Latex rubber, derived from natural rubber tree sap, excels in elasticity and tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and durability such as gloves and balloons. Butyl rubber, a synthetic elastomer, offers superior air and moisture impermeability, enhancing its use in tire inner liners, sealants, and protective clothing. Choosing between latex and butyl rubber depends on factors like resistance to weathering, chemical exposure, and specific performance requirements in industrial or consumer products.
Table of Comparison
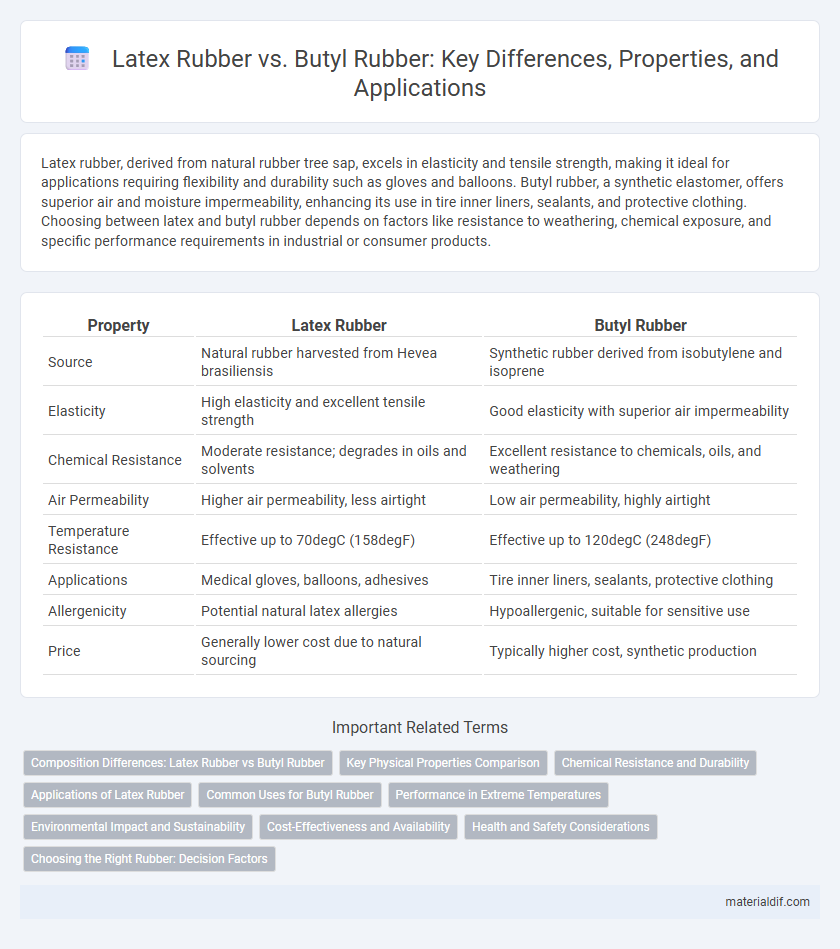
| Property | Latex Rubber | Butyl Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural rubber harvested from Hevea brasiliensis | Synthetic rubber derived from isobutylene and isoprene |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and excellent tensile strength | Good elasticity with superior air impermeability |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance; degrades in oils and solvents | Excellent resistance to chemicals, oils, and weathering |
| Air Permeability | Higher air permeability, less airtight | Low air permeability, highly airtight |
| Temperature Resistance | Effective up to 70degC (158degF) | Effective up to 120degC (248degF) |
| Applications | Medical gloves, balloons, adhesives | Tire inner liners, sealants, protective clothing |
| Allergenicity | Potential natural latex allergies | Hypoallergenic, suitable for sensitive use |
| Price | Generally lower cost due to natural sourcing | Typically higher cost, synthetic production |
Composition Differences: Latex Rubber vs Butyl Rubber
Latex rubber primarily consists of natural polymers like cis-1,4-polyisoprene obtained from the sap of rubber trees, whereas butyl rubber is a synthetic copolymer made from isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene. The high content of unsaturated polyisoprene in latex rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength, while the saturated backbone of butyl rubber imparts superior air impermeability and chemical resistance. The differing monomer compositions significantly influence their applications, with latex favored for flexibility and softness, and butyl chosen for airtight seals and damping materials.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Latex rubber, primarily composed of natural rubber, offers high elasticity, excellent tensile strength, and superior abrasion resistance, making it ideal for products requiring flexibility and resilience. Butyl rubber, a synthetic rubber, excels in impermeability to gases, outstanding air retention, and exceptional chemical resistance, which suits applications like inner tubes and sealants. Both materials differ significantly in hardness and temperature resistance, with latex providing a softer, more elastic texture, while butyl rubber maintains stability in extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Latex rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and natural resilience but has limited chemical resistance, particularly to oils, solvents, and ozone, which affects its durability in harsh environments. Butyl rubber, composed of isobutylene and isoprene, offers superior chemical resistance to acids, alkalis, and oxygenated solvents, making it highly durable in aggressive chemical conditions. Its impermeability and resilience under extreme temperatures further enhance butyl rubber's longevity compared to natural latex rubber.
Applications of Latex Rubber
