Virgin plastic offers consistent quality and durability due to its uncontaminated raw material base, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Recycled plastic reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste and conserving resources but may exhibit variability in strength and appearance. Choosing between virgin and recycled plastic depends on balancing sustainability goals with product performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
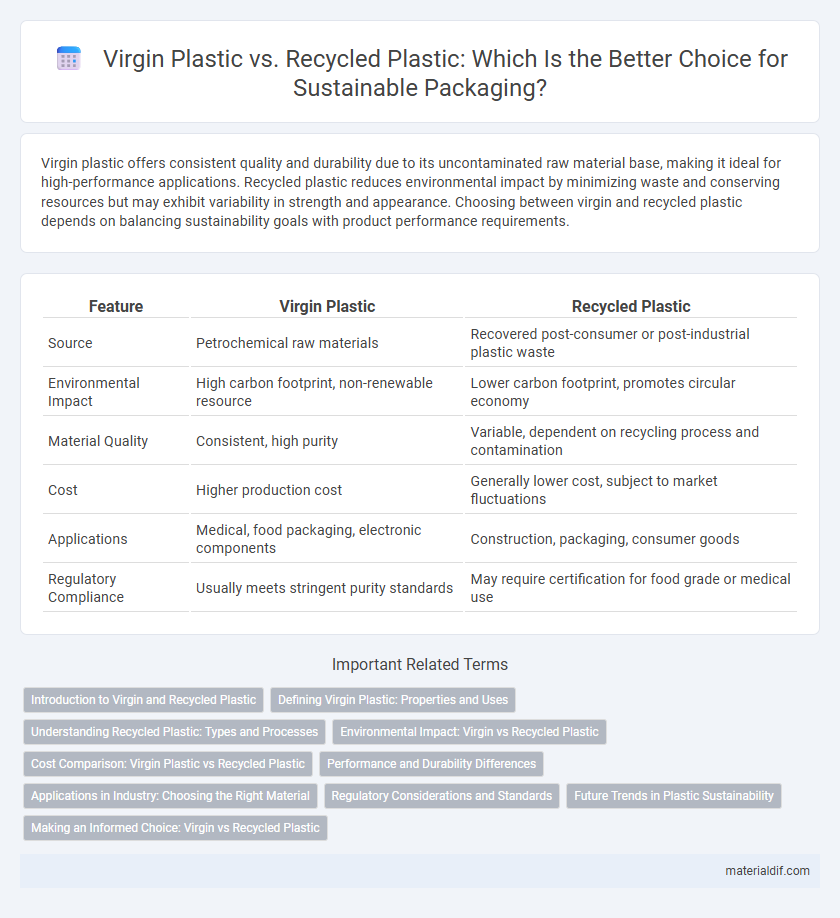
| Feature | Virgin Plastic | Recycled Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Petrochemical raw materials | Recovered post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste |
| Environmental Impact | High carbon footprint, non-renewable resource | Lower carbon footprint, promotes circular economy |
| Material Quality | Consistent, high purity | Variable, dependent on recycling process and contamination |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Generally lower cost, subject to market fluctuations |
| Applications | Medical, food packaging, electronic components | Construction, packaging, consumer goods |
| Regulatory Compliance | Usually meets stringent purity standards | May require certification for food grade or medical use |
Introduction to Virgin and Recycled Plastic
Virgin plastic is produced directly from petrochemical feedstocks, offering high purity and consistent quality essential for manufacturing durable goods. Recycled plastic, sourced from processed waste materials, reduces environmental impact by minimizing new resource extraction and lowering carbon emissions. Both types play crucial roles in the plastic lifecycle, balancing performance needs with sustainability goals.
Defining Virgin Plastic: Properties and Uses
Virgin plastic is a polymer material produced directly from petrochemical feedstocks, characterized by its high purity, consistent molecular structure, and superior mechanical properties. It exhibits excellent strength, clarity, and resistance to contamination, making it ideal for applications in packaging, medical devices, and automotive components where material performance and reliability are critical. The use of virgin plastic ensures product quality and regulatory compliance, especially in sectors requiring stringent standards.
Understanding Recycled Plastic: Types and Processes
Recycled plastic involves collecting used plastic waste, which is sorted into types such as PET, HDPE, and PP before undergoing mechanical or chemical recycling processes to convert it back into usable material. Mechanical recycling shreds and melts plastics to produce pellets, while chemical recycling breaks polymers down into monomers for repolymerization, enhancing material purity and quality. Understanding these processes is essential for optimizing recycled plastic's applications in packaging, construction, and automotive industries, reducing reliance on virgin plastic derived from fossil fuels.
Environmental Impact: Virgin vs Recycled Plastic
Virgin plastic production consumes significantly more energy and emits higher greenhouse gases compared to recycled plastic manufacturing. Recycled plastic reduces landfill waste and lowers carbon footprint by reusing existing materials, minimizing the need for raw fossil fuel extraction. Utilizing recycled plastic supports circular economy initiatives, conserving natural resources and reducing environmental pollution.
Cost Comparison: Virgin Plastic vs Recycled Plastic
Virgin plastic generally incurs higher production costs due to raw material extraction and energy consumption, while recycled plastic offers cost savings by using post-consumer waste as feedstock. Price volatility in virgin plastic often depends on fossil fuel market fluctuations, whereas recycled plastic benefits from reduced dependence on crude oil prices but may face processing and contamination expenses. Businesses evaluating material choices frequently consider recycled plastic as a cost-effective alternative that supports sustainability goals and reduces environmental impact.
Performance and Durability Differences
Virgin plastic offers superior performance and durability due to its consistent molecular structure and absence of contaminants, making it ideal for high-strength and precision applications. Recycled plastic may exhibit variations in mechanical properties and reduced longevity because of potential degradation during processing and the presence of mixed polymers. Advances in recycling technology and additives are improving the quality of recycled plastics, but virgin plastics generally maintain higher reliability for demanding uses.
Applications in Industry: Choosing the Right Material
Virgin plastic offers superior mechanical properties and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications in automotive, medical, and electronics industries. Recycled plastic is increasingly used in packaging, construction, and consumer goods where cost efficiency and sustainability are priorities, though it may exhibit variability in strength and purity. Selecting the right material depends on balancing durability, regulatory compliance, and environmental impact for each industrial application.
Regulatory Considerations and Standards
Virgin plastic is subject to stringent regulatory standards that ensure purity, chemical stability, and compliance with food-grade or medical-use certifications such as FDA and EU REACH regulations. Recycled plastic must also meet these regulatory considerations, often requiring rigorous testing for contaminants, traceability, and adherence to standards like ISO 14021 for environmental claims. Compliance with these standards affects market acceptance, product safety, and sustainability goals in manufacturing and packaging industries.
Future Trends in Plastic Sustainability
Virgin plastic production is expected to decline as global regulations and consumer demand favor recycled plastic to reduce environmental impact. Innovations in chemical recycling and bio-based materials are enhancing the quality and scalability of recycled plastics. Future trends indicate a shift towards circular economy models, where plastic waste is continuously reprocessed into new products, significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Making an Informed Choice: Virgin vs Recycled Plastic
Choosing between virgin plastic and recycled plastic involves weighing environmental impact, cost, and material quality. Virgin plastic offers consistent purity and strength but results in higher carbon emissions and resource depletion. Recycled plastic reduces landfill waste and energy consumption but may have variable quality, requiring careful assessment to match specific application needs.
Virgin Plastic vs Recycled Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com