Slit tape offers superior strength and precision in width customization compared to cast film, making it ideal for industrial packaging applications requiring consistent performance. Cast film provides a smoother surface and better clarity, which enhances printability and visual appeal for consumer goods packaging. Choosing between slit tape and cast film depends on the specific requirements for durability, flexibility, and aesthetic quality in polyethylene PET products.
Table of Comparison
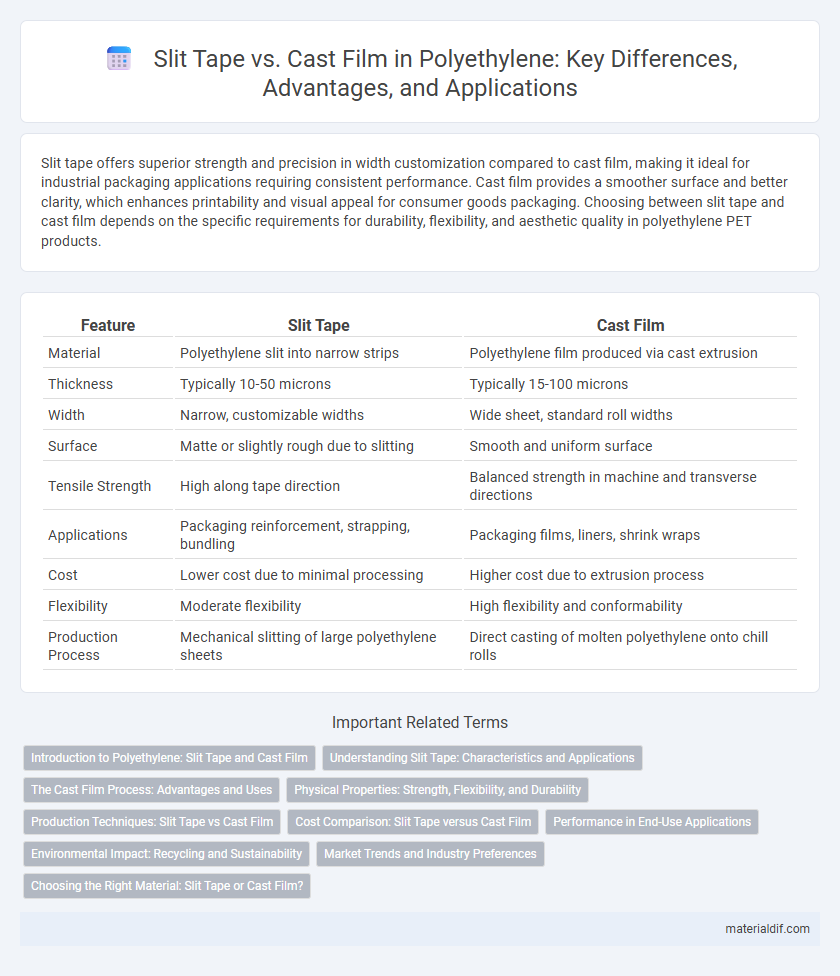
| Feature | Slit Tape | Cast Film |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyethylene slit into narrow strips | Polyethylene film produced via cast extrusion |
| Thickness | Typically 10-50 microns | Typically 15-100 microns |
| Width | Narrow, customizable widths | Wide sheet, standard roll widths |
| Surface | Matte or slightly rough due to slitting | Smooth and uniform surface |
| Tensile Strength | High along tape direction | Balanced strength in machine and transverse directions |
| Applications | Packaging reinforcement, strapping, bundling | Packaging films, liners, shrink wraps |
| Cost | Lower cost due to minimal processing | Higher cost due to extrusion process |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility and conformability |
| Production Process | Mechanical slitting of large polyethylene sheets | Direct casting of molten polyethylene onto chill rolls |
Introduction to Polyethylene: Slit Tape and Cast Film
Polyethylene, a versatile polymer, is commonly processed into slit tape and cast film forms for diverse industrial applications. Slit tape, derived from wider polyethylene films, offers narrow, precision-cut strips ideal for packaging and strapping due to its strength and flexibility. Cast film, produced through the extrusion of molten polyethylene onto a chilled roller, provides uniform thickness and enhanced clarity, making it suitable for high-quality packaging and lamination.
