Isoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience, closely mimicking natural rubber properties, making it ideal for high-performance applications like tires and footwear. Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) provides superior abrasion resistance and aging stability, commonly used in automotive tires and conveyor belts. Both rubbers serve critical roles in industrial applications, with isoprene rubber favored for flexibility and SBR preferred for durability and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
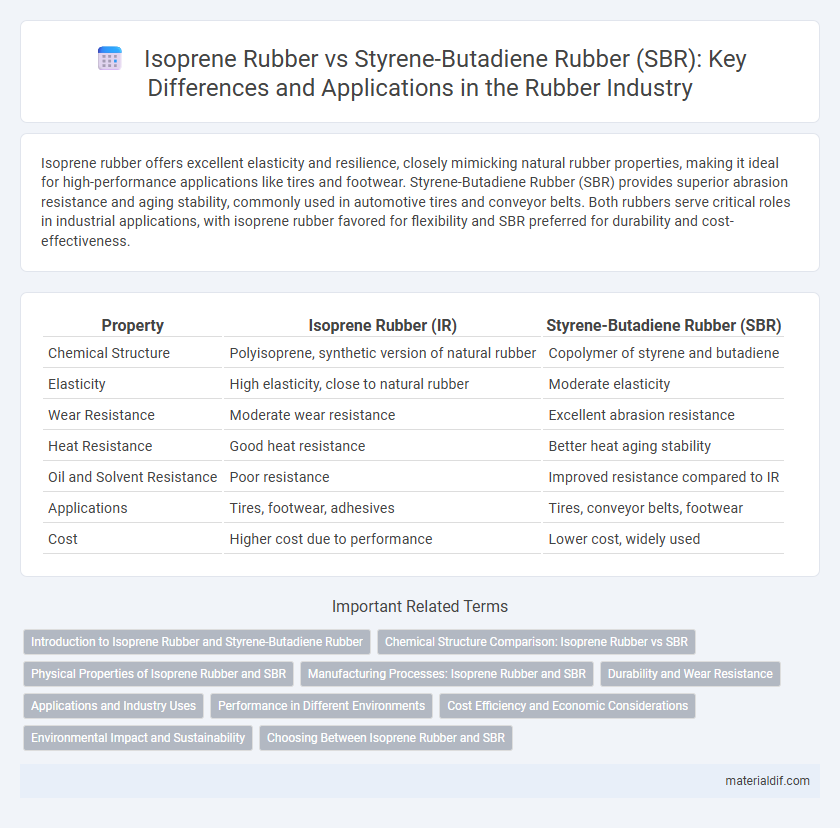
| Property | Isoprene Rubber (IR) | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Polyisoprene, synthetic version of natural rubber | Copolymer of styrene and butadiene |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, close to natural rubber | Moderate elasticity |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate wear resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Good heat resistance | Better heat aging stability |
| Oil and Solvent Resistance | Poor resistance | Improved resistance compared to IR |
| Applications | Tires, footwear, adhesives | Tires, conveyor belts, footwear |
| Cost | Higher cost due to performance | Lower cost, widely used |
Introduction to Isoprene Rubber and Styrene-Butadiene Rubber
Isoprene rubber, a synthetic polymer resembling natural rubber, offers excellent elasticity, resilience, and resistance to abrasion, making it widely used in automotive tires and footwear. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) combines styrene and butadiene monomers to create a versatile material with good wear resistance, aging stability, and cost-effectiveness, prominently utilized in tire treads and conveyor belts. Both rubbers play critical roles in the rubber industry due to their distinct mechanical properties and application-specific advantages.
Chemical Structure Comparison: Isoprene Rubber vs SBR
Isoprene rubber (IR) consists of repeating isoprene units with a cis-1,4-polyisoprene structure, providing high elasticity and resilience similar to natural rubber. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a copolymer composed of styrene and butadiene monomers, featuring a random arrangement with both 1,2- and 1,4-addition in butadiene units, which influences its abrasion resistance and aging properties. The chemical structure differences between IR and SBR directly affect their mechanical properties and application performance in tire manufacturing and industrial goods.
Physical Properties of Isoprene Rubber and SBR
Isoprene rubber (IR) exhibits excellent elasticity, high tensile strength, and good resilience, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and durability. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, moderate tensile strength, and enhanced aging stability, commonly used in automotive tires and industrial goods. Both rubbers differ significantly in their physical properties, with IR favoring elasticity and SBR excelling in wear resistance and heat aging performance.
Manufacturing Processes: Isoprene Rubber and SBR
Isoprene rubber is produced primarily through the polymerization of isoprene monomers using a coordination catalyst system that ensures high cis-1,4 content, resulting in excellent elasticity and resilience. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is manufactured using emulsion polymerization, where styrene and butadiene monomers are copolymerized in the presence of surfactants and free-radical initiators, allowing precise control over the styrene-to-butadiene ratio to tailor mechanical properties. Both processes involve complex reaction conditions and purification steps to achieve the desired molecular weight distribution and material characteristics for diverse industrial applications.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Isoprene rubber exhibits superior wear resistance due to its high resilience and elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting durability. Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and better aging performance, especially under harsh environmental conditions. The choice between isoprene and SBR depends on specific durability requirements, with SBR often preferred in tire manufacturing for its balanced wear resistance and toughness.
Applications and Industry Uses
Isoprene rubber, primarily used in medical gloves, adhesives, and automotive parts, offers excellent elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for products requiring high tensile strength and flexibility. Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) dominates tire manufacturing due to its abrasion resistance and aging stability, also serving key roles in footwear soles and conveyor belts for heavy industries. Both elastomers are integral to the automotive and manufacturing sectors, but SBR's cost-effectiveness and durability drive broader industrial applications.
Performance in Different Environments
Isoprene rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring high resilience in dry conditions. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) excels in wet traction and aging resistance, which enhances performance in automotive tires and external environments. SBR outperforms isoprene rubber in heat resistance and resistance to oxidative degradation, broadening its suitability for harsher environmental conditions.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Isoprene rubber typically has higher production costs compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) due to more complex synthesis processes and raw material expenses. SBR offers superior cost efficiency for mass production, benefiting from lower raw material prices and widespread availability, making it the preferred choice in economic-sensitive industries like tire manufacturing. Economic considerations favor SBR for applications requiring a balance between performance and affordability, whereas isoprene rubber is reserved for specialized uses where higher cost is justified by enhanced elasticity and resilience.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Isoprene rubber, derived primarily from natural latex, offers greater biodegradability and a smaller carbon footprint compared to Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which is petrochemical-based and less eco-friendly. SBR production results in higher greenhouse gas emissions and limited recyclability, posing challenges for sustainable manufacturing. The preference for isoprene rubber supports environmental sustainability goals due to its renewable origin and reduced ecological impact.
Choosing Between Isoprene Rubber and SBR
Isoprene rubber offers superior elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for products requiring high tensile strength and excellent wear resistance, such as premium tires and medical devices. Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is more cost-effective and provides good abrasion resistance and aging stability, commonly used in automotive tires and footwear applications. Selecting between isoprene rubber and SBR depends on balancing performance requirements with budget constraints, emphasizing the need for durability versus economic feasibility in specific industrial uses.
Isoprene Rubber vs Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com