Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications requiring durability under harsh conditions. Neoprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and aging resistance, making it suitable for outdoor use and environments exposed to sunlight and temperature variations. Both materials exhibit good flexibility and abrasion resistance, but nitrile is preferred for fluid handling while neoprene excels in general-purpose sealing and gasketing.
Table of Comparison
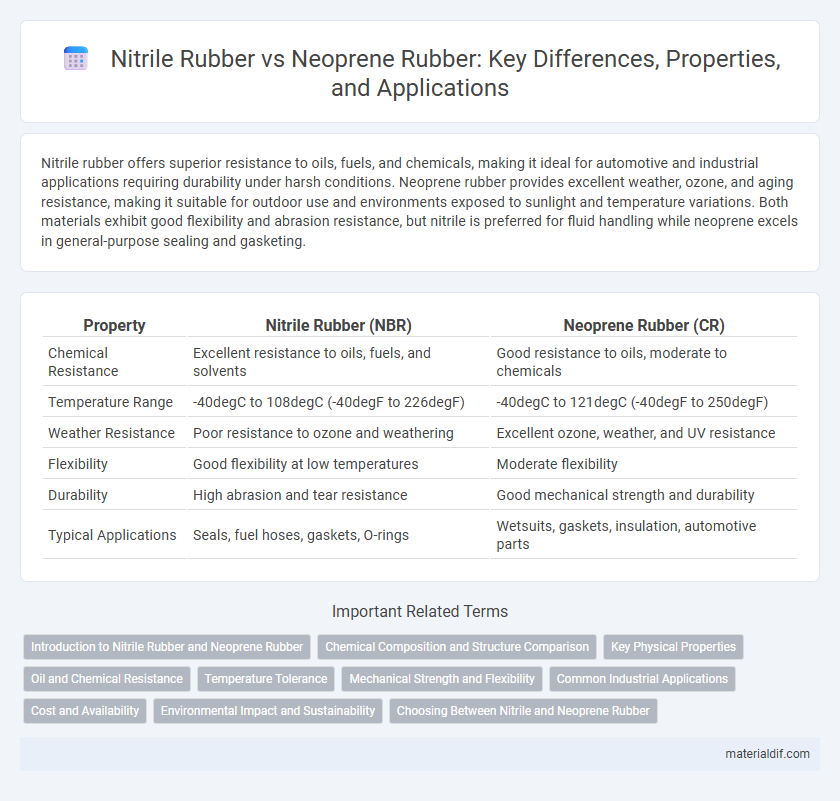
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Neoprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Good resistance to oils, moderate to chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 108degC (-40degF to 226degF) | -40degC to 121degC (-40degF to 250degF) |
| Weather Resistance | Poor resistance to ozone and weathering | Excellent ozone, weather, and UV resistance |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility |
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Good mechanical strength and durability |
| Typical Applications | Seals, fuel hoses, gaskets, O-rings | Wetsuits, gaskets, insulation, automotive parts |
Introduction to Nitrile Rubber and Neoprene Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Neoprene rubber (CR) offers moderate chemical stability and excellent weather, ozone, and abrasion resistance, commonly used in wetsuits, gaskets, and hoses. Both materials provide distinct advantages: Nitrile excels in oil resistance and flexibility under low temperatures, while Neoprene delivers balanced performance with superior environmental resilience.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, characterized by its high resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals due to the polar nitrile groups in its molecular structure. Neoprene rubber (polychloroprene) is a synthetic rubber composed of chloroprene monomers, offering excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance attributed to its stable chlorine-containing polymer backbone. The distinct chemical compositions result in NBR providing superior oil resistance, while neoprene excels in environmental durability and flexibility under varying temperature conditions.
Key Physical Properties
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals with a tensile strength of 14-28 MPa and elongation at break ranging from 300% to 600%. Neoprene rubber offers excellent weather, ozone, and flame resistance, with tensile strength typically between 9-21 MPa and elongation at break around 200%-600%. Both materials differ significantly in hardness and temperature resistance, with nitrile operating effectively between -40degC to 120degC, while neoprene withstands -40degC to 125degC.
Oil and Chemical Resistance
Nitrile rubber offers superior oil and fuel resistance due to its high acrylonitrile content, making it ideal for applications involving petroleum-based fluids. Neoprene rubber exhibits excellent resistance to a broad range of chemicals, including ozone, weathering, and moderate oil exposure, providing versatility in harsh environments. Both materials serve distinct roles, with nitrile preferred for oil-intensive conditions and neoprene for chemical and environmental durability.
Temperature Tolerance
Nitrile rubber exhibits excellent temperature tolerance ranging from -40degC to 108degC, making it highly suitable for applications involving exposure to oils and fuels at elevated temperatures. Neoprene rubber offers a broader temperature range, typically from -40degC to 120degC, with superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate heat. The choice between nitrile and neoprene rubber depends on specific operating temperature requirements and environmental conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength and resistance to wear and tear, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under stress. Neoprene rubber offers greater flexibility and excellent weather resistance, sustaining its elasticity across a broad temperature range. Comparing both, nitrile is preferred for high-impact environments, while neoprene excels where flexibility and chemical stability are critical.
Common Industrial Applications
Nitrile rubber is widely used in automotive fuel systems, seals, and gaskets due to its excellent oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for applications involving petroleum-based products. Neoprene rubber offers superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, which suits it for hoses, conveyor belts, and protective clothing in harsh environmental conditions. Industrial sectors routinely select nitrile for fuel handling and neoprene for outdoor equipment to optimize durability and performance.
Cost and Availability
Nitrile rubber typically offers a more cost-effective option compared to neoprene rubber, making it favorable for budget-sensitive applications. Availability of nitrile rubber is generally higher due to its widespread use in automotive and industrial sectors, ensuring steady supply. Neoprene rubber, while more expensive, is less readily available but preferred for specialized chemical resistance and weather durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to oils and fuels but presents challenges in biodegradability, as it is a synthetic polymer derived from petroleum. Neoprene rubber, also petroleum-based, tends to have a higher environmental footprint due to chlorine content in its production, which can generate harmful byproducts. Sustainable alternatives focus on improving recyclability and developing bio-based versions of both rubbers to reduce ecological impact.
Choosing Between Nitrile and Neoprene Rubber
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications where exposure to hydrocarbons is common. Neoprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and aging resistance, as well as good flexibility over a wide temperature range, which suits outdoor and marine environments. Selecting between nitrile and neoprene depends on specific environmental conditions and chemical exposures to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Nitrile Rubber vs Neoprene Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com