Nylon offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and impact absorption. Polycarbonate excels in transparency and high impact resistance, commonly used in optical lenses and protective gear. Choosing between nylon and polycarbonate depends on the specific requirements for strength, flexibility, and clarity in the intended application.
Table of Comparison
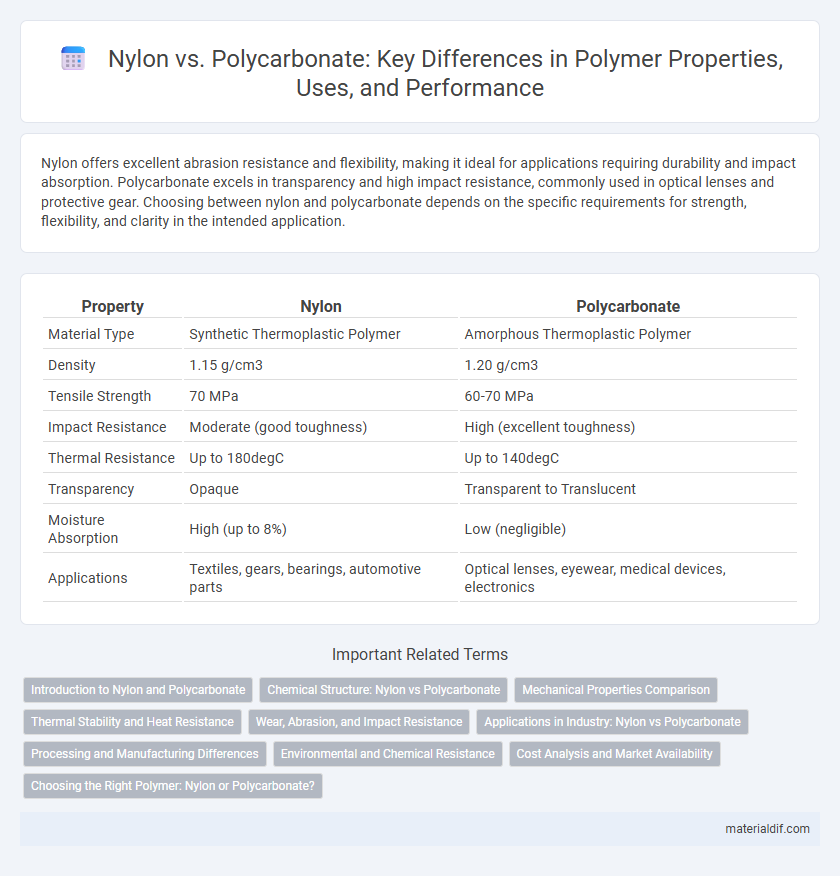
| Property | Nylon | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Thermoplastic Polymer | Amorphous Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Density | 1.15 g/cm3 | 1.20 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 70 MPa | 60-70 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate (good toughness) | High (excellent toughness) |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 180degC | Up to 140degC |
| Transparency | Opaque | Transparent to Translucent |
| Moisture Absorption | High (up to 8%) | Low (negligible) |
| Applications | Textiles, gears, bearings, automotive parts | Optical lenses, eyewear, medical devices, electronics |
Introduction to Nylon and Polycarbonate
Nylon is a synthetic polymer known for its high tensile strength, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for textiles and engineering applications. Polycarbonate is a durable thermoplastic prized for its impact resistance, transparency, and thermal stability, commonly used in eyewear lenses and electronic components. Both polymers exhibit distinct chemical structures and physical properties that determine their suitability across various industrial uses.
Chemical Structure: Nylon vs Polycarbonate
Nylon is a synthetic polyamide characterized by repeating amide linkages (-CONH-) formed through condensation polymerization of diamines and dicarboxylic acids, resulting in a linear, semi-crystalline structure that enhances strength and flexibility. Polycarbonate consists of carbonate groups (-O-(C=O)-O-) in its backbone, produced via condensation polymerization of bisphenol A and phosgene, yielding an amorphous, transparent thermoplastic known for high impact resistance and thermal stability. The distinct chemical structures influence their physical properties, with nylon's hydrogen bonding promoting toughness and polycarbonate's aromatic rings providing rigidity and dimensional stability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nylon exhibits high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and good flexibility, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and wear resistance. Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance, higher stiffness, and better dimensional stability under heat, ideal for structural components exposed to dynamic loads. Comparing mechanical properties, Nylon excels in toughness and fatigue resistance, while Polycarbonate outperforms in stiffness and impact strength.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Nylon exhibits moderate thermal stability with a melting point typically around 220degC, making it suitable for applications requiring heat resistance up to this temperature. Polycarbonate offers superior heat resistance, with a glass transition temperature near 147degC but maintains structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 130degC without deformation. Polycarbonate's higher thermal stability and impact resistance make it preferable for components exposed to sustained heat and mechanical stress.
Wear, Abrasion, and Impact Resistance
Nylon exhibits excellent wear and abrasion resistance due to its high toughness and self-lubricating properties, making it ideal for applications involving friction and repetitive motion. Polycarbonate surpasses Nylon in impact resistance, offering superior toughness and high impact strength, which is essential for protective gear and structural components. Choosing between Nylon and Polycarbonate depends on the specific demands for abrasion durability versus impact resilience in the intended application.
Applications in Industry: Nylon vs Polycarbonate
Nylon is extensively used in automotive parts, textile fibers, and industrial machinery due to its excellent abrasion resistance and chemical stability. Polycarbonate finds applications in electronics, safety equipment, and optical lenses because of its superior impact resistance and transparency. Both polymers are critical in manufacturing but are chosen based on specific mechanical and thermal performance requirements.
Processing and Manufacturing Differences
Nylon is typically processed through injection molding and extrusion, benefiting from its thermoplastic nature and moisture absorption properties that affect molding cycles and climate control during manufacturing. Polycarbonate, known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity, is commonly processed via injection molding and extrusion but requires precise temperature control to prevent degradation and maintain clarity. The manufacturing of polycarbonate often involves slower cooling rates compared to nylon to avoid internal stress and achieve optimal mechanical properties.
Environmental and Chemical Resistance
Nylon exhibits strong chemical resistance to oils, greases, and solvents but tends to absorb moisture, which can impact its mechanical properties and dimensional stability. Polycarbonate offers excellent environmental resistance, including UV stability and low water absorption, making it suitable for outdoor applications and exposure to harsh chemicals. Both polymers provide distinct advantages, with polycarbonate generally outperforming nylon in resistance to environmental degradation and nylon excelling in resistance to certain chemical exposures.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Nylon generally offers a lower cost per kilogram compared to polycarbonate, making it a more budget-friendly option for mass production in industries like automotive and textiles. Polycarbonate, while more expensive, provides superior impact resistance and optical clarity, driving demand in electronics and safety equipment markets. Market availability of nylon is widespread due to its longstanding use and established supply chains, whereas polycarbonate's availability can be influenced by fluctuations in raw material prices and manufacturing complexities.
Choosing the Right Polymer: Nylon or Polycarbonate?
Nylon offers excellent mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for automotive parts and industrial components requiring durability. Polycarbonate excels in impact resistance, optical clarity, and dimensional stability, suitable for applications like eyewear lenses, electronic housings, and safety equipment. Selecting between Nylon and Polycarbonate depends on specific performance criteria such as mechanical stress, environmental exposure, and transparency requirements.
Nylon vs Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com