Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability to gases and superior resistance to heat, oxidation, and chemicals, making it ideal for inner tubes and sealants. Neoprene rubber provides balanced flexibility, good weathering, and oil resistance, commonly used in wetsuits and industrial applications. Choosing between butyl and neoprene depends on specific requirements like air retention, chemical exposure, and mechanical durability.
Table of Comparison
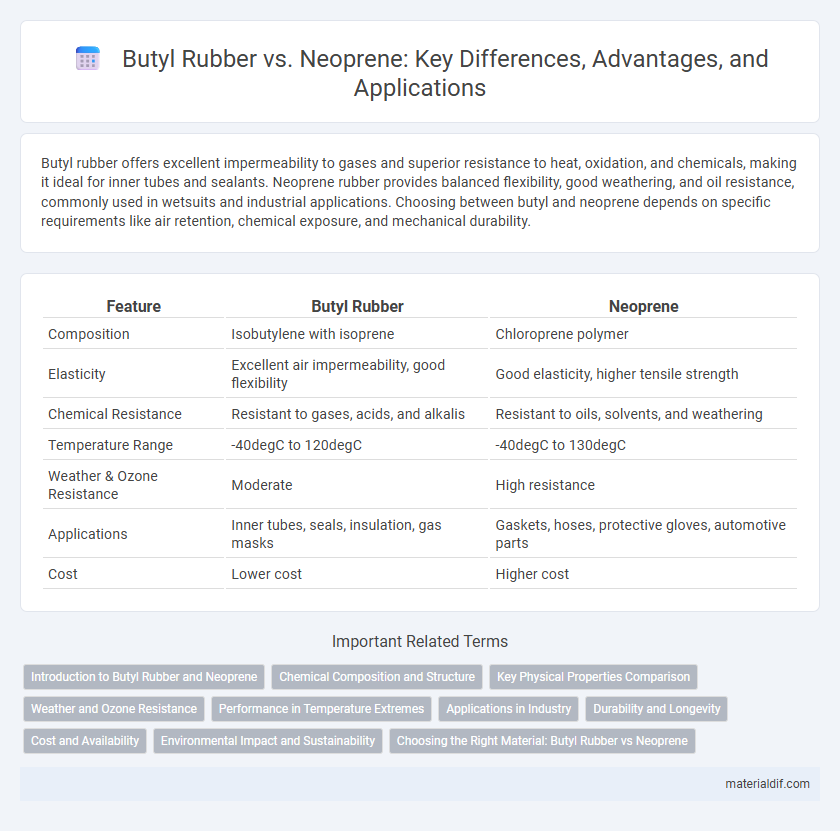
| Feature | Butyl Rubber | Neoprene |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Isobutylene with isoprene | Chloroprene polymer |
| Elasticity | Excellent air impermeability, good flexibility | Good elasticity, higher tensile strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to gases, acids, and alkalis | Resistant to oils, solvents, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 130degC |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Moderate | High resistance |
| Applications | Inner tubes, seals, insulation, gas masks | Gaskets, hoses, protective gloves, automotive parts |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Butyl Rubber and Neoprene
Butyl rubber, a synthetic elastomer derived from isobutylene and isoprene, is prized for its excellent air impermeability and chemical resistance, commonly used in tire inner linings and sealants. Neoprene, or polychloroprene, is a versatile synthetic rubber known for its superior weather, ozone, and heat resistance, making it ideal for automotive parts, wetsuits, and industrial applications. Both materials offer distinct advantages in durability and flexibility, with butyl rubber excelling in airtightness and neoprene in environmental resilience.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Butyl rubber is a copolymer of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, characterized by a saturated polyisobutylene backbone that provides excellent impermeability and chemical stability. Neoprene, or polychloroprene, is a synthetic rubber composed of chloroprene monomers, offering a partially unsaturated polymer chain with chlorine atoms that enhance oil resistance and weather durability. The distinct chemical compositions of butyl and neoprene impart unique physical properties, with butyl's low permeability ideal for airtight applications and neoprene's versatility suited for exposure to oils and environmental elements.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Butyl rubber exhibits superior gas impermeability and excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for inner tubes, seals, and protective clothing. Neoprene excels in oil, ozone, and flame resistance with good flexibility over a wide temperature range, commonly used in automotive parts, gaskets, and wetsuits. Both rubbers offer strong durability, but butyl's low permeability contrasts with neoprene's enhanced mechanical strength and chemical resistance properties.
Weather and Ozone Resistance
Butyl rubber exhibits excellent resistance to ozone and weathering, making it highly suitable for outdoor applications where prolonged exposure to harsh environmental conditions occurs. Neoprene also offers good weather resistance but tends to degrade faster than butyl when exposed to ozone and UV radiation over extended periods. For applications requiring superior durability against ozone and weather elements, butyl rubber is generally the preferred choice.
Performance in Temperature Extremes
Butyl rubber exhibits exceptional resistance to heat and cold, maintaining flexibility and resilience in temperatures ranging from -50degC to 120degC, making it ideal for extreme weather applications. Neoprene also performs well under temperature extremes, tolerating a range from -40degC to 120degC, but it offers superior stability at high temperatures and better ozone and weathering resistance. Choosing between butyl and neoprene depends on the specific temperature conditions and environmental exposure requirements for optimal durability and performance.
Applications in Industry
Butyl rubber excels in airtight seals, inner tubes, and pharmaceutical stoppers due to its low permeability and chemical resistance, making it essential in automotive and medical industries. Neoprene offers superior resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering, making it ideal for industrial gaskets, hoses, and protective coatings in construction and marine applications. Both elastomers serve critical roles, with butyl favored for impermeability and neoprene for durability under harsh chemical and environmental exposure.
Durability and Longevity
Butyl rubber exhibits superior durability and longevity due to its exceptional resistance to ozone, weathering, and aging, making it ideal for applications requiring extended life spans. Neoprene offers moderate durability with resistance to oil, chemicals, and temperature variations but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure compared to butyl rubber. The inherent impermeability of butyl rubber further enhances its longevity, outperforming neoprene in sealing and insulation applications over time.
Cost and Availability
Butyl rubber generally costs more than neoprene due to its superior airtight and chemical-resistant properties, making it essential in specialized applications such as inner tubes and sealants. Neoprene, widely available and produced at a larger scale, offers a cost-effective solution with moderate resistance to oils and weathering, commonly used in wetsuits and gaskets. The availability of neoprene in various grades results in a broader range of pricing options, whereas butyl rubber's limited production leads to higher prices and less market availability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Butyl rubber, derived from isobutylene and isoprene, offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it more resistant to degradation and extending product lifespan, which reduces waste generation. Neoprene, a chloroprene-based synthetic rubber, poses greater environmental concerns due to chlorine content and challenges in recycling, leading to higher toxicity and potential release of hazardous substances during production and disposal. The sustainability of butyl rubber is enhanced by its energy-efficient manufacturing process and lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to neoprene, promoting better environmental performance in various industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Material: Butyl Rubber vs Neoprene
Butyl rubber offers superior impermeability to gases and excellent resistance to weathering, making it ideal for inner tubes and sealing applications where airtight performance is critical. Neoprene provides enhanced resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature extremes, suitable for industrial hoses, gaskets, and protective gear requiring robust chemical stability. Selection between butyl and neoprene depends on specific application needs such as gas barrier properties or chemical exposure requirements.
Butyl Rubber vs Neoprene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com