Understanding Slit Tape: Characteristics and Applications
Slit tape, a narrow strip of polyethylene film, is precisely cut from larger rolls to enhance flexibility and ease of use in packaging applications, especially for bundling and strapping. Its superior tensile strength and uniform thickness make it ideal for secure, durable bindings in industrial and commercial settings, outperforming cast film in dimensional stability. Slit tape's specialized slit width options and consistent edge quality ensure reliability and efficiency in automated wrapping and sealing processes.
The Cast Film Process: Advantages and Uses
The cast film process involves extruding molten polyethylene onto a chilled roller, producing a uniform, thin film with excellent clarity and strength. This method offers superior control over film thickness and surface finish compared to slit tape, making it ideal for packaging, medical, and graphic applications where precision and transparency are critical. Cast films also exhibit enhanced flexibility and sealability, increasing their versatility across various industrial uses.
Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Slit tape made from polyethylene offers enhanced strength and durability due to its uniform thickness and controlled extrusion process, resulting in higher tensile strength and resistance to tearing compared to cast film. The cast film exhibits superior flexibility and clarity but tends to have lower puncture resistance and mechanical strength because of its rapid cooling and less consistent molecular orientation. For applications requiring robust performance and long-term durability, slit tape polyethylene is preferred, whereas cast film suits uses where flexibility and optical properties are critical.
Production Techniques: Slit Tape vs Cast Film
Slit tape production involves extruding polyethylene into thick sheets that are subsequently slit into narrower tapes, enabling high tensile strength and precise dimensional control ideal for industrial applications. Cast film production uses a process where molten polyethylene is extruded through a flat die onto chill rolls, quickly solidifying into thin, uniform films with superior clarity and surface smoothness. The choice between slit tape and cast film depends on the desired film thickness, mechanical properties, and end-use performance in packaging or industrial manufacturing.
Cost Comparison: Slit Tape versus Cast Film
Slit tape production generally incurs lower material costs than cast film due to reduced raw material wastage and simpler manufacturing processes. Cast film offers superior film uniformity and properties but often requires higher capital investment and energy consumption, increasing overall expenses. Businesses seeking cost-efficient solutions often prefer slit tape for applications prioritizing budget over film performance.
Performance in End-Use Applications
Slit tape offers enhanced tensile strength and uniform thickness, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging and industrial applications where durability is critical. Cast film exhibits superior clarity and flexibility, which benefits end-use products like food packaging and medical wrap requiring high barrier properties and aesthetic appeal. Performance differences between slit tape and cast film directly impact product protection, handling, and shelf-life in their respective end-use scenarios.
Environmental Impact: Recycling and Sustainability
Slit tape from polyethylene typically generates less waste during production compared to cast film due to precise cutting methods, enhancing material efficiency. Cast film recycling generally benefits from uniform thickness and composition, making it more straightforward to reprocess in standard polyethylene recycling streams. Both materials contribute to sustainability efforts, but optimizing slit tape production and recycling can further reduce environmental impact by minimizing raw material consumption and waste.
Market Trends and Industry Preferences
The polyethylene market trends reveal a growing preference for slit tape in packaging due to its enhanced strength and cost efficiency compared to cast film, which remains favored for applications requiring superior clarity and flexibility. Industrial demand shifts favor slit tape in sectors like construction and agriculture for its ease of handling and recyclability, while cast film continues to dominate in food packaging and medical industries where barrier properties are critical. Current market analysis highlights innovation in slit tape production technologies driving expanded adoption, although cast film maintains substantial market share driven by specialized application requirements.
Choosing the Right Material: Slit Tape or Cast Film?
Slit tape offers superior strength and tear resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring secure bundling and packaging, while cast film provides enhanced clarity and flexibility suitable for wrapping and protective coverings. Polyethylene cast films generally exhibit lower thickness variation and higher optical properties compared to slit tapes, which are often produced from blown films. Selecting the right material depends on the specific demands of the application, including mechanical performance, visual quality, and cost-efficiency.
Slit Tape vs Cast Film Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com