Dense rubber offers superior durability and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring long-lasting performance. Sponge rubber provides excellent cushioning and flexibility due to its porous structure, which absorbs shocks and reduces vibrations in lighter-duty uses. Selecting between dense and sponge rubber depends on the specific needs of resistance, flexibility, and impact absorption in the intended application.
Table of Comparison
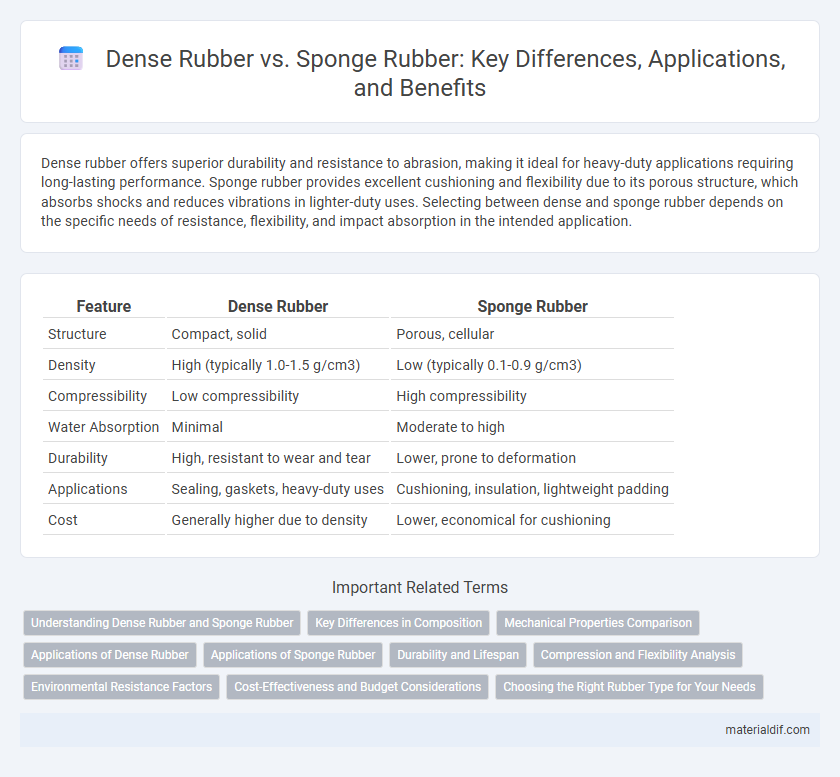
| Feature | Dense Rubber | Sponge Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Compact, solid | Porous, cellular |
| Density | High (typically 1.0-1.5 g/cm3) | Low (typically 0.1-0.9 g/cm3) |
| Compressibility | Low compressibility | High compressibility |
| Water Absorption | Minimal | Moderate to high |
| Durability | High, resistant to wear and tear | Lower, prone to deformation |
| Applications | Sealing, gaskets, heavy-duty uses | Cushioning, insulation, lightweight padding |
| Cost | Generally higher due to density | Lower, economical for cushioning |
Understanding Dense Rubber and Sponge Rubber
Dense rubber features a compact molecular structure that provides excellent durability, high tensile strength, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Sponge rubber, characterized by its cellular, porous composition, offers superior cushioning, flexibility, and sound absorption, which is essential for sealing, vibration dampening, and insulation purposes. Each type's distinct physical properties cater to specific industrial uses, where dense rubber excels in strength-dependent tasks and sponge rubber in compression and cushioning roles.
Key Differences in Composition
Dense rubber is characterized by a tightly packed polymer matrix with minimal air pockets, resulting in high durability, resistance to abrasion, and low compressibility, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Sponge rubber contains numerous microscopic air cells uniformly distributed throughout its structure, providing enhanced cushioning, flexibility, and superior shock absorption, but sacrificing some tensile strength. The key compositional difference lies in the cellular structure: dense rubber is solid and compact, while sponge rubber incorporates a foamed, porous network that influences mechanical and thermal properties.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Dense rubber exhibits higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to sponge rubber, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and load-bearing capacity. Sponge rubber, characterized by its cellular structure, offers superior compression resilience and cushioning properties, ideal for shock absorption and sealing. The choice between dense and sponge rubber depends on the specific mechanical demands, such as hardness, elasticity, and impact resistance, required for the intended use.
Applications of Dense Rubber
Dense rubber finds extensive use in industrial seals, gaskets, and vibration dampening components due to its high tensile strength and low porosity. Its durability and resistance to oils, chemicals, and abrasion make it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications requiring long-lasting, reliable performance. Dense rubber is also preferred in manufacturing conveyor belts and hoses where structural integrity and wear resistance are critical.
Applications of Sponge Rubber
Sponge rubber's porous structure provides excellent cushioning and insulation, making it ideal for sealing gaskets, padding in automotive interiors, and noise reduction in industrial equipment. Its lightweight and flexible nature allow for better shock absorption and vibration dampening compared to dense rubber. These properties enable sponge rubber to be widely used in construction, electronics, and packaging industries.
Durability and Lifespan
Dense rubber exhibits superior durability and a longer lifespan due to its compact molecular structure, which resists wear, abrasion, and environmental degradation more effectively. Sponge rubber is more prone to compression set and tearing, leading to a reduced lifespan in high-stress applications. Selecting dense rubber enhances longevity in industrial seals, gaskets, and vibration dampening components.
Compression and Flexibility Analysis
Dense rubber exhibits higher compression resistance due to its tightly packed molecular structure, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and minimal deformation under load. Sponge rubber offers superior flexibility and cushioning, attributed to its porous matrix that absorbs shocks and rebounds efficiently. Compression analysis shows dense rubber maintains shape under sustained pressure, while sponge rubber provides enhanced elasticity and energy absorption in dynamic environments.
Environmental Resistance Factors
Dense rubber exhibits superior environmental resistance due to its low porosity, making it highly effective against water, oils, and chemicals, ideal for harsh industrial applications. Sponge rubber, characterized by its cellular structure, offers enhanced compression and cushioning but is more susceptible to moisture absorption and environmental degradation. Choosing between dense and sponge rubber depends on balancing durability with flexibility requirements in specific environmental conditions.
Cost-Effectiveness and Budget Considerations
Dense rubber offers superior durability and resistance to wear, providing long-term cost savings for applications requiring high performance under pressure. Sponge rubber, while less durable, is more affordable upfront and ideal for budget-conscious projects needing cushioning or flexibility. Evaluating the balance between initial costs and lifespan helps determine the most cost-effective choice for specific industrial or commercial uses.
Choosing the Right Rubber Type for Your Needs
Dense rubber offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for applications requiring high strength and longevity, such as seals and gaskets. Sponge rubber, characterized by its cellular structure, provides excellent cushioning, flexibility, and shock absorption, suitable for soundproofing and padding needs. Selecting the right rubber type depends on balancing factors like compression resistance, flexibility, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal performance in specific industrial or commercial applications.
Dense Rubber vs Sponge Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com