Polyester offers excellent resistance to chemicals and UV rays, making it ideal for outdoor fabrics, while polyamide is known for its superior strength and elasticity, commonly used in activewear. Polyester fibers tend to retain their shape and resist wrinkles, whereas polyamide provides better abrasion resistance and moisture-wicking properties. Choosing between polyester and polyamide depends on the specific performance needs such as durability, comfort, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
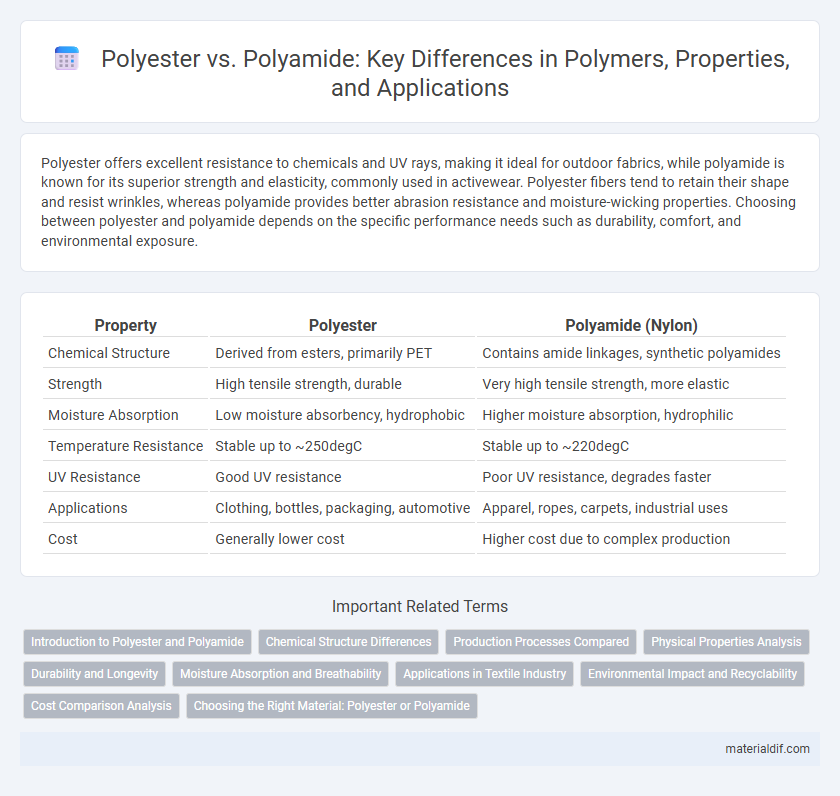
| Property | Polyester | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Derived from esters, primarily PET | Contains amide linkages, synthetic polyamides |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Very high tensile strength, more elastic |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorbency, hydrophobic | Higher moisture absorption, hydrophilic |
| Temperature Resistance | Stable up to ~250degC | Stable up to ~220degC |
| UV Resistance | Good UV resistance | Poor UV resistance, degrades faster |
| Applications | Clothing, bottles, packaging, automotive | Apparel, ropes, carpets, industrial uses |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complex production |
Introduction to Polyester and Polyamide
Polyester is a synthetic polymer known for its durability, resistance to shrinking and stretching, and quick-drying properties, commonly used in textiles and packaging. Polyamide, also referred to as nylon, features excellent abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and elasticity, making it ideal for industrial applications and performance apparel. Both polymers belong to the category of synthetic fibers but differ significantly in chemical structure and mechanical performance.
Chemical Structure Differences
Polyester consists of ester functional groups (-COO-) linking the monomers, typically formed from the reaction of dicarboxylic acids and diols, resulting in a more rigid and hydrophobic molecular backbone. Polyamide contains amide linkages (-CONH-) between monomers, formed from diamines and dicarboxylic acids, which enhance hydrogen bonding and increase durability and moisture absorption. The chemical structure differences between ester and amide bonds directly impact their thermal stability, mechanical properties, and resistance to chemicals.
Production Processes Compared
Polyester production primarily involves the polycondensation of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, resulting in polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is extruded and spun into fibers. In contrast, polyamide, such as nylon, is synthesized through ring-opening polymerization or condensation polymerization of diamines and dicarboxylic acids, producing fibers with higher crystallinity and strength. The energy consumption and chemical complexity in polyamide production typically exceed those of polyester, impacting manufacturing costs and environmental footprint.
Physical Properties Analysis
Polyester exhibits high tensile strength and excellent resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation and moisture, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, offers superior elasticity and abrasion resistance, which enhances durability in high-stress environments. The thermal stability of polyester is generally higher, while polyamide shows better impact resistance and flexibility under mechanical stress.
Durability and Longevity
Polyester exhibits superior durability due to its high resistance to stretching, shrinking, and abrasion, making it ideal for long-lasting textile applications. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, offers exceptional strength and elasticity but is more prone to degradation from prolonged exposure to UV light and moisture. Polyester's inherent resistance to environmental factors ensures greater longevity in outdoor and high-wear conditions compared to polyamide fibers.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Polyester exhibits low moisture absorption, typically absorbing less than 0.4% of water, making it highly effective at repelling moisture and maintaining breathability in textiles. Polyamide, such as nylon, absorbs more moisture, around 4-5%, which enhances its breathability and comfort in moisture-rich environments but may reduce drying speed. The contrasting moisture management properties influence their suitability for activewear, with polyester favored for moisture-wicking and polyamide preferred for soft, breathable fabric performance.
Applications in Textile Industry
Polyester is widely used in textiles for its durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for activewear, home furnishings, and industrial fabrics. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, offers superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and strength, which suits applications like hosiery, swimwear, and performance sportswear. Both polymers are essential in technical textiles, with polyester favored for dimensional stability and polyamide for stretch and resilience.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyester, derived primarily from petroleum, has a lower biodegradability rate but benefits from established recycling systems such as PET bottle recycling, enhancing its circular economy potential. Polyamide, or nylon, involves energy-intensive production processes and releases nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas, raising concerns over its environmental footprint despite being recyclable through emerging technologies. Both polymers face challenges with microfiber pollution during washing, yet advances in chemical recycling aim to mitigate long-term ecological impacts and improve material recovery rates.
Cost Comparison Analysis
Polyester generally offers a lower production cost due to cheaper raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes compared to polyamide. Polyamide involves higher energy consumption and more complex polymerization, resulting in increased material and processing expenses. Cost analysis shows polyester as a more economical choice for mass-market applications, while polyamide's higher price is justified by superior durability and performance in technical uses.
Choosing the Right Material: Polyester or Polyamide
Polyester offers excellent durability, resistance to shrinking and stretching, and quick-drying properties, making it ideal for outdoor apparel and industrial applications. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, provides superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and moisture-wicking capabilities, which are essential for activewear and performance fabrics. Selecting between polyester and polyamide depends on the application's need for strength, flexibility, or moisture management.
Polyester vs Polyamide Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com