsh environmental conditions. EPDM effectively withstands ozone degradation due to its saturated rubber backbone, whereas nitrile rubber's unsaturated structure is more prone to cracking and deterioration when exposed to ozone. This enhanced durability allows EPDM to maintain flexibility and performance in weather-exposed environments, outperforming nitrile in long-term resistance to UV rays and atmospheric aging.
Applications of EPDM Rubber
EPDM rubber is widely used in automotive weatherstripping, seals, and hoses due to its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering. Its superior elasticity and durability make it ideal for roofing membranes and electrical insulation in construction and industrial applications. EPDM's ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions outperforms nitrile rubber in outdoor and high-temperature applications.
Applications of Nitrile Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is widely used in automotive fuel and oil handling hoses, seals, and gaskets due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels. Its strong impermeability to gases and resistance to abrasion make it ideal for manufacturing gloves, seals, and grommets in industrial applications. High durability in harsh environments also enables nitrile rubber to be a preferred choice for hydraulic system components and conveyor belts.
Cost and Availability Factors
EPDM rubber generally offers lower cost and higher availability due to its widespread production and use in automotive and construction industries. Nitrile rubber tends to be more expensive, reflecting its specialized applications in oil-resistant and fuel-handling environments. Availability of nitrile rubber can be more limited compared to EPDM, especially in bulk quantities for general manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Needs
EPDM rubber excels in weather resistance, ozone tolerance, and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for outdoor seals and automotive applications. Nitrile rubber offers superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, preferred in industrial hoses and gaskets exposed to petroleum-based fluids. Selecting between EPDM and nitrile rubber hinges on environmental exposure and chemical compatibility requirements specific to the application.
EPDM vs Nitrile Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com