Polystyrene resin offers excellent clarity and ease of molding, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and detailed surface finishes, while ABS resin provides superior impact resistance and toughness for durable, high-strength products. Polystyrene resin is more cost-effective and easier to process, but ABS resin outperforms in thermal stability and mechanical properties. Choosing between polystyrene resin and ABS resin depends on the balance needed between aesthetic qualities and structural durability for specific pet-related applications.
Table of Comparison
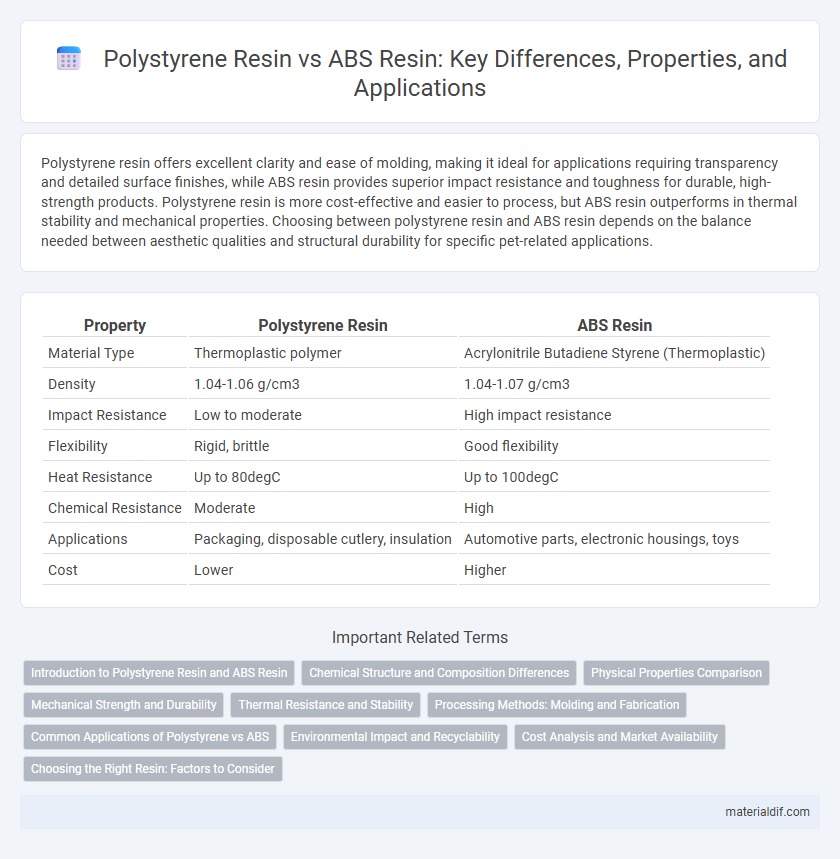
| Property | Polystyrene Resin | ABS Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (Thermoplastic) |
| Density | 1.04-1.06 g/cm3 | 1.04-1.07 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Low to moderate | High impact resistance |
| Flexibility | Rigid, brittle | Good flexibility |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 80degC | Up to 100degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Applications | Packaging, disposable cutlery, insulation | Automotive parts, electronic housings, toys |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Polystyrene Resin and ABS Resin
Polystyrene resin is a versatile, lightweight thermoplastic known for its clarity, rigidity, and ease of molding, widely used in packaging, insulation, and disposable cutlery. ABS resin, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, offers superior impact resistance, toughness, and heat resistance, making it ideal for automotive parts, electronics housings, and consumer goods. Both resins originate from different polymer families, with polystyrene providing excellent rigidity and ABS delivering enhanced durability and flexibility.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Polystyrene resin consists of repeating styrene monomers forming a rigid, transparent polymer with a simple chemical structure characterized by a phenyl group attached to a carbon backbone. ABS resin is a terpolymer made from acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, combining rigidity, toughness, and impact resistance due to its complex structure with rubbery butadiene segments and polar acrylonitrile units. The presence of butadiene in ABS introduces elastomeric properties absent in polystyrene, while acrylonitrile enhances chemical resistance, resulting in a material composition and performance profile distinct from polystyrene's brittle and more chemically limited framework.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polystyrene resin exhibits higher rigidity and excellent clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring transparent and brittle materials, while ABS resin offers superior impact resistance and toughness due to its rubber content. Polystyrene's lower tensile strength and poor heat resistance contrast with ABS's enhanced durability and ability to withstand temperatures up to 100degC. The density of polystyrene typically ranges around 1.04 g/cm3, whereas ABS resin is denser, approximately 1.04 to 1.06 g/cm3, contributing to its heavier and more durable nature.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polystyrene resin offers moderate mechanical strength and is known for its lightweight properties but tends to be brittle under impact stress, limiting its durability in high-stress applications. ABS resin, composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, provides superior mechanical strength with excellent impact resistance and durability, making it suitable for automotive and consumer products requiring toughness. The butadiene component in ABS enhances flexibility and impact absorption, significantly outperforming polystyrene in terms of long-term durability and structural integrity.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Polystyrene resin exhibits lower thermal resistance with a maximum service temperature around 80degC, whereas ABS resin offers superior thermal stability, functioning effectively up to 90-100degC. Polystyrene tends to soften and deform more quickly under heat compared to ABS, which maintains dimensional stability and impact resistance under higher temperatures. The enhanced thermal resilience of ABS resin makes it preferable for applications requiring long-term exposure to elevated temperatures and mechanical stress.
Processing Methods: Molding and Fabrication
Polystyrene resin is commonly processed through injection molding and thermoforming, offering excellent dimensional stability and ease of shaping for products like disposable cutlery and packaging. ABS resin, favored for injection molding and extrusion, provides superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for automotive parts and electronic housings. Both resins allow rapid fabrication but differ in optimal processing conditions, with polystyrene requiring lower temperatures and ABS benefiting from higher heat and controlled cooling to enhance mechanical properties.
Common Applications of Polystyrene vs ABS
Polystyrene resin is widely used in packaging materials, disposable cutlery, and insulation due to its rigidity, clarity, and cost-effectiveness. ABS resin is favored for applications requiring higher impact resistance and toughness such as automotive parts, electronic housings, and consumer goods like toys and helmets. Both resins serve distinct roles in manufacturing, with polystyrene excelling in lightweight, disposable products and ABS in durable, high-performance components.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene resin exhibits lower environmental impact compared to ABS resin due to its simpler chemical structure, facilitating more efficient recycling processes and reduced energy consumption during recovery. ABS resin, composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, poses greater challenges in recyclability because of its composite nature, often requiring specialized facilities and resulting in limited reuse. Both materials contribute to plastic waste concerns, but polystyrene's widespread availability in municipal recycling programs enhances its sustainability profile relative to ABS.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polystyrene resin offers a lower cost advantage compared to ABS resin, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications in packaging and disposable products. ABS resin commands a higher price due to its superior impact resistance and durability, but this cost premium limits its use predominantly to automotive, electronics, and high-performance consumer goods. Market availability for polystyrene resin is widespread and consistent globally, while ABS resin availability can fluctuate based on feedstock supply and regional demand variations.
Choosing the Right Resin: Factors to Consider
Choosing between polystyrene resin and ABS resin depends on factors such as impact resistance, cost, and application requirements. Polystyrene offers excellent clarity and is cost-effective for lightweight, rigid products, while ABS resin provides superior toughness, heat resistance, and flexibility for more demanding mechanical applications. Evaluating the intended use environment, durability needs, and budget constraints ensures the optimal resin selection for performance and longevity.
Polystyrene Resin vs ABS Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com