Latex rubber is widely used in medical gloves, balloons, and adhesives due to its excellent elasticity, softness, and biodegradability. It offers superior tactile sensitivity, making it ideal for surgical gloves and medical devices that require precise handling. The water resistance and flexibility of latex rubber also enable its application in household products such as condoms, balloons, and elastic bands.
Common Uses for Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber is widely used in automotive inner tubes, tire liners, and sealants due to its excellent impermeability to gases and resistance to heat and chemicals. It is also common in the production of protective clothing, adhesives, and pharmaceutical stoppers. Compared to natural latex rubber, butyl rubber offers superior airtight properties and durability in harsh environments.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Latex rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and flexibility at low temperatures but tends to degrade under prolonged exposure to heat and ultraviolet light. Butyl rubber demonstrates superior thermal stability, maintaining its resilience and airtight properties even in extreme heat and cold conditions. This makes butyl rubber the preferred choice for applications requiring durable performance across a wide temperature range.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Latex rubber, derived from natural rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), is biodegradable and renewable, contributing to lower environmental impact compared to synthetic alternatives. Butyl rubber, a synthetic rubber made from isobutylene and isoprene, resists degradation but relies on non-renewable petrochemical resources, raising sustainability concerns. The production and disposal of latex rubber generate fewer greenhouse gases and support circular economy practices, while butyl rubber's durability extends product lifespan but complicates recycling efforts.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Latex rubber is generally more cost-effective and widely available due to its natural source from rubber trees, making it suitable for applications requiring flexibility and elasticity at a lower price point. Butyl rubber, derived synthetically, tends to be more expensive but offers superior air impermeability and chemical resistance, leading to higher performance in specialized uses such as inner tubes and medical gloves. Availability of latex is greater globally, while butyl rubber's niche production results in more limited supply and higher costs.
Health and Safety Considerations
Latex rubber, derived from natural rubber latex, can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals due to its protein content, necessitating careful handling and alternative materials in medical applications. Butyl rubber, a synthetic elastomer, offers superior chemical resistance and low permeability, making it safer in contexts involving exposure to gases and chemicals, with minimal allergenic risks. Both materials require adherence to proper ventilation and protective measures during processing to mitigate inhalation of airborne particles and volatile compounds.
Choosing the Right Rubber: Decision Factors
Choosing the right rubber depends on application-specific factors such as elasticity, chemical resistance, and durability. Latex rubber offers superior flexibility and biodegradability, ideal for medical and consumer products, while butyl rubber excels in air impermeability and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it suitable for automotive and industrial seals. Evaluating environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and lifespan requirements ensures optimal material performance.
Latex Rubber vs Butyl Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com